A sub-volume is a volumetric part of the simulation domain. It is a concept used in Forte's Automatic Mesh Generation (AMG) approach. Sub-volumes can be used to identify distinct and individual regions in the domain. Once created, sub-volumes have several use cases:
Use sub-volumes in mesh controls: Sub-volumes can be used as “secondary volumes” in mesh controls. See Mesh Controls for Automatic Meshing for details.
Use sub-volumes in initialization: Since sub-volumes identify distinct regions of the domain, they can be used as the basis for defining initial conditions. See Configuration of Initialization Regions for Automatic-mesh Generation for details.
Use sub-volumes in monitor probes: You may monitor spatially-averaged solution variables in a sub-volume region. See Probes for Instantaneous, Spatially Averaged Data for details.
To create a sub-volume, go to the Geometry node (see Geometry Node) and select the Sub-volumes
sub-node  . Then, click New Sub-Volume
. Then, click New Sub-Volume  .
.
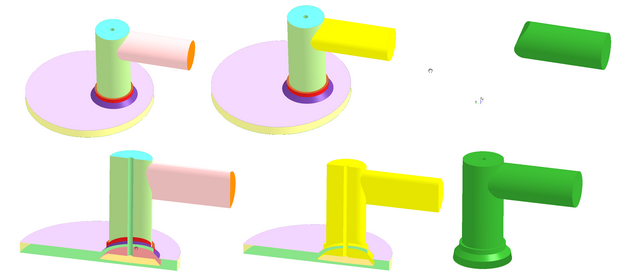
To create a sub-volume, select the surfaces in the mesh that surround the desired volume to isolate. Since watertight geometry will contain continuous manifolds, there will inevitably be a boundary at which the selected surfaces meet with unselected surfaces. At this boundary, a surface capping technique will be applied to the geometry to complete the volume, as illustrated in Figure 2.22: Specifying a sub-volume via Geometry, then selecting, then actual sub-volume displayed. The top row illustrates the Geometry, then selection, then resulting sub-volume. The second row uses a clipping plane to better illustrate the selection.
A sub-volume mesh control requires a material point. The material point defines the nature of the control: if the material point is placed within the sub-volume, the control will act on the sub-volume. If the material point is placed outside of the sub-volume (but still within the domain) the control will act on the volume not enclosed by the sub-volume.