The real-world example problems presented here showcase the broad simulation capabilities of Ansys Mechanical APDL. The problems demonstrate how to use Mechanical APDL to effectively and accurately solve interdisciplinary problems from a variety of industries and engineering fields.
The problems are more substantive and complex than examples found in the standard documentation set. The documentation thoroughly examines the physics involved with each problem and the considerations necessary for translating problems into numerical models.
Approximation issues, accuracy considerations, and recommended practices are discussed.
Examining a given problem is an effective way to learn about powerful Mechanical APDL features and capabilities that you can use to create a similar simulation of your own.
How Problems Are Presented
Each problem description provides information about the nature and physical characteristics of the problem, specific modeling techniques, material properties, boundary conditions and loading, analysis details and solution controls.
A comprehensive results and discussion section carefully examines analysis results (often comparing them to baseline or known-good results using more traditional analysis methods), and illustrates why specific strategies and methods were chosen.
Each problem concludes with hints and recommendations for performing a similar type of analysis. In many cases, references are provided for additional background information.
Your Results May Vary
The results shown for each problem may differ slightly from those that you obtain, depending on the computer hardware and operating system platform used.
Use of Ansys Mechanical APDL Assumed
The problem descriptions are presented via Mechanical APDL commands, element types, procedures, and material models.
It is entirely feasible, however, to use another Ansys, Inc. application such as Ansys Mechanical to accomplish similar simulation goals but with a different workflow. For more information, see the Ansys Mechanical Mechanical Technology Showcase: Example Problems.
Obtaining the Input Files
The input files for each example problem reside in a .zip file named
td-nn (where
nn corresponds to the given problem number).
To download the zipped file set for a given problem:
Use the link provided under Input Files in the documentation for each problem, or
Use the "Download files" link for each problem in the summary table below.
You
can also in
a single zip filedownload all td-nn file sets
After obtaining the .zip file:
Some problems involve more than one analysis. In such cases, a separate .dat file is provided for each analysis.
Problem Summary
The following example problems are available:
| td-1 |
Brake-Squeal Analysis

| Solves a brake squeal problem. Three analysis methods are highlighted: linear non-prestressed modal, partial nonlinear prestressed modal, and full nonlinear prestressed modal. The problem demonstrates sliding frictional contact and uses complex eigensolvers to predict unstable modes. |
| td-2 |
Nonlinear Analysis of a 2D Hyperelastic Seal
Using Rezoning
| A nonlinear analysis of a 2D hyperelastic seal assembly using manual rezoning with remeshing via the element-splitting method. The problem shows how multiple vertical rezoning steps can be used to ensure convergence and completion of an analysis. |
| td-3 |
Fluid-Pressure-Penetration Analysis of a Sealing
System
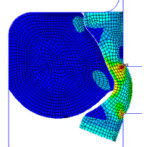
| Analyzes fluid-pressure-penetration effects on a sealing system. The use of seals is primarily to prevent the transfer of fluid (liquid, solid, or gas) between two or more regions. |
| td-4 |
Ring-Gear Forging Simulation with
Rezoning
| Demonstrates the efficiency and usefulness of rezoning in a 2D simulation of metal-forming processes. Rezoning facilitates the convergence of a nonlinear finite element simulation in which excessive element distortion occurs. |
| td-5 |
Delamination of a Stiffened Composite Panel Under a
Compressive Load
| Uses solid-shell element technology to model a layered-composite structure. The problem simulates interface delamination through the debonding capability of contact elements. |
| td-6 |
Thermal Stress Analysis of a Cooled Turbine
Blade
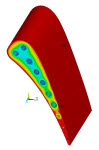
| Shows how to easily set up and perform a thermal-stress analysis of a cooled turbine blade. The problem uses surface-effect capabilities to simulate convection loading on solid regions, and one-dimensional fluid-flow capabilities to obtain a highly accurate thermal solution for convection loading. |
| td-7 |
Nonlinear Transient Analysis of a Camshaft
Assembly
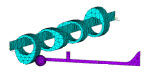
| Shows how to easily set up and perform an analysis involving both axisymmetric and nonaxisymmetric components. The problem demonstrates how modeling with general axisymmetric element technology can reduce computational resources significantly while maintaining the same degree of accuracy as a simulation using a full 3D model. |
| td-8 |
Nuclear Piping System Under Seismic
Loading
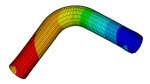
| Demonstrates the advantages of elbow element technology over traditional shell and pipe element technology for modeling pipe bends in a typical nuclear piping system. |
| td-9 |
Reliability Study of a Composite
Overwrapped Pressure Vessel
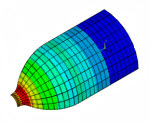
| A reliability study of a composite overwrapped pressure vessel (COPV). The model uses reinforcing fibers in a layered composite. A finite-element simulation of a COPV is performed first to gain insight into its mechanical behaviors, then simulation results are processed using failure analysis to determine the most vulnerable layer. The problem generates linearized stress output for pressure-vessel design optimization and code compliance. |
| td-10 |
Lumbar Motion Segment Simulation
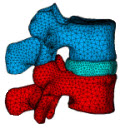
| Uses coupled pore-pressure element technology to study the creep response of a lumbar motion segment under compression. The simulation reveals the interaction between the solid phase and the fluid phase in soft tissues. |
| td-11 |
Rocket Nozzle Extension Simulation:
Fabrication
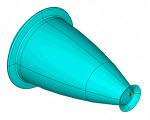
| Simulates thermal stresses during the manufacturing of a rocket nozzle. Uses current structural-shell element technology to accurately model the orthotropic thermal expansion in curved-shell structures. Section offsets are applied when connecting shell-to-shell or to shell-to-other element types. |
| td-12 |
Dynamic Simulation of a Nuclear Piping System
Using RSA Methods
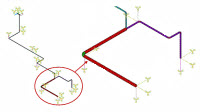
| Accounts for the missing-mass effect and rigid-response effects in a spectrum analysis, and demonstrates how including those effects improves results accuracy (as compared to full-transient analysis results). Uses a piping system model from an actual nuclear power plant. |
| td-13 |
Centrifugal Impeller Analysis Using Cyclic
Symmetry and Linear Perturbation

| A centrifugal impeller blade analysis using cyclic modeling methods and linear-perturbation solution approaches. The problem includes a modal analysis, a full-harmonic analysis, a prestressed modal analysis using linear perturbation, and a prestressed full-harmonic analysis using linear perturbation. |
| td-14 |
Rotordynamics of a Shaft Assembly Based
Representative Model of Nelson-Vaugh Rotor

| A rotordynamic analysis of a rotating structure. A 2D axisymmetric geometry is extracted from a 3D solid model of the rotating structure. Modal, Campbell diagram, and unbalance response analyses are performed for the 2D and 3D models. Results for the 2D axisymmetric model are compared to the full 3D solid model results. |
| td-15 |
Calibrating and Validating a Hyperelastic
Constitutive Model
| Uses hyperelastic curve-fitting to select constitutive model parameters to fit experimental data. Several issues influencing the accuracy of the curve fit are discussed. Validation of the resulting constitutive model is demonstrated by comparison with a tension-torsion experiment. |
| td-16 |
Evaluation of Mixed-Mode Stress Intensity
Factors and T-stress for 3D Surface Flaws

| Demonstrates the linear elastic fracture mechanics of 3D structures. The problem shows how fracture mechanics can be used to evaluate mixed-mode stress-intensity factors, J-integrals, and T-stresses. Analyses of a simple semicircular surface flaw in a rectangular block and a warped flaw along a tubular joint are discussed. |
| td-17 |
Impact of a Metal Bar on a Rigid Wall
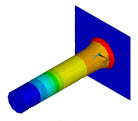
|
An impact simulation using a model of a 3D metal bar hitting a rigid wall. The problem shows the advantages of using impact constraints for modeling contact in a nonlinear transient dynamic analysis. Several combinations of available time-integration methods and contact algorithms are also investigated, using different material models to show how various choices affect the performance and accuracy of the finite-element solution of impact problems. |
| td-18 |
Viscoelastic Analysis of an All-Ceramic Fixed
Partial Denture (FPD)
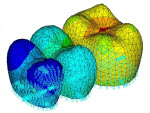
| Demonstrates the fictive-temperature model using the Tool-Narayanaswamy (TN) shift function to study residual stresses in an all-ceramic fixed partial denture (FPD). A coupled-field solution process, including transient thermal and nonlinear structural analyses, is used. |
| td-19 |
Transient Dynamic Analysis of a Digger-Arm
Assembly

| A digger-arm assembly problem demonstrating a transient dynamic analysis of a multibody system. The problem shows how to model joints and rigid/flexible parts, mitigate overconstraints, and represent flexible parts using component mode synthesis (CMS). |
| td-20 |
Dynamic Simulation of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
Assembly Using Modal Analysis Methods
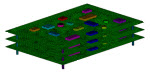
| Uses residual vectors to improve the solution accuracy in modal subspace based analysis methods, such as modal superposition and power spectral density (PSD) analyses. The problem includes a study of the computational efficiency of the results-expansion procedure used to obtain the full-model solution. |
| td-21 |
Buckling and Post-Buckling Analysis of a
Ring-Stiffened Cylinder Using Nonlinear Stabilization
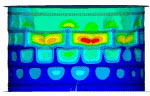
| A nonlinear buckling and post-buckling analysis using nonlinear stabilization. The problem uses a stiffened cylinder subjected to uniform external pressure to demonstrate how to find the nonlinear buckling loads, achieve convergence at the post-buckling stage, and interpret the results. |
| td-22 |
Modal and Harmonic Frequency Analyses of an
Automotive Suspension Assembly Using CMS

| Modal and full-harmonic analyses of an automotive suspension assembly exhibiting harmonic displacement excitation at the wheel bottoms. Component mode synthesis (CMS) is used to generate dynamic superelements for use in downstream linear dynamics analyses. Analysis results from the full (non-substructure) and CMS-generated models are compared to highlight the benefits of CMS technology. |
| td-23 |
Modal Analysis of a Wind Turbine Blade Using
Beam Elements
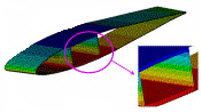
| Simulates a wind turbine blade, a slender composite structure, using a beam element. A simplified 1D beam-based model of the typically complex blade geometry is especially useful in the early design stage, when small design variations can lead to partial or even complete reconstruction of a 3D model, generally an impractical solution given the difficulty of building the model. |
| td-24 |
Hydrostatic Fluid Analysis of an Inflating and
Rolling Tire
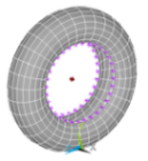
| Models a fluid that is fully enclosed within a solid (container). Shows how loading and deformation on the container affects the contained fluid pressure, volume, density and mass. |
| td-25 |
Cardiovascular Stent Simulation
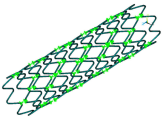
| Simulates stent-artery interaction during and after stent placement. The analysis uses advanced modeling techniques including contact, element birth and death, mixed u-P formulation, and nonlinear stabilization |
| td-26 |
Nonlinear Analysis of a Rubber Boot Seal
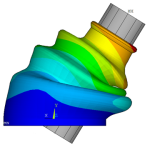
| A nonlinear analysis of a rubber boot seal that includes geometric nonlinearities (large strain and large deformation), nonlinear material behavior (incompressible hyperelastic material model), and changing status nonlinearities (contact). The analysis demonstrates the advantages of the surface-projection-based contact contact method. |
| td-27 |
Hot-Rolling Structural Steel Analysis with 3D
Rezoning
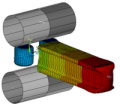
| A 3D large-deformation problem demonstrating the use of rezoning to repair a severely distorted mesh. The example also uses contact technology and symmetric expansion. |
| td-28 |
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Simulation
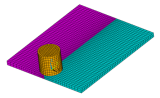
| Simulates the friction stir welding (FSW) process. Several characteristics of FSW are presented, including plastic deformation, tool-workpiece surface interaction, and heat generation due to friction and plastic deformation. Thermal and mechanical behaviors are mutually dependent and coupled together during the FSW process. A nonlinear direct coupled-field analysis is performed. |
| td-29 |
Rocket Nozzle Extension Simulation:
Operation
| Simulates the thermal stresses induced during the operation of a rocket nozzle. Hot gases flow through the nozzle, subjecting the inside and outside of the nozzle body to convection heat loading. Solid thermal and structural elements accurately simulate the multiphysics of the problem. |
| td-30 |
Acoustic Analysis of a Small Speaker
System
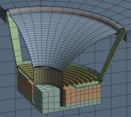
| Uses acoustic elements coupled with structural elements to analyze the performance of a speaker assembly. Features structural-acoustic coupling using fluid-structure interaction (FSI) in 3D, a symmetric FSI algorithm, perfectly matched layers (PML) to absorb outgoing acoustic waves, postprocessing sound pressure level (SPL) and velocity, far-field postprocessing of acoustic field, and user-defined symmetric expansion options. |
| td-31 |
Fitting Parameters for a Chaboche Kinematic
Hardening Model
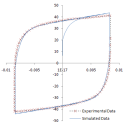
|
Determines material parameters for a third–order Chaboche kinematic hardening model using the curve-fitting tool. A method is presented to estimate the initial parameters and obtain a least-squares best fit to the data. The fitted parameters are validated by conducting uniaxial simulations using a single element and comparing the results with the experimental data. |
| td-32 |
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Simulation
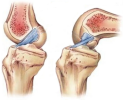
| Simulates the response of an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) of a human knee subjected to tension, flexion, and rotation. The problem uses an anisotropic hyperelastic material model with viscoelasticity. |
| td-33 |
Analysis of a Piezoelectric Flextensional
Transducer in Water

| Couples structural, piezoelectric, and acoustic elements to analyze the acoustic response of a flextensional transducer to voltage excitation. The problem highlights fluid-structure interaction (FSI), piezoelectric materials, infinite acoustic elements, the Robin boundary condition, and far-field postprocessing. |
| td-34 |
Dynamic Simulation of a Nuclear Island
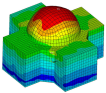
| A power spectral density (PSD) analysis of a nuclear island component of a nuclear power plant (NPP). The problem shows the analysis methods available to simulate the response of an NPP to a seismic event, accounting for motion incoherency and wave-passage effects. |
| td-35 |
Elastoplastic Creep Analysis of Lead-Free
Solder Bumps
| A thermomechanical analysis of lead-free solder bumps subjected to cyclic thermal loading. The problem shows how to obtain implicit creep material constants using experimental data, uses creep and plasticity material models to simulate viscoplastic behavior, and determines accumulated creep strain due to thermal loading. |
| td-36 |
VCCT-Based Crack-Growth
Simulation of a Composite Laminated T-Joint
| Simulates interfacial crack-growth occurring in a laminated T-Joint using the virtual crack closure technique (VCCT). Involves growing an existing crack along a predefined path using interface elements. |
| td-37 |
Bolt Thread
Simulation

| A comparison of three modeling techniques for bolt threading: true threading simulation, the bolt section method, and the multi-point constraint (MPC) method. The comparison shows that the bolt section method offers accurate results while requiring significantly less computational time. |
| td-38 |
Large-Deformation
Neo-Hookean Analysis (with UserMat
Subroutine)
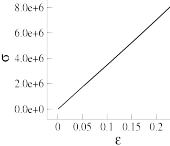
| Formulates a 3D large deformation, hyperelastic material to
demonstrate the user-defined material capability in nonlinear geometry
analyses. Also serves as a usage example of the UserMat subroutine, a user-programmable feature for developing a custom,
constitutive model to define the stress-strain behavior of a
material. |
| td-39 |
Wire Bonding Ultrasonic Transducer

| Simulates electrical excitation of an ultrasonic transducer used for wire bonding applications. Includes piezoelectric material definition, and prestressed modal and harmonic-response analyses. |
| td-40 |
Shape Memory Alloy (SMA)
with Thermal Effect
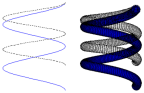
| Two shape memory alloy (SMA) simulations: a spinal spacer implant and a spring actuator. An SMA is a material that, after being subjected to mechanical loading/unloading cycles, is able to undergo large deformations without showing residual strains (pseudoelasticity) or that can recover from large deformations via temperature change (shape memory effect). The simulations demonstrate the utility of the SMA material model using martensite and austenite (nitinol), and the behavior of the SMA with thermal loading. |
| td-41 |
Acoustic Analysis of a
Viscothermal Resonator
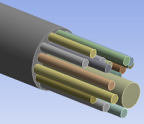
| Uses acoustic elements and viscothermal losses comparing the boundary layer impedance (BLI) model and the low reduced frequency (LRF) model to analyze the noise reduction of sound-absorbing trim panels with quarter-wave resonators. |
| td-42 |
Wire Crimping Modeled with General Contact
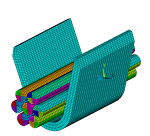
| Demonstrates the ease of contact modeling using the general contact method. The method offers automated contact creation and requires minimal user input. It is especially useful when the model has a large number of contacting surfaces and the geometry makes it difficult to determine contact pairs. |
| td-43 |
Contact Surface Wear
Simulation
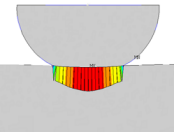
| Demonstrates how to model contact surface wear using the Archard wear model or a user-defined wear model (userwear subroutine). The wear model calculates how much, and in what direction, a contact node is to be moved to simulate wear based on the contact results. Nonlinear mesh adaptivity based on a wear criterion is used to improve the mesh during the wear process. |
| td-44 |
C*-integral Evaluation for
3D Surface Flaws
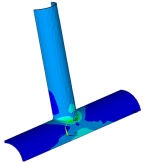
| Evaluates the C*-integral for cracks in structural components. Analyses of a simple semicircular surface flaw in a rectangular block and a warped flaw along a tubular joint are presented. |
| td-45 |
Forced-Response Analysis of a Mistuned
Bladed Disk with Aerodamping
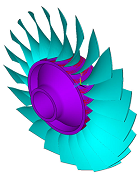
| Demonstrates the free vibration and forced-response analysis of a tuned and mistuned NASA Rotor 67 fan using cyclic modeling methods, linear perturbation, and aerocoupling solution approaches. Includes a modal analysis, a prestressed modal analysis using linear perturbation, and a prestressed mode-superposition harmonic analysis using linear perturbation. |
| td-46 |
Surface Subsidence Caused by Reservoir
Depletion
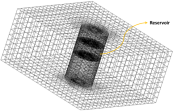
| Predicts solid deformation caused by the coupling of pore-pressure diffusion and solid-matrix deformation. Surface subsidence of a disc-shaped compartmentalized reservoir in a homogenous poroelastic continuum is used as a demonstration case. The problem highlights geomechanics (soil analysis), coupled pore-pressure mechanical solid elements, and the modified Cam-clay soil material model. |
| td-47 |
Electromigration in a Solder Ball
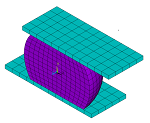
| A transient electromigration analysis of a solder ball. The coupled-field solution calculates the deviation in atomic concentration from an initial unit value due to the combined effects of diffusion, electromigration, stress migration, and thermomigration. |
| td-48 |
Active and Passive Lateral Earth Pressure
Analysis
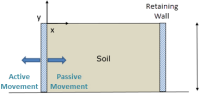
| Simulates soil behavior under active and passive earth-pressure loadings. Shows how the nonlinear plastic behavior of soil can be modeled with a Mohr-Coulomb material. |
| td-49 |
Load Limit Analysis of a Reinforced Concrete
Slab
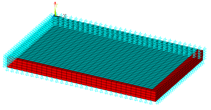
| A load-limit analysis of a reinforced concrete slab showing how the nonlinear plastic behavior of concrete can be modeled using a modified Drucker-Prager material. |
| td-50 |
Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Analysis
Using Hyperelastic Material

|
A nonlinear analysis of normal-pressure hydrocephalus under combined structural-thermal loading using coupled pore-pressure-thermal elements. Shows how displacement, pore pressure, and temperature can be solved via the coupled elements using a hyperelastic material under combined normal pressure and thermal loading. |
| td-51 |
Multi-Filar Coil Inside a Tube Modeled with
Beam-to-Beam Contact
| Three methods for modeling a multi-filar coil inside of a tube. Each model uses a different contact scenario: surface-to-surface, beam-to-surface, or beam-to-beam. A comparison shows that the beam model using beam-to-beam contact offers the best advantage in terms of simplified modeling and reduced computation time. |
| td-52 |
Sequential Construction of an Embankment on a
Clay Layer

| A method for modeling nonlinear consolidation using soil analysis, where the load applied to the model is the self-weight. The Cam-clay material model is highlighted. |
| td-53 |
Acoustic Analysis of a MEMS
Microphone
| Analyzes the response of a silicon micro-machined microphone using acoustic elements and electrostatic-structural coupled-field elements. |
| td-54 |
Reinforced Concrete Joint Analysis
| A reinforced concrete beam-column joint simulation using a gradient-enhanced coupled damage-plasticity microplane model. |
| td-55 |
Inverse-Solving Analysis of a Rotor Fan Blade
with Disk
| A simulation of a rotor fan blade with disk using a nonlinear static analysis with inverse solving to obtain the cold geometry from the hot geometry in a single solution. |
| td-56 |
Threaded Connection Analysis
| A threaded-pipe connection analysis demonstrating the capabilities and advantages of a 2D to 3D analysis. The analysis requires extending a 2D model solution to a corresponding extruded 3D body so that the solution can continue based on the 3D model. |
| td-57 |
Tire Performance Simulation
| Simulates radial tire operation under various operating conditions. The simulation highlights 2D to 3D analysis and steady-state rolling analysis. |
| td-58 |
Suction Pile Analysis
| Simulates the interaction between a soil environment and a steel suction-pile structure. The nonlinear plastic behavior of soil is modeled using a Mohr-Coulomb material. The problem examines the influence of imperfections on the structural response. |
| td-59 |
Thermal-Structural Analysis of a
Printed Circuit Board
| Uses mesh-independent reinforcing elements in a thermal-structural analysis of a printed circuit board (PCB). The model includes both discrete and smeared reinforcing. The problem solution involves a thermal analysis followed by a downstream structural analysis. |
| td-60 |
Accelerated Thermomechanical Fatigue Analysis of
Thermal Barrier Coatings
| Uses cyclic loading and the cycle-jump method to accelerate a thermomechanical fatigue analysis of gas turbine blade thermal-barrier coatings. |
| td-61 |
Underconstrained Coil Spring Under Compression
| Demonstrates various stabilization methods to successfully solve an underconstrained coil spring model, including the quasi-static solver and nonlinear stabilization. |
| td-62 |
Inverse-Solving Analysis of a
Cardiovascular Structure
| A nonlinear static analysis using inverse solving to investigate the biomechanics of a cardiovascular system. |
| td-63 | To be provided. | To be provided. |
| td-64 | To be provided. | To be provided. |
| td-65 |
FFT Calculation
of Frequency Based on Impulse Load
| Demonstrates how to use *FFT (an APDL Math command) to determine the natural frequencies of a model based on its dynamic response to an impulse load. Shows how to obtain the most accurate frequencies using a ping test. |
| td-66 | Sintering Simulation of
a Printed Bridge |
Simulates the sintering process of a printed bridge using a sintering material model. Illustrates the shrinkage that occurs during sintering in binder jetting-metal additive manufacturing (BJ-MAM). |
| td-67 | Crystal Plasticity
with Hall-Petch Effect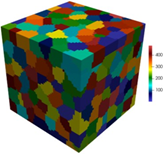 | Two crystal plasticity simulations, one demonstrating the Hall-Petch effect with decreasing average grain sizes, the other showing two methods for applying initial hardness. |
| td-68 | Hydrostatic Extrusion of
Hyperelastic-Plastic Material | Simulates hydrostatic extrusion of a polymer using fluid-pressure-penetration loading. The problem uses multiplicative-decomposition-based large deformation and a combined hyperelastic-plastic material model (Neo-Hookean hyperelasticity combined and von Mises plasticity with linear isotropic hardening). |
| td-69 | Accelerated Fatigue
Analysis of Solder Joints in a Chip Resistor Assembly | Uses the cycle-jump method with nonlocal damage to accelerate a thermomechanical fatigue analysis of solder joints in chip resistor assemblies. |
| td-70 | Adaptive
Crack-Initiation and -Propagation | Simulates crack-initiation and fatigue crack-propagation in a structural component. The analysis uses Mechanical APDL SMART technology. The structure is a CT specimen with holes. |