The Plots task page allows you to create plots (XY, histograms, profiles, and so on) of your computational results. See Displaying Graphics for more information.
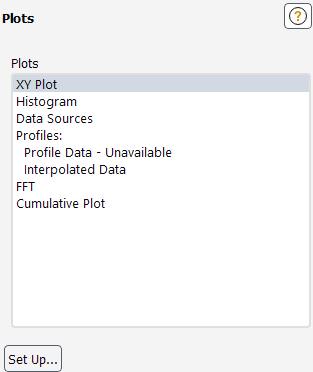
Controls
- Plots
contains a listing of the various plot types available in Ansys Fluent.
You can double-click an item in the Plots list to open the corresponding dialog box, or you can select the item in the list and click the Set Up... button.
- XY Plot
selecting this item and clicking the Set Up... button opens the Solution XY Plot Dialog Box.
- Histogram
selecting this item and clicking the Set Up... button opens the Histogram Dialog Box.
- File
selecting this item and clicking the Set Up... button opens the Plot Data Sources Dialog Box.
- Profiles
two types of profile plots are available:
- Profile Data
selecting this item and clicking the Set Up... button opens the Plot Profile Data Dialog Box.
- Interpolated Data
selecting this item and clicking the Set Up... button opens the Plot Interpolated Data Dialog Box.
- FFT
selecting this item and clicking the Set Up... button opens the Fourier Transform Dialog Box.
- Set Up...
displays the dialog box corresponding to the selected item in the Plots list.
For additional information, see the following sections:
- 51.19.1. Solution XY Plot Dialog Box
- 51.19.2. Histogram Dialog Box
- 51.19.3. Plot Data Sources Dialog Box
- 51.19.4. Plot Profile Data Dialog Box
- 51.19.5. Plot Interpolated Data Dialog Box
- 51.19.6. Fourier Transform Dialog Box
- 51.19.7. Ansys Sound Analysis Dialog Box
- 51.19.8. Cumulative Plot Dialog Box
- 51.19.9. Plot/Modify Input Signal Dialog Box
- 51.19.10. Axes Dialog Box
- 51.19.11. Curves Dialog Box
The Solution XY Plot dialog box allows you to display zone, surface and file data in an XY plot format. See Steps for Generating Solution XY Plots for details about the items below.
You can also access the Solution XY Plot dialog box through the Postprocessing ribbon tab.
Postprocessing → Plots
→ XY Plot → New...
Note:
The "global"/non-persistent form of graphics objects is hidden by default. If this interrupts your workflow, you can make them available by enabling the Expose legacy non-persistent graphics option in the Graphics branch of Preferences (accessed via File>Preferences...).
(When you click Edit... instead of New..., it opens the "global"/non-persistent version of the Solution XY Plot dialog box. This version of the dialog box does not have a Name field and it is not saved with the case file.
You are encouraged to use the persistent version that is accessed by clicking New....
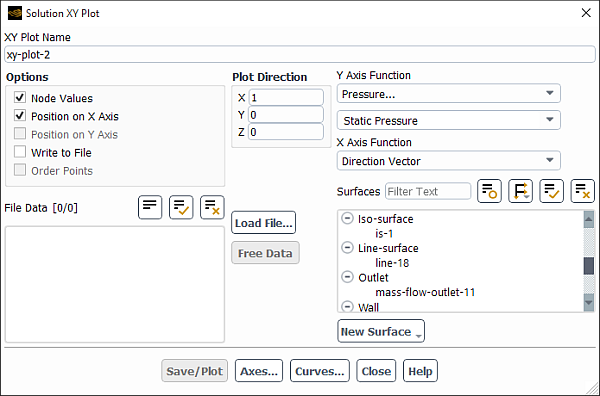
Controls
- XY Plot Name
is the name for a solution XY plot definition. You can specify a name or use the default name
xy-plot-. This control appears only for solution XY plot definitions.id- Options
contains check buttons that control the presentation of node or cell-averaged values, the selection of axis functions, and the ability to write the plot data to a file.
- Node Values
toggles the node averaging of the data presented in the plot. If the option is disabled, boundary face values are presented. See Choosing Node or Cell Values for details.
- Position on X Axis, Position on Y Axis
set the
-axis or
-axis function to be the position. If one of these options is turned on, the other will automatically be turned off. You can turn both options off to generate a plot of one flow-field function vs. another, selecting the function for each axis using the X Axis Function and Y Axis Function drop-down lists.
- Write to File
activates the file-writing option. When this option is selected, the Plot push button will change to Write.... Clicking on the Write... button will open the Select File dialog box (The Select File Dialog Box), in which you can specify a name and save a file containing the plot data. The format of this file is described in XY Plot File Format.
- Order Points
specifies that plot data being saved to a file should be sorted in order of ascending
axis value. This option is available only when the Write to File option is turned on.
- Plot Direction
contains inputs for defining the plot direction.
If Direction Vector (the default) is selected in the X Axis Function or Y Axis Function drop-down list (whichever is the position axis), the inputs are the components of the direction vector. The position axis of the plot will have coordinate values that correspond to the dot product of the data coordinate vector with the plot direction vector. See Steps for Generating Solution XY Plots for details.
- X
is the component in the
direction.
- Y
is the component in the
direction.
- Z
is the component in the
direction.
If Curve Length is selected in the X Axis Function or Y Axis Function drop-down list (whichever is the position axis), the inputs are the direction along the length of the surface selected in the Surfaces list. See Steps for Generating Solution XY Plots for details.
- Default
specifies the plot direction as the direction of increasing curve length.
- Reverse
specifies the plot direction as the direction of decreasing curve length.
- Show
displays the selected surface in the graphics window, marking the start of the surface with a blue dot and the end of the surface with a red dot. Ansys Fluent will also display arrows on the surface showing the direction in which the variable will be plotted.
- Y Axis Function, X Axis Function
contain lists of solution variables that can be used for the
or
axis of the plot. If the Position on X Axis option is turned on, X Axis Function will become a single drop-down list, containing two options: Direction Vector (to plot the selected variable as a function of position along a specified direction vector) and Curve Length (to plot the selected variable as a function of position along the length of a specified curvilinear surface). See Steps for Generating Solution XY Plots for details.
Likewise, if Position on Y Axis is turned on, Y Axis Function will become a single drop-down list containing Direction Vector and Curve Length. If both Position on X Axis and Position on Y Axis are turned off, you can select field functions for both axes using the X Axis Function and Y Axis Function lists.
Note: When running the parallel version of Ansys Fluent, Curve Length is only supported when the curvilinear surface is contained within a single partition.
- File Data
is a selectable list of the plot titles associated with the loaded external data files. You may choose any number of files for the data plot. The files are loaded using the Load File... push button. The format of these files is presented in XY Plot File Format. See Including External Data in the Solution XY Plot for details.
- Load File...
opens the Select File dialog box (The Select File Dialog Box), in which you can select the plot file to be read. See Including External Data in the Solution XY Plot for details. After the external file is loaded, its plot title will be displayed in the File Data list.
- Free Data
removes the files selected in the File Data list.
- Surfaces
is a selectable list of surfaces in the solution domain. You may choose any number of surfaces for the data plot.
- New Surface
is a drop-down list button that contains a list of surface options:
- Point
opens the Point Surface Dialog Box.
- Line/Rake
opens the Line/Rake Surface Dialog Box.
- Plane
opens the Plane Surface Dialog Box.
- Quadric
opens the Quadric Surface Dialog Box.
- Iso-Surface
opens the Iso-Surface Dialog Box.
- Iso-Clip
opens the Iso-Clip Dialog Box.
- Structural Point
opens the Structural Point Surface Dialog Box.
- Plot
plots the specified surface and/or file data in the active graphics window using the current axis and curve attributes. If the Write to File option is turned on, this button becomes the Write... button.
- Write...
opens the Select File dialog box (The Select File Dialog Box), in which you can save the plot data to a file. This button replaces the Plot button when the Write to File option is turned on.
- Axes...
opens the Axes Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- Curves...
opens the Curves Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the XY plot.
- Save/Plot
plots the specified surface and/or file data in the active graphics window using the current axis and curve attributes and saves the XY plot definition. This button appears only for solution XY plot definitions and replaces the Plot button.
The Histogram dialog box allows you to create histograms of selected geometric or physical data. See Steps for Generating Histogram Plots for details about the items below.
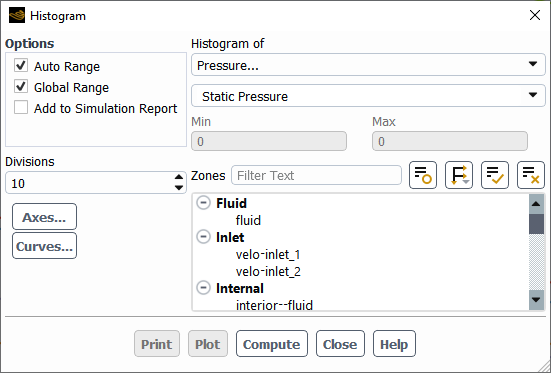
Controls
- Options
contains the check buttons for current histogram options.
- Auto Range
toggles the ability to specify the minimum and maximum range of scalar values in the histogram print or plot. If the option is not active, the Min and Max fields are editable, and you may specify the desired range. If the option is active, the range is defined by the minimum and maximum values in the computational domain.
- Global Range
toggles the ability to specify the minimum and maximum values on the range of values on the selected surfaces, rather than in the entire domain.
- Add to Simulation Report
toggles the ability to add the histogram and its data to your simulation report.
- Divisions
sets the number of data intervals that will exist in the histogram.
- Zone Types
contains a list of available face or cell zone types.
- Axes...
opens the Axes Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- Curves...
opens the Curves Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the histogram plot.
- Histogram of
contains a list of scalar quantities that can be used in the histogram.
- Min
displays or allows definition of the minimum value of the selected scalar quantity used in the histogram.
- Max
displays or allows definition of the maximum value of the selected scalar quantity used in the histogram.
- Zones
contains a list of available face or cell zones.
displays the histogram interval.
- Plot
displays a plot of the percentage of the total number of cells versus the scalar quantity in the active graphics window.
- Add To Report
adds the histogram and its data to the simulation report (when the Add to Simulation Report option is enabled).
- Compute
computes the minimum and maximum cell values of the selected scalar quantity. The values are displayed in Min and Max.
The Plot Data Sources dialog box allows you display data read from one or more files (in an abscissa/ordinate plot form) and combine them with data from XY plot objects and report plots. The format of the plot file is described in XY Plot File Format. See Steps for Generating XY Plots of Data from Multiple Sources for details about the items below.
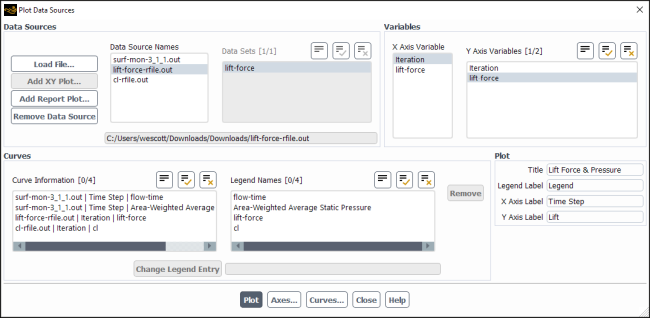
Controls
- Data Sources
contains operations and information related to the selected files/plots.
- Load file...
opens the Select File dialog box, where you can select the file(s) you want to plot.
- Add XY Plot...
opens the Select Plots dialog box, where you can select the plot(s) you want to include.
- Add Report Plot...
opens the Select Plots dialog box, where you can select the report plot(s) you want to include.
- Remove Data Source
removes the selected data source from the Data Source Names list. This also removes any curves associated with that file.
- Data Source Names
lists the files and plots that you have loaded.
- Data Sets
lists the available data sets for files and plots (typically
.xy) that contain two columns monitoring the same value at different locations. You can select which data sets you want to plot by selecting/de-selecting the listed items.
- Variables
lists X and Y variables for the selected file.
- X Axis Variable
lists the variables that you can select for the X axis. The highlighted X variable will be added to the Curve Information list in coordination with the selected Y Axis Variables. Changing the selected X Axis Variable updates all the related curves shown in the Curve Information list.
- Y Axis Variables
lists the variables that you can select for the Y axis. The highlighted Y variables will be added to the Curve Information list in coordination with the selected X Axis Variable. Changing the selected Y Axis Variables updates how many curves are shown in the Curve Information list.
- Curves
lists what items will be plotted and how they will be labeled in the legend.
- Curve Information
lists the curves that will be plotted.
Information about each curve is shown in the following order:
The name of the file where the data originated.
[2 column file (typically
.xy)only] The location on the model where the data originated.X Variable.
Y Variable.
- Legend Names
lists the name for each curve that will be listed in the legend when the plot is displayed in the graphics window. (see Change Legend Entry to learn how to change the legend name for a curve).
removes the selected curve from the Curve Information list.
- Change Legend Entry
allows you to change the name that will appear in the plot legend in the graphics window for a particular curve.
To use:
Select a name in the Legend Names list.
Enter the new name in the text entry box to the right of the button.
Click .
- Plot
contains text entry boxes for the various plot labels.
- Title
lets you enter a title for the plot.
- Legend Label
lets you enter a title for the legend.
- X Axis Label
lets you label the X axis.
- Y Axis Label
lets you label the Y axis.
- (button)
click Plot to plot the data listed in the Curve Information list.
- (button)
opens the Axes dialog box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- (button)
opens the Curves dialog box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the XY plot.
The Plot Profile Data dialog box allows you to display an XY plot of the original data points of a boundary profile before it is interpolated onto the cell faces of a boundary. See Steps for Generating Plots of Profile Data for details about the items below.
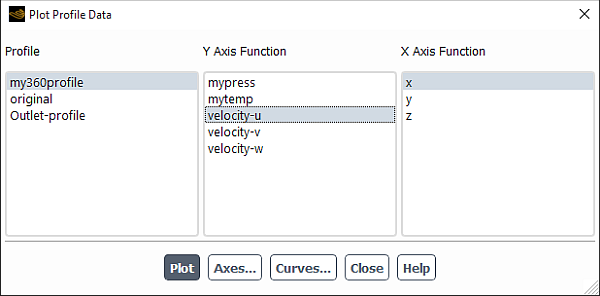
Controls
- Profile
contains a selectable list of available profiles. When a profile is selected its available fields are displayed under Y Axis Function.
- Y Axis Function
contains a selectable list of the fields available in the selected profile that can be used for the
axis of the plot.
- X Axis Function
contains a selectable list of the variables that can be used for the
axis of the plot.
- Plot
displays an XY plot of the data points from the selected profile.
- Axes...
opens the Axes Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- Curves...
opens the Curves Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the XY plot.
The Plot Interpolated Data dialog box allows you to display an XY plot of the values assigned to the cell faces when a profile file has been interpolated on a boundary. See Steps for Generating Plots of Interpolated Profile Data for details about the items below.
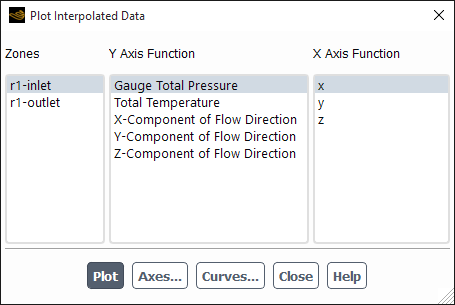
Controls
- Zones
contains a selectable list of the zones for which a profile field has been set as one or more of the parameters are displayed under Y Axis Function.
- Y Axis Function
contains a selectable list of the profile-related parameters in the selected zone that can be used for the
axis of the plot. The name of the parameter will be the same as that of the drop-down list in the boundary condition dialog box from which the profile field was selected.
- X Axis Function
contains a selectable list of the geometry variables that can be used for the
axis of the plot.
- Plot
displays an XY plot of the cell face values (as interpolated from the data points of the profile file) of the selected zone.
- Axes...
opens the Axes Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- Curves...
opens the Curves Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the XY plot.
The Fourier Transform dialog box allows you to analyze your time dependent data using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm. See Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Postprocessing for details about the items below.
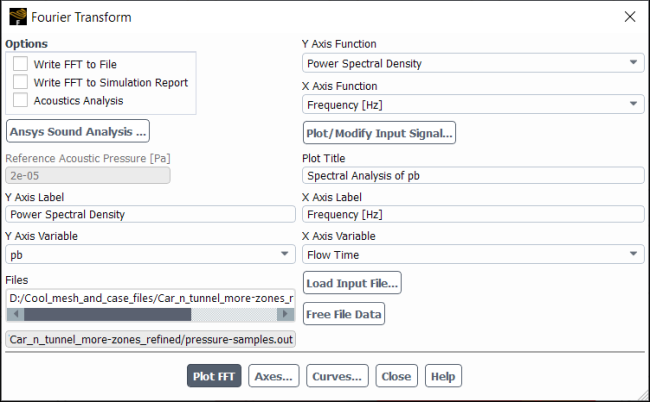
Controls
- Options
lets you write the FFT data to a file or display the FFT data in a graphics window.
- Write FFT to File
allows you to write out the FFT data directly to a file. When selected, the Plot FFT... buttons becomes the Write FFT... button.
- Acoustics Analysis
enables the acoustics-relevant spectrum options (sound pressure level spectra and frequency band charts), and specifies that the overall sound pressure level is calculated and displayed in the console when you plot or write the FFT data. All dB-measured quantities are based on the Reference Acoustic Pressure.
opens the Ansys Sound Analysis Dialog Box.
- Process Options
contains options to analyze signal data.
- Process Receiver
allows you to analyze receiver data stored in memory.
- Process File Data
allows you to analyze signal data from an existing input file.
- Y Axis Function
contains a list from which you can select the function for the
axis.
- X Axis Function
contains a list from which you can select the function for the
axis.
- Receiver
contains a list of receivers from which you can select when the Process Receiver option is enabled.
- Plot/Modify Input Signal...
opens the Plot/Modify Input Signal Dialog Box, which you can use to plot the input signal, as well as customize the data set and define spectrum smoothing in preparation for applying the FFT algorithm.
- Reference Acoustic Pressure
allows you to specify the reference acoustic pressure (for example,
in Equation 40–15) used to calculate the dB-measured quantities when the Acoustics Analysis option is enabled.
- Plot Title
lets you create a new title or edit the original title for the FFT plot. By default, Ansys Fluent adds the string "Spectral Analysis of" to the title originally applied to the input signal plot.
- Y Axis Label
allows you to create a new
axis label or edit the original
axis label. By default, the Y Axis Label corresponds to the selection in the Y Axis Function drop-down list.
- X Axis Label
allows you to create a new
axis label or edit the original
axis label. By default, the X Axis Label corresponds to the selection in the X Axis Function drop-down list.
- Y Axis Variable
if your input report file contains multiple report definitions, this allows you to specify the
axis variable.
- X Axis Variable
if your input report file contains multiple report definitions, this allows you to specify the
axis variable.
- Files
lists the loaded input signal data files.
- Load Input File...
loads an input signal data file into Ansys Fluent for FFT analysis. The input file is listed under Files.
- Free File Data
removes data from FFT analysis once the input signal data file is selected in the Files list.
- Plot FFT
displays the FFT data in a graphic window and, if Acoustics Analysis is enabled, calculates the overall sound pressure level in dB (based on the Reference Acoustic Pressure) and displays it in the console. If the Write FFT to File option is selected, then this button becomes the Write FFT button, which opens a file selection dialog box so that you write the FFT data to a file.
- Write FFT
opens The Select File Dialog Box in which you can specify a name and save the FFT data to a file. If Acoustics Analysis is enabled, the overall sound pressure level will be calculated in dB (based on the Reference Acoustic Pressure) and displayed in the console at this time. If the Write FFT to File option is selected, then the Plot FFT button changes to the Write FFT button.
- Axes...
opens the Axes Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- Curves...
opens the Curves Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the plot.
Refer to Performing an Ansys Sound Analysis for additional information on this dialog box.
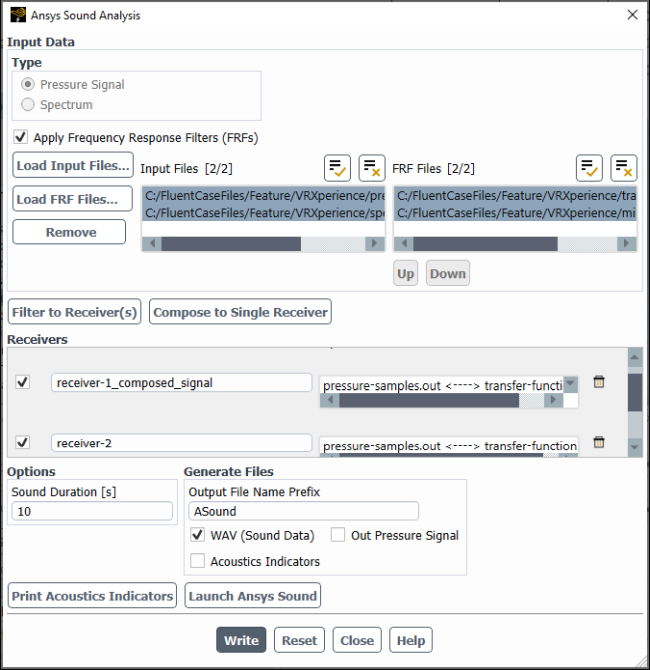
Controls
- Input Data
- Pressure Signal
specifies that the input file you select is an acoustic pressure file (two column file of time vs. pressure).
- Spectrum
specifies that the input file you select is an FFT output file (two column file of frequency vs. power spectral density).
- Apply Frequency Response Filters (FRFs)
allows you to load a frequency response filter (FRF) file.
allows you to read in either a pressure data or spectrum input file.
allows you to read in frequency response filter files.
removes the selected file from the Input Files and FRF Files lists.
- Input Files
lists the loaded input pressure signal or spectrum files.
- FRF Files
lists the loaded frequency response filter (FRF) files.
moves the selected FRF file up in the list.
moves the selected FRF file down in the list.
adds one or more receivers (based on the number of selected files) that are mapped with one input file and one frequency response filter file per receiver to the Receivers list. For example, you could have 3 input files and 3 FRF files selected and this would result in 3 new receivers. You could also have 1 input file selected and 3 FRF files selected, which would also result in 3 new receivers.
combines the selected input files and corresponding FRF files into a single receiver that gets added to the Receivers list.
- Receivers
lists the defined receivers and their comprising input and FRF files, with arrows indicating how they correspond.
- Active
indicates whether the receiver is active. That is, whether or not the receiver will be included or evaluated when you click any of the following buttons: , , .
- Name
displays the (editable) name of each defined receiver.
- Input Files <---> FRF Files
displays the input and FRF files included within a receiver. The arrow indicates which input file is modified by which FRF file.
- Options
- Sound Duration
specifies the length of the sound clip for saving a WAV file.
- Generate Files
- Output File Name Prefix
specifies the name (aside from the extension) for any files saved when you click .
- WAV (Sound Data)
specifies that a WAV sound file will be written when you click .
- Out Pressure Signal
specifies that a pressure signal file will be written when you click .
- Acoustic Indicators
specifies that a file containing the computed acoustic indicators will be written when you click .
computes the acoustic indicators for the selected files and prints them to the console.
launches Ansys Sound and loads the defined receivers.
computes the acoustic indicators for the selected files and prints them to the console.
clears all settings and default changes from the dialog box.
The Cumulative Plot dialog box allows you to analyze the development of force, moments, or coefficients for your model in the any desired location or direction. See Cumulative Force, Moment, and Coefficients Plots for details about the items below.
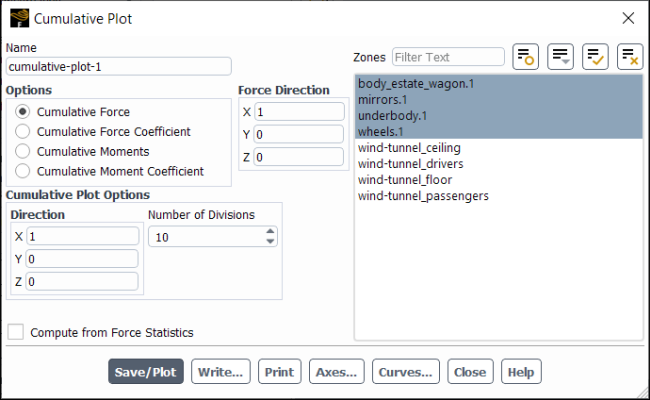
Controls
- Name
name of the cumulative plot object.
- Options
lets you select which type of plot to display.
- Cumulative Force
displays the force development for the specified direction and walls.
- Cumulative Force Coefficient
displays the force coefficient development for the specified direction and walls.
- Cumulative Moments
displays the moment development for the specified direction and walls.
- Cumulative Moment Coefficient
displays the moment coefficient development for the specified direction and walls.
- Cumulative Plot Options
contains options to specify the direction and number of divisions where Fluent will calculate and plot the selected variable.
- Direction
allows you to specify the direction along which the cumulative force or moments will be computed.
- Number of Divisions
specifies the number of slices across the selected wall zones where the force or moments will be evaluated for the resulting cumulative plot. The planes will be created perpendicular to the Direction.
- Compute from Force Statistics
use averaged values computed from force statistics instead of the default instantaneous values.
- Force Direction
(Cumulative Force and Cumulative Force Coefficient only) allows you to specify the force component direction.
- Moment Center
(Cumulative Moments and Cumulative Moment Coefficient only) allows you to specify the coordinates of the moment center.
- Moment Axis
(Cumulative Moments and Cumulative Moment Coefficient only) allows you to specify the coordinates of the moment axis.
- Zones
lists the zones that you can select for the cumulative plot.
- Save/Plot
saves the cumulative plot object and plots the cumulative force, force coefficient, moments, or moment coefficient.
- Write...
opens The Select File Dialog Box, allowing you to save the plot data to a file.
prints the value of the force or moment at each division to the console.
- Axes...
opens the Axes Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- Curves...
opens the Curves Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the plot.
The Plot/Modify Input Signal dialog box allows you to plot the input signal, as well as customize the data set and define spectrum smoothing in preparation for applying the FFT algorithm. It is opened from the Fourier Transform Dialog Box. See Using the FFT Utility for details about the items below.
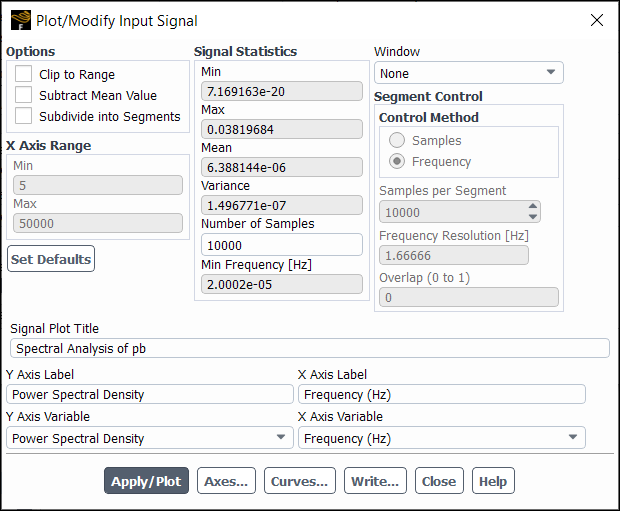
Controls
- Options
allows you to process some or all of the input signal data.
- Clip to Range
allows you to analyze a portion of the input signal by specifying data range.
- Subtract Mean Value
reduces y axis quantities by the mean value of the relevant signal property.
- Subdivide into Segments
enables / disables spectrum smoothing, which can suppress spurious amplitude fluctuations in the Fourier spectrum by splitting the input signal into multiple overlapping segments, so that Ansys Fluent can apply the FFT algorithm on each segment and then average the resulting spectra. The spectrum smoothing is controlled by the settings in the Segment Control group box. See Customizing the Input and Defining the Spectrum Smoothing for further details.
- Signal Statistics
displays signal information.
- Min
displays the minimum value for the input signal.
- Max
displays the maximum value for the input signal.
- Mean
displays the average value for the input signal.
- Variance
displays the variance for the input signal.
- Number of Samples
displays the total number of samples in the input signal data set.
- Min Frequency
displays the finest possible frequency resolution for the input signal.
- X Axis Range
allows for a portion of the input signal to be analyzed when the Process the whole data option is turned off.
- Min
specifies a minimum value for the
axis.
- Max
specifies a maximum value for the
axis.
- Set Defaults
resets the
axis minimum and maximum values to their original value and turns on the Process the whole data option.
- Signal Plot Title
lets you create a new title or edit the original title for the input signal plot. By default, the Signal Plot Title corresponds with the title originally applied to the input signal plot.
- Y Axis Label
allows you to create a new
axis label or edit the original
axis label. By default, the Y Axis Label corresponds with the
axis label originally applied to the input signal plot.
- X Axis Label
allows you to create a new
axis label or edit the original
axis label. By default, the X Axis Label corresponds with the
axis label originally applied to the input signal plot.
- Y Axis Variable
if your input report file contains multiple report definitions, this allows you to specify the
axis variable.
- X Axis Variable
if your input report file contains multiple report definitions, this allows you to specify the
axis variable.
- Window
lets you specify a windowing technique to remove discontinuities in the FFT calculation.
- None
applies no windowing technique. This is the default setting.
- Hamming
applies the Hamming technique.
- Hanning
applies the Hanning technique.
- Bartlett
applies the Bartlett technique.
- Blackman
applies the Blackman technique.
- Segment Control
provides settings that control the spectrum smoothing when Subdivide into Segments is enabled.
- Control Method
allows you to specify how you want to define the segment size from the following:
- Samples
bases the segment size on the Samples per Segment.
- Frequency
bases the segment size on the Frequency Resolution
in Hertz units.
- Samples per Segment
defines the number of samples in each segment when Samples is selected from the Control Method list.
- Frequency Resolution
defines the desired frequency resolution
in Hertz units when Frequency is selected from the Control Method list.
- Overlap
ranges from 0 to 1 and defines how much adjacent segments overlap. This setting is applicable regardless of which Control Method you select.
- Apply/Plot
applies any changes you have made in the dialog box and displays the input signal data in a graphics window.
- Axes...
opens the Axes Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the plot axes.
- Curves...
opens the Curves Dialog Box, which allows you to customize the curves used in the plot.
- Write...
opens The Select File Dialog Box, in which you can save the signals to a file.
The Axes dialog box allows you to independently control the characteristics of the ordinate and abscissa on an XY plot or histogram. You can change the titles, scale, range, number format, and major and minor rules visibility and appearance. Note that the title following Axes in the dialog box indicates which plot environment you are changing. You can set different parameters for each type of plot that Ansys Fluent can generate. See Using the Axes Dialog Box for details about the items below.
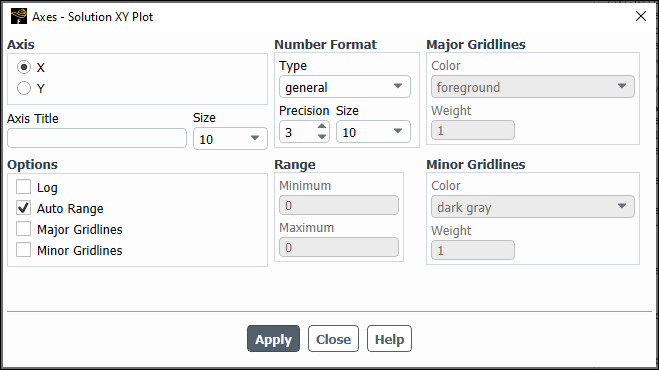
Controls
- Axis
contains check buttons that allow you to set abscissa (
-axis) or ordinate (
-axis) characteristics.
- X
allows you to specify the abscissa characteristics.
- Y
allows you to specify the ordinate characteristics.
- Axis Title
defines the character string that will label the active axis (the one selected in Axis) in the display.
- Size
specifies the font size of the Axis Title.
- Options
contains check buttons that (de)activate scale, range, major rules, and minor rules.
- Log
toggles logarithmic scaling of the active axis. By default, decimal scaling is used.
- Auto Range
toggles automatic computation of the range of the active axis. If you deactivate this option, you may input the Minimum and Maximum values in the Range box.
- Major Rules
toggles the display of major rules on the active axis. Major rules are the horizontal or vertical lines that mark the primary data divisions and span the whole plot window to produce a "grid."
- Minor Rules
toggles the display of minor rules on the active axis. Minor rules are the horizontal or vertical lines that mark the secondary data divisions and span the whole plot window to produce a "grid."
- Number Format
contains controls for changing the format of the data labels on the active axis. Data labels are the character strings used to define the primary data divisions on the axes.
- Type
sets the form of the data labels. You may select from a drop-down list of options, including the following:
- general
displays the real value with either float or exponential form based on the size of the number and the defined Precision.
- float
displays the real value with an integral and fractional part (for example, 1.0000), where the number of digits in the fractional part is determined by Precision.
- exponential
displays the real value with a mantissa and exponent (for example, 1.0e-02), where the number of digits in the fractional part of the mantissa is determined by Precision.
- Precision
defines the number of fractional digits displayed in the data labels.
- Size
specifies the size of the font used for the data labels.
- Range
contains the range or extents of the active axis. To set the range manually, you must turn off Auto Range. Otherwise the extents are computed automatically.
- Minimum
sets the minimum data value for the active axis.
- Maximum
sets the maximum data value for the active axis.
- Major Rules
contains controls for modifying the appearance of the major rules. To use these controls you must activate Major Rules in the Options list.
- Color
sets the color of the major rules from a drop-down list with numerous color selections.
- Weight
sets the line thickness of the major rule. A line of weight 1.0 is normally 1 pixel wide. A weight of 2.0 would make the line twice as thick (2 pixels wide).
- Minor Rules
contains controls for modifying the appearance of the minor rules. To use these controls you must activate Minor Rules in the Options list.
The Curves dialog box allows you to modify the appearance of the lines and markers used in XY plots. Note that the title following Curves in the dialog box indicates which plot environment you are changing. You can set different parameters for each type of plot that Ansys Fluent can generate. See Using the Curves Dialog Box for details about the items below.
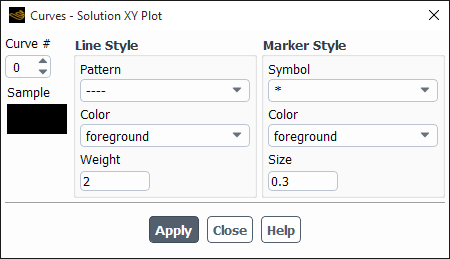
Controls
- Curve #
defines the active curve number. The present and future marker and line styles apply to the defined curve number. The curves are numbered sequentially, starting from 0. For example, if you were plotting flow-field values on two zones, the first zone would be curve 0, and the second, curve 1. If the plot contains only one curve, the Curve # is set to 0 and is not editable.
- Sample
displays a single marker and line with the current style attributes.
- Line Style
contains controls for modifying the appearance of the active curve.
- Pattern
sets the pattern of the active curve. A drop-down list allows you to set the line pattern. Except for center and phantom lines, the list displays examples of the pattern choices. A center line alternates a very long dash and a short dash and a phantom line alternates a very long dash and a double short dash.
- Color
sets the color of the active curve. A drop-down list allows you to select from a list of color names.
- Weight
sets the thickness of the active curve. A line weight of 1.0 is normally 1 pixel wide. Therefore, a weight of 2.0 would make the line twice as thick (2 pixels wide).
- Marker Style
contains controls for modifying the appearance of the active curve’s marker.
- Symbol
sets the symbol used to mark data. You can select the symbol from a drop-down list that contains all the symbol choices. The Sample box will allow you to experiment with various markers. For example, in plotting pressure-coefficient data on the upper and lower surfaces of an airfoil, the symbol
/*\(filled-in upward-pointing triangle) could be used for the marker representing the upper surface data, and the symbol\*/(filled-in downward-pointing triangle) could be used for the marker representing the lower surface data.- Color
sets the color of the marker on the active line number. A drop-down list allows you to select from a list of color names.
- Size
sets the size of the data marker. A symbol of size 1.0 is 3.0% of the height of the display screen, except for the "." symbol, which is always one pixel.


