This feature is supported for stand-alone Static Structural and Modal analysis types only. It enables you to export your simulation as a NASTRAN Bulk Data file. You can use the capabilities of Mechanical and run the resulting simulation with your choice of NASTRAN solver. Currently, the NASTRAN Export capability is designed to export the common features of static structural and modal simulations. However, not all features are supported. Review the following subsections for additional information about exported what is supported as well as the limitations associated with this feature:
Application
Select the Environment object and select the Export NASTRAN File option from the Tools group of the Environment Context Tab (the option is also available via right-click on the Environment object). Based on your analysis type, one of the following dialogs displays.
You use these property options to further define how you wish to export your simulation. Review the property descriptions listed below.
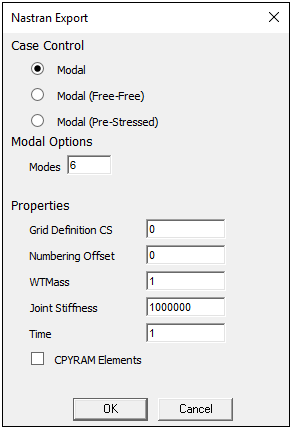
Static Structural Modal 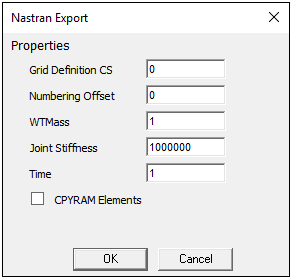
Click OK to begin the export process. You are prompted to enter a file name and specify the file extension, .dat, .bdf or .nas.
Note: The contents of each file type (.bdf, .nas, and .dat) are identical.
As needed, you can open the log file (filename.log) produced during the NASTRAN Export process to review certain translation details of the export. This file is placed in the same location as your NASTRAN file.
Property Definition
- General Properties
Each dialog includes the following identical Properties:
Grid Definition CS: This property determines which Mechanical Cartesian coordinate system is used as the NASTRAN basic coordinate system. When set to 0 (the usual case), the Mechanical global coordinate system will be used. You may instead choose any local Cartesian coordinate system in Mechanical to be used as the NASTRAN basic coordinate system, thereby translating and/or rotating the grid for export. To do so, set this property value to the desired Mechanical coordinate system reference number.
Unless you have a specific reason for doing so, do not choose a cylindrical or other non-Cartesian system for this property. Doing so will cause R, Θ, and, Z coordinates, for example, to be interpreted as X, Y, and Z values, causing a cylindrical mesh to be unrolled (developed) into a planar mesh.
Numbering Offset: This property is used to add a specified integer offset to the numbering of all node, element, material, property, and coordinate system IDs. This property can be used to prevent numbering conflicts if the exported data is to be combined with data from additional exports or other sources. Enter the offset value for the property value.
WTMass: This property writes the parameter WTMASS into the export file to specify a global change in Mass units. Mechanical does not use this property to scale any values that are written to the exported file.
Joint Stiffness: This property is used to specify the stiffness of any rigidly restrained degrees of freedom for NASTRAN CBUSH joint elements (created from Mechanical MPC184 joint elements). This stiffness is used as-is and is unaffected by any unit conversions. A value greater than 1e6 may cause an ill-conditioned matrix in the NASTRAN solver.
Time: In the case of a Mechanical model with time-varying applied loads, this property specifies which load values are to be used as the static loads for the export. Repeating the export with a different Time property value will calculate a new set of load values at the new time.
CPYRAM Elements: This option suppresses (unchecked) or allows (checked) the creation of NASTRAN pyramid elements. Not all NASTRAN versions support pyramid elements. Using this option, you can customize the export to the capabilities of the target NASTRAN version.
Note: If pyramid elements are present in the Mechanical model and this option is left unchecked (pyramid elements are suppressed), there will be voids in the exported mesh in place of the pyramid elements.
- Modal Analysis Specific Properties
The modal analysis dialog includes the additional options described below.
Case Control: From this group of options, select the type of modal analysis you want the NASTRAN Export to do:
Modal: Modal analysis of a constrained model, without pre-stress.
Modal (Free-Free): Modal analysis of an unconstrained model, without pre-stress. The first modes will be rigid body modes at nominally 0 Hz.
Modal (Pre-Stressed): Static analysis of a constrained model, using the exported applied loads, followed by a modal analysis of the pre-stressed model.
Modal Options: This group contains the following properties/options:
Modes: Specify the number of modes (increasing in frequency) to be calculated.
Perform Ground Check: This option displays when the Modal (Free-Free) Case Control is selected. Activating (checking) this option will direct that a ground check be performed to discover any unintentionally constrained rigid body modes.


