Your Ansys Fluent model includes the -
SST turbulence model by default. You need to choose the appropriate
model and options, and supply turbulent boundary conditions. These inputs are described
in this section.
The procedure for setting up a turbulent flow problem is described below. (Note that this procedure includes only those steps necessary for the turbulence model itself; you will need to define the other settings—for example, other models, boundary conditions—as usual.)
Define the turbulence model settings.
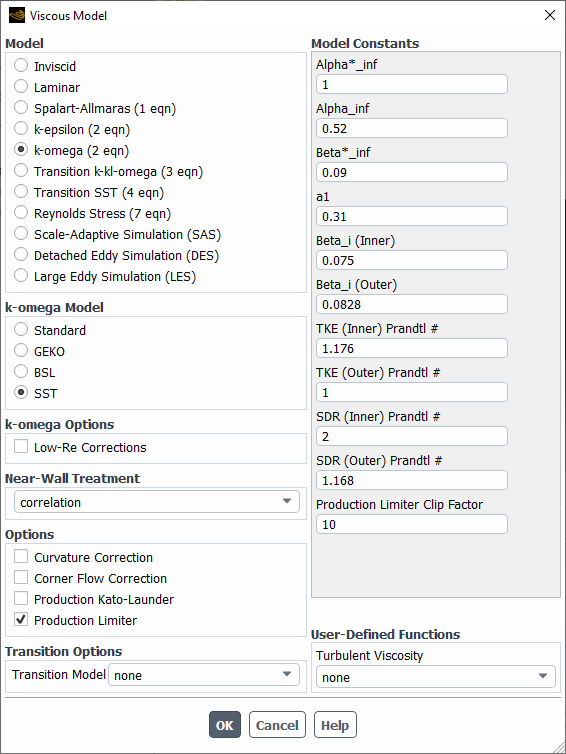
Open the Viscous Model Dialog Box (Figure 15.6: The Viscous Model Dialog Box) by right-clicking Viscous in the tree (under Setup/Models) and clicking Edit... in the menu that opens.
Setup → Models → Viscous
Edit...
Select either Spalart-Allmaras, k-epsilon, k-omega, Transition k-kl-omega, Transition SST, Reynolds Stress, Scale-Adaptive Simulation (SAS), Detached Eddy Simulation (DES), or Large Eddy Simulation (LES) from the Model list.
If you choose the k-epsilon model, select either Standard, RNG, or Realizable from the k-epsilon Model list. If you choose the k-omega model, select Standard, GEKO, BSL, or SST from the k-omega Model list.
Important: The Large Eddy Simulation (LES) model is available only for 3D cases.
If the flow involves walls, and you are using one of the
-
models or the
-based Reynolds stress models, choose one of the following options from the Near-Wall Treatment list in the Viscous Model dialog box:
Standard Wall Functions
Scalable Wall Functions
Non-Equilibrium Wall Functions
Enhanced Wall Treatment
Menter-Lechner (for
-
models only)
User-Defined Wall Functions
For more information about these near-wall options, see Near-Wall Treatments for Wall-Bounded Turbulent Flows in the Theory Guide. By default, the standard wall function is enabled.
For more information about the automatically defined near-wall treatment for the Spalart-Allmaras model, see Wall Boundary Conditions in the Theory Guide.
For more information about the automatically defined near-wall treatment for the
-
model, see y+-Insensitive Near-Wall Treatment for ω-based Turbulence Models in the Fluent Theory Guide.
For LES model, the following options from the Near-Wall Treatment dropdown list in the Viscous Model dialog box are available:
Kader blending Wall Functions (current default option)
Harmonic blending Wall Functions based on r+ (recommended option)
Werner-Wengle Wall Treatment
For more information about the near-wall treatments for the LES model, see LES Near-Wall Treatment in the Fluent Theory Guide.
Enable the other appropriate turbulence modeling options in the Viscous Model dialog box, as appropriate. See Setup Options for All Turbulence Modeling
Specify the boundary conditions for the solution variables in the appropriate boundary condition dialog boxes. The boundary condition dialog boxes can be opened by right-clicking the boundary name in the tree (under Setup/Boundary Conditions) and clicking Edit... in the menu that opens; alternatively, you can open them from the Boundary Conditions task page:
Setup →
 Boundary Conditions
Boundary Conditions
See Defining Turbulence Boundary Conditions for details.
Specify the initial guess for the solution variables in the Solution Initialization task page.
Solution →
 Initialization
Initialization
See Providing an Initial Guess for k and ε (or k and ω) for details. Note that Reynolds stresses are automatically initialized using
, and therefore need not be initialized explicitly.