Autoignition phenomena in engines are due to the effects of chemical kinetics of the reacting flow inside the cylinder. There are two types of autoignition models considered in Ansys Fluent:
knock model in spark-ignited (SI) engines
ignition delay model in diesel engines
For information regarding the theory behind autoignition models, see Autoignition Models in the Theory Guide.
To use the autoignition model, perform the following steps:
Select Transient from the Time list in the General task page (or from the General → Analysis Type in the tree).
Select an appropriate reaction model in the Species Model dialog box.
Setup → Models → Species
Edit...
The models in the Species Model dialog box that are compatible with the autoignition model are Species Transport, Premixed Combustion, and Partially Premixed Combustion.
The Autoignition model will now appear in the Models task page and under the Models tree item.
Important:If you select Species Transport, you must also enable the Volumetric option in the Reactions group box.
The Premixed Combustion and Partially Premixed Combustion models are only available for turbulent flows using the pressure-based solver.
Select the Autoignition model.
Setup → Models → Species → Autoignition
Edit...
If Species Transport is selected in the Species Model dialog box, you can only select the Ignition Delay Model.
If Premixed Combustion is selected in the Species Model dialog box, you can only select the Knock Model.
If Partially Premixed Combustion is selected in the Species Model dialog box, you can select either the Knock Model or the Ignition Delay Model.
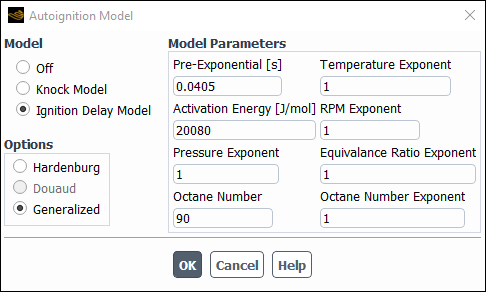
When the Ignition Delay Model is enabled, the dialog box expands to include the modeling parameters for this model (Figure 21.5: The Ignition Delay Model for the Partially Premixed Combustion Model). The two correlation options that exist with this model are Hardenburg and Generalized. Depending on which correlation option is selected, the appropriate modeling parameters will appear in the dialog box.
The Hardenburg option is typically used for heavy duty diesel engines. With this option, the following parameters are available:
Pre-Exponential
Pressure Exponent
Activation Energy
Cetane Number
For the Species Transport model, Fuel Species is selected from the drop-down list.
The Generalized option is described by Equation 10–9 in the Theory Guide. With this option, the following parameters are available:
Pre-Exponential
Temperature Exponent
Activation Energy
RPM Exponent
Pressure Exponent
Equivalence Ratio Exponent
Octane Number
Octane Number Exponent
For the Species Transport model, Fuel Species is selected from the drop-down list.
Default values of these parameters can be found in Default Values of the Variables in the Hardenburg Correlation in the Fluent Theory Guide.
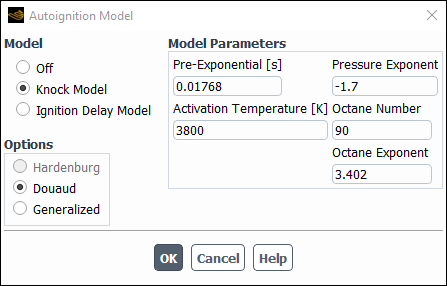
When the Knock Model is enabled, the dialog box expands to include modeling parameters for this model (Figure 21.6: The Knock Model with the Partially Premixed Combustion Model Enabled). The two correlation options that exist with this model are Douaud and Generalized. Depending on which correlation option is selected, the appropriate modeling parameters will appear in the dialog box.
The Douaud option is used for knock in SI engines. The modeling parameters that are specified in the Autoignition Model dialog box for this option are the Pre-Exponential, Pressure Exponent, Activation Temperature, Octane Number, and Octane Exponent (Equation 10–8 in the Theory Guide).
The Generalized option (Equation 10–9 in the Theory Guide) in the knock model requires the same parameters as in the ignition delay model.