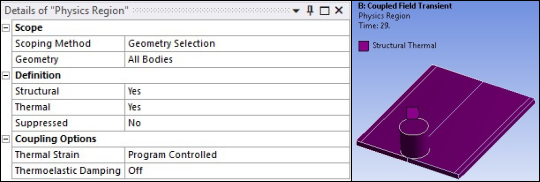
A nonlinear Coupled Field Transient Analysis is performed in three load steps. The analysis includes structural and thermal degrees of freedom as shown in the details view of the Physics Region object in the figure below. FSW simulation includes factors such as nonlinearity, contact, friction, large plastic deformation, structural-thermal coupling, and different loadings at each load step. The solution settings applied consider all of these factors.
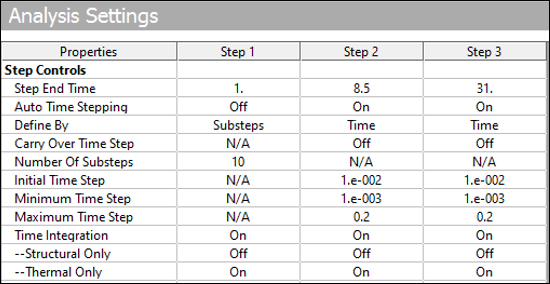
The first load step in the solution process converges within a few substeps, but the second and third load steps converge only after applying the proper solution settings as shown in the following table.
To allow for a faster solution, automatic time-stepping (AUTOTS) is off for first load step, and after the first load step, it is activated. The initial time step size (DELTIM) is set to 0.1, and the minimum time step is set to 0.001. The maximum time step is set as 0.2 in load steps 2 and 3. A higher maximum time-step size may result in an unconverged solution.
The time step values are determined based on mesh or element size. For stability, no time-step limitation exists for the implicit integration algorithm. Because this problem is inherently nonlinear and an accurate solution is necessary, a disturbance must not propagate to more than one element in a time step. Therefore, an upper limit on the time step size is required. It is important to choose a time step size that does not violate the subsequent criterion (minimum element size, maximum thermal conductivity over the whole model, minimum density, and minimum specific heat).
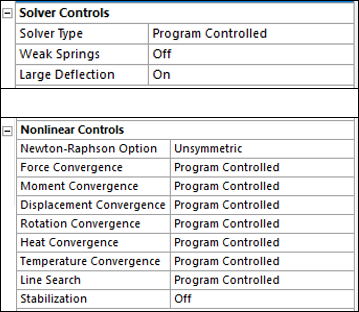
Note: Apart from above analysis settings and solver controls, the following commands must also be issued. Defaults in the Mechanical Application differ from those in Mechanical APDL. In the Mechanical Application, the HHT method is used by default.