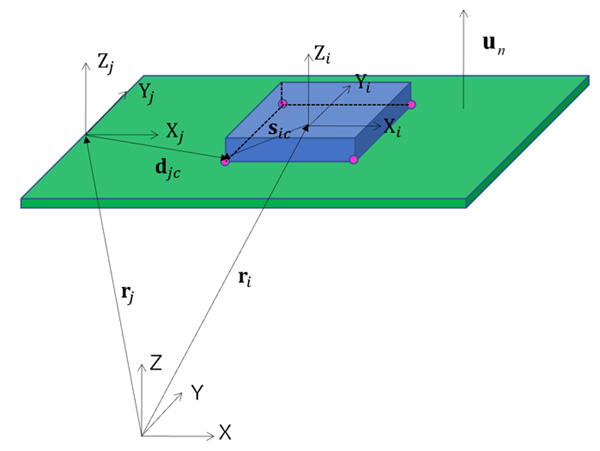
The Soil Interaction entity is used to calculate the interaction force between soil and a body. A lot of tracked vehicles operate not only on the hard ground but also on soft ground which is usually called soil. Though the Hertz contact and Coulomb friction approach was enough to represent hard ground, they were insufficient for soft soil. To represent soft soil, the contact formulations of Bekker's normal pressure, Wong's shear stress, and Dynamic sinkage are used.
Bekker's equation for normal pressure:
(12–1) |
where,
: cohesive modulus of soil deformation
: frictional modulus of soil deformation
: track width
: sinkage
: sinkage exponent
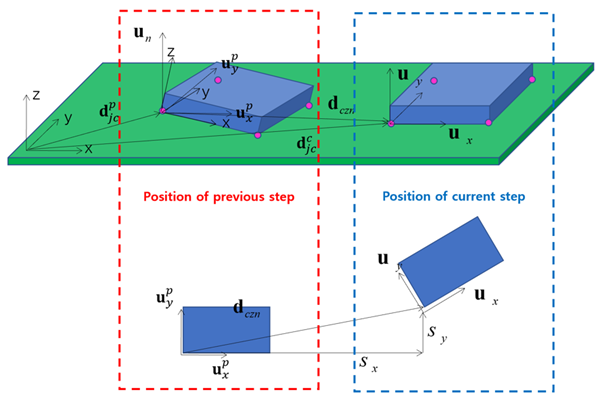
Kinematics for sinkage:
(12–2) |
(12–3) |
Geometric sinkage from relative distance:
(12–4) |
(12–5) |
Contact condition:
(12–6) |
Differentiation of sinkage:
(12–7) |
Wong's equation for shear pressure:
(12–8) |
(12–9) |
(12–10) |
where,
: sensitivity
: maximum shear displacement
: friction angle (degrees)
: normal pressure
: shear displacement
Moving displacement:
(12–11) |
Longitudinal slip:
(12–12) |
Lateral slip:
(12–13) |
Bekker's formula has only the stiffness term. As a result, it triggers vibration of the body that defines the soil force. To mitigate this issue, a damping term is added. This formula was developed in a form similar to General Contact .
Soil Interaction provides a set (library) of soil characteristics. User-defined characteristic values can be defined.