Frequency response results enable you to plot graphs that display how the given response (stress, strain, etc.) varies with frequency.
Go to a section topic:
Result Options
The Frequency Response menu of options is accessed from the Solution object context tab, or by right-clicking the Solution object, or an existing result object, and selecting > . Menu options include:
You can view these options as a value graphed along a specified frequency range. In addition, you can parameterize these frequency results. The plot will include all the frequency points at which a solution was obtained. When you generate frequency response results, the default plot (Bode) shows the amplitude and phase angle.
Equivalent radiated power results estimate the radiated structure-borne sound power from a vibrating structural surface. These results are available in 3D Harmonic Response and Harmonic Acoustics (if you define a structural Physics Region) analyses. The result is evaluated on faces that you select, either using face geometry section or face-based Named Selections, and the result is displayed on a graph over the specified frequency range. You specify the frequency range using the setting for the Frequency Range property. When you generate frequency response results, the plot shows Equivalent Radiated Power (ERP) or Equivalent Radiated Power Level (ERPL) as a function of the frequency. See the expressions described below as well as the PLAS command for the ERP and ERPL acoustic quantities.
Note: You can specify a weighting filter (A, B, and C) for the Equivalent Radiated Power Level result.
Important: For Equivalent Radiated Power and Equivalent Radiated Power Level results, if the Multiple Step Type property is set to in the Analysis Settings, the result file must exist for the result to be displayed.
Scoping
These results support the following scoping options:
Geometry selection (vertex, face, edge, or nodes)
Support Boundary Conditions (Fixed Support, Displacement, Frictionless Support, Cylindrical Support)
Requirement: Equivalent Radiated Power and Equivalent Radiated Power Level results must be scoped to surfaces.
Note: Direct graphical node selection requires you to generate the mesh and have the Node selection option active.
Limitations
If the Store Results At All Frequencies property in the Options category of the Analysis Settings is set to , the Frequency Response results for force reactions cannot be extracted.
Result Calculations
The following equations describe how frequency graphs are defined and plotted for the supported types.
- Stress and Strain Results
The strain result is calculated using the displacement result. Using the Young’s Modulus and strain result, the stress result can be evaluated. Because of this reason, the stress and strain results are in phase with the displacement result.
- Deformation Result
The displacement vector on a structure subjected to harmonic loading may be expressed as:
EQUATION 1
The Frequency Response chart for displacement is calculated by expressing Equation (1) in time domain as follows:
EQUATION 2
where:
- Velocity Result
The equation for velocity
can be obtained by taking a time derivative of Equation (1). The frequency response for velocity in time domain is calculated as follows:
EQUATION 3
where:
- Acceleration Result
The equation for acceleration
can be obtained by taking a double time derivative of Equation (1). The frequency response for acceleration in time domain is calculated as follows:
EQUATION 4
where:
- Force Reaction
The Frequency Response for Force Reaction is calculated by replacing displacement with force in Equation (2) as shown below.
EQUATION 5
where:
(Amplitude)
(Phase Angle)
- Equivalent Radiated Power
Equivalent Radiated Power (ERP) is expressed as:
Where:
= speed of sound (equal to 343.25 m/s).
= mass density (equal to 1.2041 kg/m3).
= radiation factor (equal to 1).
= normal velocity of vibrating structural surface
- Equivalent Radiated Power Level
The Equivalent Radiated Power Level (ERPL) is expressed as:
ERPL = 10 Log (ERP/Wref) Where Wref is the reference sound power (equal to 10-12W).
- Krylov Residual Norm
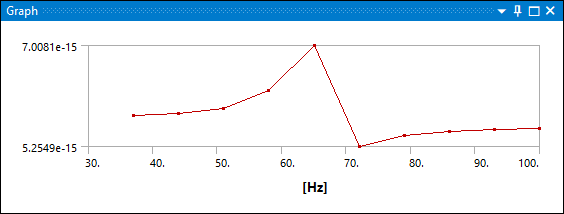
This result plots error estimations (residuals) across a frequency range for the harmonic distribution. The result displays the lowest residual value at the frequency where the Krylov subspace is built. High residual values indicate the error between the actual and the approximated solution for a given high frequency. The plot can provide information on how to best split the whole frequency range into multiple ranges. The Krylov Residual Norm is calculated using the following equation:
Where:
is the applied force.
is the approximated force using the Krylov method.
For , K, M, and C are the system matrices and the Residuals are calculated for all the solved frequency points ωi.
Example Plot
Display Options
- Panel Contribution and Data Filtering
For the , , , , and result types, the Details pane provides the following property categories:
Panel Contribution: Visually compare the results of multiple solid bodies or of specified Named Selections as a mosaic chart.
Chart and Tabular Display: Filter result data in the Graph and Tabular Data windows. This category also includes properties related to Panel Contribution if the option is active.
- Display Property
The Display Property property of the frequency response results provides the following results values for graphs:
(default setting - plots both Amplitude and Phase Angle)
- Chart Viewing Style Property
The Chart Viewing Style property provides the following options to plot results for a scale of an axis:
: this option plots the result values linearly.
: this option plots the X-Axis logarithmically. If negative axis values or a zero value exists, this option is not supported and the graph plots linearly.
(default when graph has Amplitude): this option plots the Y-Axis is plotted logarithmically. If negative axis values or a zero value exists, this option is not supported and the graph plots linearly.
: this option plots the X-Axis and Y-Axis logarithmically. If negative axis values or a zero value exists, this option is not supported and the graph plots linearly.
For edges, faces, surface bodies, and multiple vertex selections (which contain multiple nodes), the results can be scoped as minimum, maximum, or average using the Spatial Resolution option. This option is also available for frequency and phase response results scoped on a single vertex.
Note: The Spatial Resolution option is especially important for results scoped to a shell vertex, where the default option, , may yield unexpected results.
The and settings of the Spatial Resolution option are based on the amplitude and are therefore reported from the location with either the largest or smallest amplitude. The setting calculates the average by calculating the real and imaginary components separately.
Note: You cannot use the Mechanical application convergence capabilities for any results item under a harmonic analysis. Instead, you can first do a convergence study on a modal analysis and reuse the mesh from that analysis.
Presented below is an example of a Frequency Response plot:
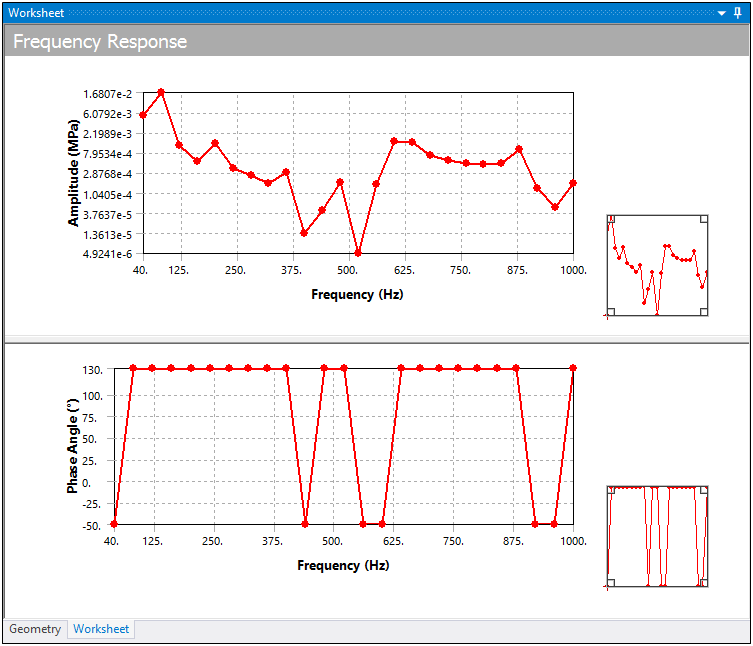
The average, minimum, or maximum value can be chosen for selected entities. Stress, Strain, Deformation, Velocity, and Acceleration components vary sinusoidally, so these are the only result types that can be reviewed in this manner. (Note that items such as Principal Stress or Equivalent Stress do not behave in a sinusoidal manner since these are derived quantities.)
Creating Contour Result from Frequency Response Results
You can use Frequency Response result types (not including Velocity and Acceleration) to generate new result objects of the same type, orientation, frequency. The phase angle of the contour result will be opposite in sign with the same magnitude as the frequency response result type. The sign of the phase in the Sweeping Phase property of the contour result is reversed so that the response amplitude of the frequency response plot for that frequency and phase defined by the Duration property matches with the contour results. To create a Contour Result in a Harmonic Analysis:
Select and right-click the desired Harmonic result in the solution tree.
Choose .
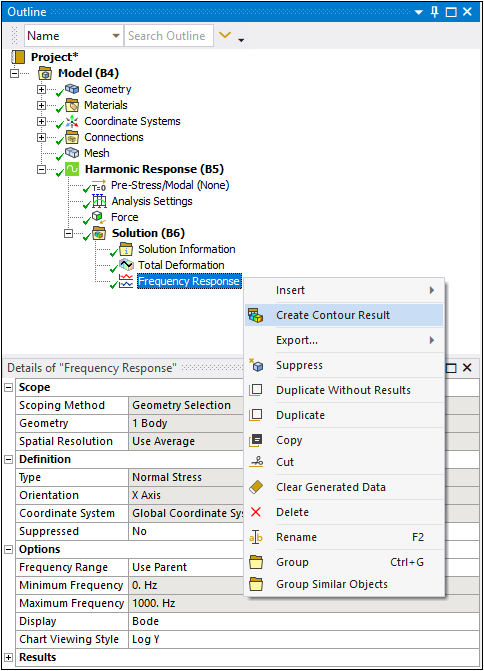
As illustrated here, you can see how the feature automatically scopes the Type, Orientation, Coordinate System, Frequency, and Sweeping Phase.

The Reported Frequency in the Information category is the frequency at which contour results were found and plotted. This frequency can be potentially different from the frequency you requested.


