VM-WB-MECH-107
VM-WB-MECH-107
Cable/Pipe Supporting Hanging Loads
Overview
| Reference: | Beer, F. P. & Johnston, E.R., Jr., (1962). Vector Mechanics for Engineers, Statics and Dynamics. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. 260. |
| Solver |
Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Static, Stress Stiffening Analysis |
| Element Type(s): |
3-D Link and 3-D Cable |
Test Case
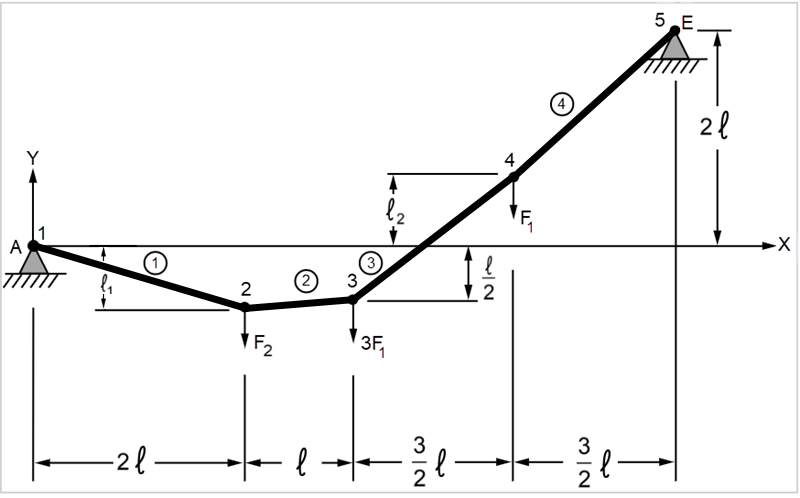
Cable/link AE supports three vertical loads from the points indicated below (points 2, 3, and 4). For the equilibrium position shown, determine the horizontal Ax and vertical Ay reaction forces at point A and the maximum tension T in the cable/link.
This test case also appears in the Mechanical APDL Verification Manual. See VM31.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
Geometry is imported from DesignModeler containing one line body with four edges and five vertices. Both end vertices have fixed supports applied. All vertices (other than the end vertices) have Force applied in the downward direction with values 6000, 12000, and 4000 from the left side respectively. Displacement is constrained on these vertices to avoid displacement in the Z direction.
First, a Lower Order (Linear) mesh is set to create a single element on each edge for the Link analysis. Then a Higher Order (Quadratic) mesh is set to create two elements on each edge for the Cable analysis. Initial Strain (1 x 10-7) is applied using a command snippet for INISTATE. Force reaction is calculated on the left fixed support for X (Ax) and Y (Ay) for each analysis.