Determines life, damage, and factor of safety information using a stress-life or strain-life approach. The Fatigue Tool folder is available for Static Structural, Transient Structural, Harmonic Response, and Random Vibration (spectral fatigue) analyses only.
Applies to the following objects:
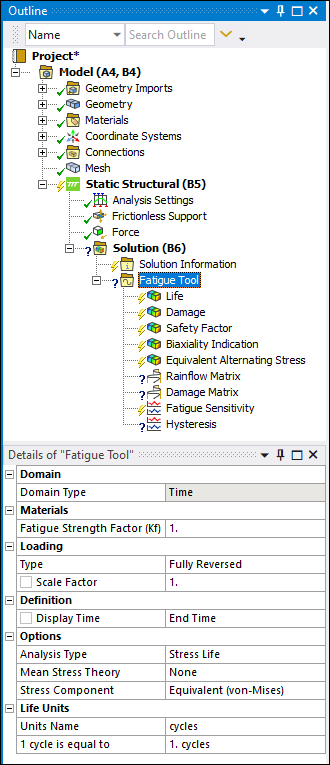
| Fatigue Tool for a Structural analysis: | |
 |
Properties for the Contour Results Menu Options |
|
Fatigue Tool for a Harmonic Response analysis: 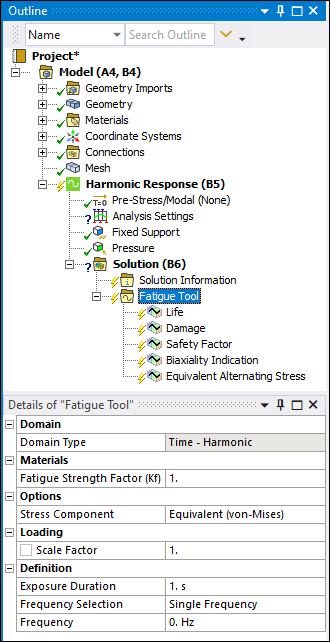 | |
|
Fatigue Tool for a Random Vibration analysis: 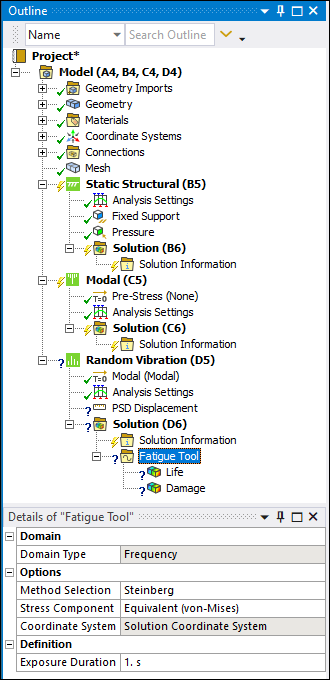 |
Object Properties
The Details Pane for this object includes the following properties.
Fatigue Tool
The Details view categories and properties differ based on the analysis type. For Static Structural, Transient Structural, and Harmonic Response analyses, the Details of the Fatigue Tool include:
| Category | Properties/Options/Descriptions |
|---|---|
|
Domain |
Domain Type: Read-only property that displays the following content based on the analysis type:
|
|
Materials | |
|
Loading |
Loading Ratio: Only appears if the Type property is set to Ratio. History Data Location: Only appears if the Type property is set to History Data. |
|
Definition |
Display Time: Enter a time value (within the analysis time limit) to display results at that moment of the analysis. |
|
Options |
Bin Size: Only appears if the Type property is set to History Data. Use Quick Rainflow Counting: Only appears if the Type property is set to History Data. Infinite Life: Only appears if the Analysis Type property is set to Strain Life; or if the Analysis Type property is set to Stress Life and the Type property is set to History Data. Maximum Data Points to Plot: Only appears if the Type property is set to History Data. |
|
Life Units |
For a Random Vibration analysis, the Details of the Fatigue Tool include:
| Category | Properties/Options/Descriptions |
|---|---|
|
Domain |
Domain Type: Read-only property that displays the following content based on the analysis type.
|
|
Options |
Method Selection: Specifies the method to calculate the Probability Density Function (PDF) from the available PSD stress response. Exposure Duration: Specifies the time duration for which the loading is applied. The resulting damage is for this entire duration. By default, this is set to 1 second This means that the calculated damage is damage per second. |
Properties for the Contour Results Menu Options
The properties for the Contour Results menu options (Life, Damage, Safety Factor, Biaxiality Indication, and Equivalent Alternating Stress) include:
| Category | Properties/Options/Descriptions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Scope |
Scoping Method: Specify as (default), , , or . Based on your selection, related properties display.
Geometry: When you specify Path or Surface as the Scoping Method, this additional property displays in the Scope category. Use selection filters to pick geometry, click in the Geometry field, then click . | ||||
|
Definition |
Design Life: Only available for the Damage and Safety Factor objects. Type: Read-only indication of the fatigue object name. Identifier Suppressed: Suppress the object as desired. | ||||
|
Integration Point Results |
Average Across Bodies: Averages results across separate bodies. The default setting is . | ||||
|
Results (read-only indications of min/max) |
Minimum: Available for Life, Safety Factor, Biaxiality Indication, Equivalent Alternating Stress. Minimum Occurs On: Available for Life, Safety Factor, Biaxiality Indication, Equivalent Alternating Stress. Maximum: Available for Damage, Biaxiality Indication, Equivalent Alternating Stress. Maximum Occurs On: Available for Damage, Biaxiality Indication, Equivalent Alternating Stress. | ||||
|
Information - only available for Harmonic Response analyses. |
Reported Frequency |
Properties for the Graph Results Menu Options
The properties for the Graph Results menu options (Rainflow Matrix, Damage Matrix, Fatigue Sensitivity, and Hysteresis) include:
| Category | Properties/Options/Descriptions |
|---|---|
|
Scope |
Geometry: Use selection filters to pick geometry, click in the Geometry field, then click . |
|
Definition |
Sensitivity For: Only available for the Fatigue Sensitivity object. Design Life: Only available for the Damage Matrix object and the Fatigue Sensitivity object if the Sensitivity For property is set to Damage or Safety Factor. Suppressed |
|
General |
Stress Strain Type: If set to Shear Stress, the General, Options, and Results categories are replaced by a Definition category that includes a Type setting. |
|
Options |
Lower Variation: Available only for Fatigue Sensitivity. Upper Variation: Available only for Fatigue Sensitivity. Number of Fill Points: Available only for Fatigue Sensitivity. Chart Viewing Style: Available only for Damage Matrix, Fatigue Sensitivity, and Rainflow Matrix. Points per Segment: Available only for Hysteresis. |
|
Results - available only for Damage Matrix, Hysteresis, and Rainflow Matrix. Read-only indication of the following quantities. |
The following are only available for Damage Matrix and Rainflow Matrix options:
The following are only available for the Hysteresis option:
|
Tree Dependencies
Valid Parent Tree Object:
For Fatigue Tool: Solution.
For Biaxiality Indication, Damage, Damage Matrix, Equivalent Alternating Stress, Fatigue Sensitivity, Hysteresis, Life, Rainflow Matrix, and Safety Factor: Fatigue Tool.
Valid Child Tree Objects:
For Fatigue Tool: Biaxiality Indication, Comment, Damage, Damage Matrix, Equivalent Alternating Stress, Fatigue Sensitivity, Hysteresis, Image, Life, Rainflow Matrix, and Safety Factor.
For Biaxiality Indication, Damage, Equivalent Alternating Stress, Life, Safety Factor: Alert, Comment, Convergence, Figure, and Image.
For Damage Matrix, Fatigue Sensitivity, Hysteresis, and Rainflow Matrix: Comment, and Image.
Insertion Methods
For Fatigue Tool, use any of the following methods after highlighting Solution object:
Open the Toolbox drop-down menu on the Solution Context Tab and select the .
Click-right on the Solution object or in the Geometry window and select > > .
For all results of the Fatigue Tool, use any of the following methods after highlighting Fatigue Tool object:
Choose or drop-down menu and the on Fatigue Tool Context tab.
Click-right on the Fatigue Tool object or in the Geometry window and select > .
Right-click Options
In addition to common right-click options, relevant right-click options for this object include:
Evaluate All Results: Available for the Fatigue Tool and all tool child objects.
API Reference
See the Fatigue Tool section of the ACT API Reference Guide for specific scripting information.
Additional Related Information
See the following sections for more information:


