The Post-Analysis module is a comprehensive tool that displays, compares and performs queries onto meshes and solution files located in the Project View inside the framework of Fluent Icing.
Note: Post-Analysis uses the EnSight renderer. Therefore, the EnSight package must be included in the Ansys installation to leverage this capability and a post-processing license is required.
When the Post Analysis feature is first activated, a Post-Analysis node will appear in the Outline View where detailed post-processing can be performed. In general, it can be used to create more custom post-processing objects or obtain more detailed solution data than what is otherwise available from the quick post-processing objects available in the Results node of a simulation.
Fluent results supported:
Icing solutions supported:
FENSAP Airflow
Particles (Droplets, Crystals, Vapor)
Ice (Ice solution, Ice cover)
Note: Some icing solution field names displayed in EnSight will differ from Viewmerical or CFD-Post, refer to Field Name Mapping.
For more information on Post-Analysis, see Fluent Post-Analysis Workspace.
Datasets can be loaded into the Post-Analysis tool in two ways: by accessing the files in the Project View, or by using the command in the Results ribbon.
In the Project View, select a solution or case file and choose in the contextual menu.
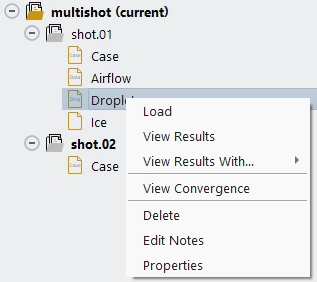
A solution file is loaded along its matching case or grid file.
To load a solution file that is not visible in the Project View, go to the Results ribbon and select .
In this mode, browse to the location in the disk where the solution file is located and select its corresponding case and solution files.
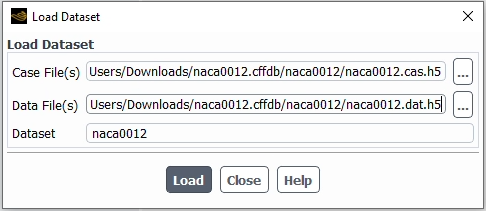
Typically, in a regular Fluent simulation, the .cas file is alongside the .dat file with a similar name. Whereas, in a Fluent Icing project folder, the simulation folder contains the master case (.cas) file. The run subfolders of Airflow type contains the Fluent Solution (.dat) file only. If the run has the Post Solution (.dat.post) output mode enabled, it will also contain the Post Case (.cas.post) to be used as the solution file for quick post-processing. In the case of Particles and Ice solution files, they should be loaded through the Project View of Fluent Icing by selecting .
See File Types for more details.
Multiple solutions or datasets can be loaded and appended to the Post-Analysis module of Fluent Icing. This can be done by selecting them through or . All solutions and datasets loaded into the Post-Analysis module are located inside the Outline View.
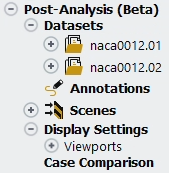
Note: Each additional dataset that is loaded will consume memory.
To remove an existing solution or dataset from Post-Analysis, right-click the location of the solution inside Datasets and select .
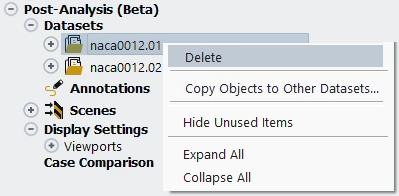
Once all datasets are loaded into Post-Analysis, each dataset can be post-processed separately by selecting the dataset of interest through the ribbon Dataset → Select Active Dataset menu or by selecting it in the Outline View.
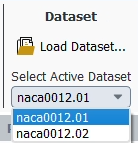
As datasets or results are selected in the Outline View, the active dataset is updated in the ribbon.
Moreover, each additional dataset is loaded in the same EnSight instance and will consume additional memory.
The following commands are available when left-clicking a Dataset name:
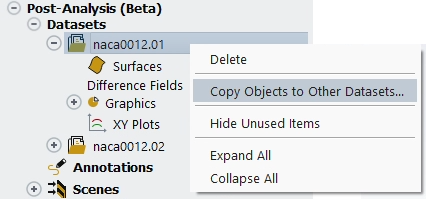
Datasets can be released and unloaded through the command. All graphical objects related to this dataset, and Scene entries, will be removed.
This command enables you to copy the state of one dataset to another, including its list of graphical objects and their settings. This enables easy dataset comparison, especially if each dataset is shown in a separate viewport.
This command enables you to hide unused graphics objects in the list For example, if only a Mesh object has been created, will reduce the list of objects under the dataset to show only the Meshes object. This can be helpful to reduce visual clutter when working with many datasets. You can select to reveal the unused hidden objects.
The following graphics display control icons are available at the left side of the Post-Analysis graphics window:
 Set Layout
Set Layout
This menu can be used to split the graphics window into multiple viewports
 Set Active Viewport
Set Active Viewport
This menu can be used to select the active viewport for graphical operations. Alternatively, the display or addition to a specific viewport can be set from the contextual menu on the graphical item by choosing →
 Link Viewports
Link Viewports
This menu is used to synchronize the camera angles and movements of all viewports
Alternatively, the display or the addition of the selected graphical object to a specific viewport can be set from the contextual menu on the graphical item:
Displays the graphics object for the selected datasets side-by-side, in the Graphics window using the viewport layout specified under the Case Comparison node.
Displays the graphics object for the selected datasets in the Graphics window.
Displays the selected Graphics object within the viewport.
Adds the selected Graphics object to the viewport.
Opens the Save Picture dialog box allowing you to save an image file of the object in the Graphics window.
Deletes the selected Graphics object.
For quick access to commonly used commands, a context-sensitive menu is available when right-clicking within the Graphics window:
Opens the Save Picture dialog box allowing you to save an image file of the object in the Graphics window.
Opens the Save Animation dialog box allowing you to save an animation file.
Note: This setting is active only for transient datasets.
Saves the Graphics window content as an object under Scenes.
Saves the Graphics window content to an existing Scene object.
Adds the selected Graphics object to the viewport.
Displays the selected Graphics object within the viewport.
Removes the selected Graphics object from the viewport.
Displays the selected Scene object in the viewport.
Displays your model to take maximum advantage of the Graphics window’s width and height.
Adjusts the overall size of your model to take maximum advantage of the viewport’s width and height.
Contains a drop-down of views, allowing you to display the model from the direction of the vector equidistant to all three axes, as well as in different axes orientations.
Allows you to select from a collection of viewport arrangements.
Synchronizes the display of the selected viewports.
In this section, the most relevant graphical objects to post-process icing results using Post-Analysis are presented. For more information regarding the graphical objects of Post-Analysis, consult Graphics Objects.
Each loaded dataset will have the following graphical objects available in Post-Analysis:
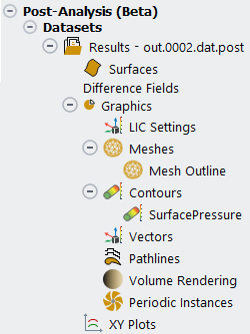
Surfaces
Generate new geometric surfaces or lines which can be used as selected surface zones when creating a mesh, contour or vector display.
Difference Fields
Generate objects to display the difference of certain data fields.
Meshes
Generate mesh objects to display all or part of the mesh.
Contours
Generate colored contour plots of solution variables contained in the solution file.
Vectors
Generate vector plots of directional variables contained in the solution file.
Pathlines
Generate pathlines along surfaces using directional variables in the solution file.
Volume Rendering
Draw vectors in the entire domain, or on selected surfaces. By default, one vector is drawn at the center of each cell (or at the center of each facet of a data surface), with the length and color of the arrows representing the velocity magnitude. The spacing, size, and coloring of the arrows can be modified, along with several other vector plot settings.
Periodic Instances
Generate periodic instances objects to display repeated periodic surfaces.
XY Plots
Generate XY plots of solution data along 1D objects in the domain.
Create 2D XY plots of your results for analyzing one variable with respect to another variable. For more details on , see Mirror Planes.
Ice Cover
The Ice cover of a single or multi-shot icing solution can be viewed by selecting from the standalone Ice solution or from from the multi-shot run in the Project View.
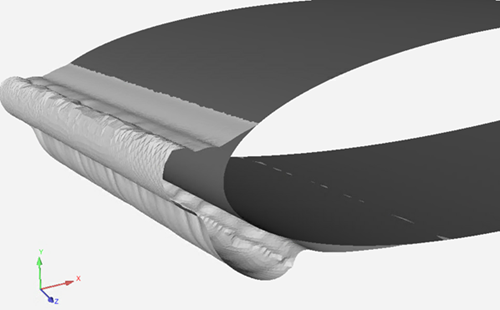
The display of the Ice Cover is a Scene (The Scene object is named icecover-*) containing:
Original Surface (Map Mesh Object Named Mesh Outline)
Wall zones of the original grid, in gray.
In a multi-shot, the original surface mesh is the original case file (input of multi-shot step #1).
Ice Surface (Ice Mesh Object Named Icecover)
Wall zones that contain the ice layer that is displayed by default in white. Only the iced surface is displayed. Surfaces with near zero ice growth are not displayed. The shading properties of the ice can be configured in the icecover mesh object.

The threshold used to display the iced surface is configured in the Iso-Clip surface iceclip.

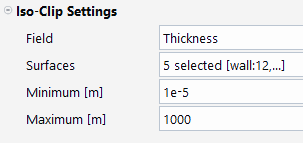
Surfaces with a Field value lower than the minimum are not displayed.
The Surface Grid and the Ice surface are then combined into a Scene.
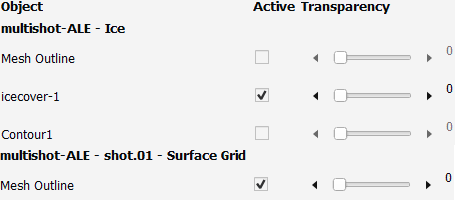
See Graphics Objects for more information on contours, vectors, pathlines and more.
XY Plots
XY Plots work on a 1D graphical object. Two main ways to create a line or curve (1D Surface) that will be used to create an XY Plot are presented below.
Surfaces → →
Allows to create an arbitrary line in the volume.
Surfaces → →
Creates a curve by intersecting an iso-surface to a list of Surfaces.
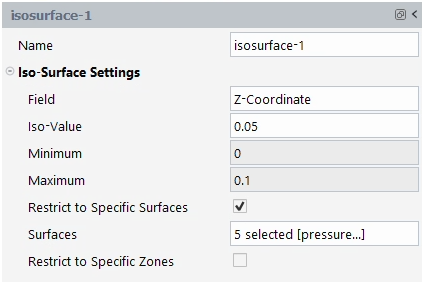
In the example above, a Z cutting plane (Iso-Surface) is selected at the middle of the domain and intersects a list of walls that represent an airfoil. This creates a curve that is located at the center of the airfoil.

In the XY plot panel, select the 1D Surfaces to display, the Field, and the X / Y / Z Plot Direction.
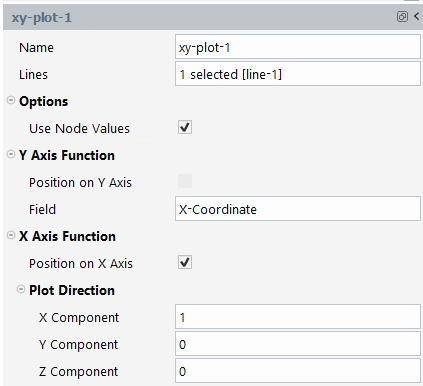
You can select multiple items in the Outline View to perform a bulk function (such as using to remove multiple surfaces at a time).
For more information on graphical objects, see Graphics Objects.
When multiple results can be loaded into Post-Analysis concurrently, the feature can be used to easily create side by side comparisons of different datasets.
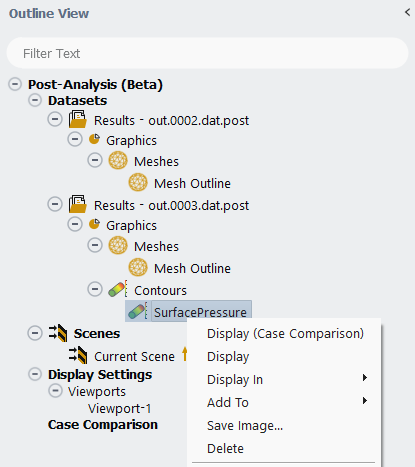
When more than one dataset is loaded into Post-Analysis, create a graphics object, for example a contour, in one of the datasets. Right-click that object and select . The graphics object will automatically be copied to all datasets, and
Scenes → Current Scenes will be automatically adjusted such that the graphics window will display a side by side comparison of the datasets.
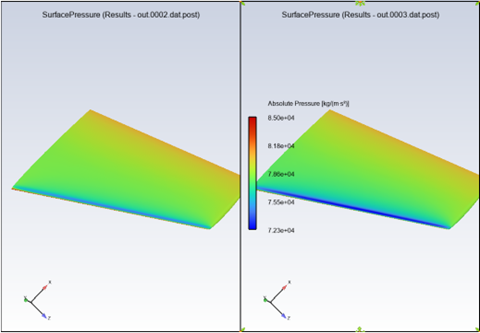
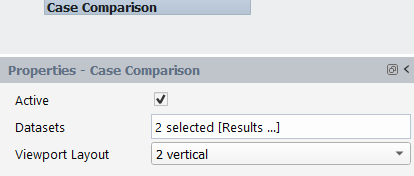
A maximum of 4 datasets will be displayed at a time. The Case Comparison object can be used to adjust datasets that are currently selected.
A Multi-Shot simulation produces a sequence of solutions of the same type. This sequence of solutions can be loaded, through the Project View, by using the command of a multi-shot run.
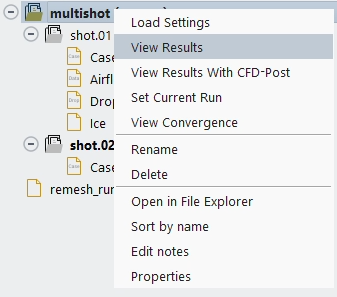
This command will offer the choice to load one of the available solution groups:
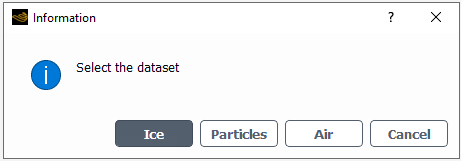
might offer two choices, Fluent Solution or Post Solution. This will depend on the Post-processing Output selected in the Solution → Airflow panel. See Airflow of this manual for more details.
In the case of , Ice Solution or Ice Cover can be selected. Ice Solution is the ice solution mapped on the input mesh at the start of a shot. Ice Cover is the ice solution mapped on the output mesh at the end of a shot.
When a sequence of solutions is loaded, use the Dataset - Sequence ribbon to display each solution of the sequence. In the case of a multi-shot solution, Shot #1 corresponds to time step 0.
The selection of a graphic object (Mesh, Contour, etc.) or Scene containing an item that is part of a sequence of solutions enables the possibility to create an animation using the button. This option is available at the bottom of the Properties panel for the selected graphical object or scene.

The animation feature (Saving Animations) enables you to save a movie file with a frame for each sequence step of the dataset.


