VM-WB-MECH-110
VM-WB-MECH-110
Centerline Temperature of an Electrical Wire
Overview
| Reference: | Rohsenow, W.M. & Choi, H.Y. (1963).Heat, Mass and Momentum Transfer (2nd printing). Englewood Cliffs, NJ. p.106, ex. 6.5. |
| Solver |
Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Coupled Field Static |
| Element Type(s): |
2D and 3D Coupled-Field Elements |
Test Case
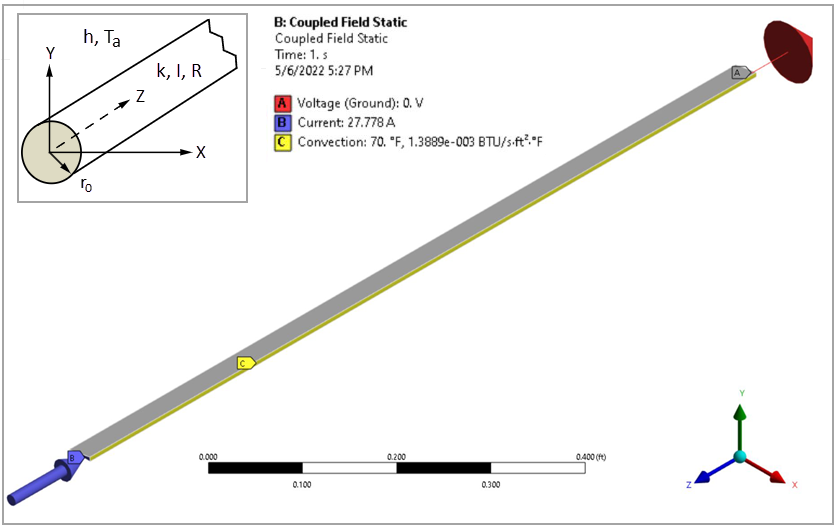
Determine the centerline temperature 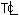 and the surface temperature Ts of a bare, steel wire carrying a current
I and having a resistance R. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the air (at
temperature Ta) is h. Also determine the heat dissipation rate q.
and the surface temperature Ts of a bare, steel wire carrying a current
I and having a resistance R. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the air (at
temperature Ta) is h. Also determine the heat dissipation rate q.
This test case is also solved using Ansys Mechanical APDL. See VM119.
Materials Properties Tables
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
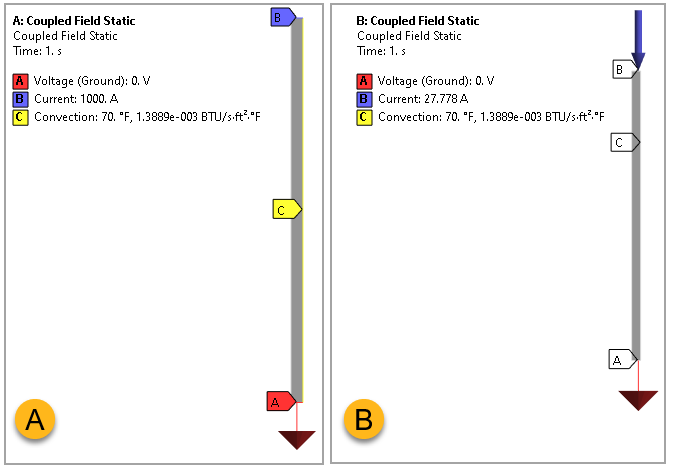
The problem is solved first using thermal-electric axisymmetric elements and then using thermal-electric solid elements.
A one foot axial length is chosen for convenience. The voltage drop per foot is IR = 0.1 volt/ft. The resistivity ρ is calculated as
| ρ = RA/L = (0.0001)(π)(0.03125)2/(1) = 3.06796 x 10-7Ω-ft |
Since the problem is axisymmetric, only a one-element sector is needed. A small angle Θ = 10° sector is used for approximating the circular boundary for the 3D element. The initial temperature is set to 70°F.
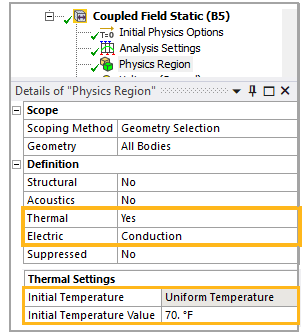
In Coupled Field Static for thermal-electric conduction coupling, the Thermal definition set to Yes and the Electric definition is set to Conduction as shown in the image below.
Results Comparison
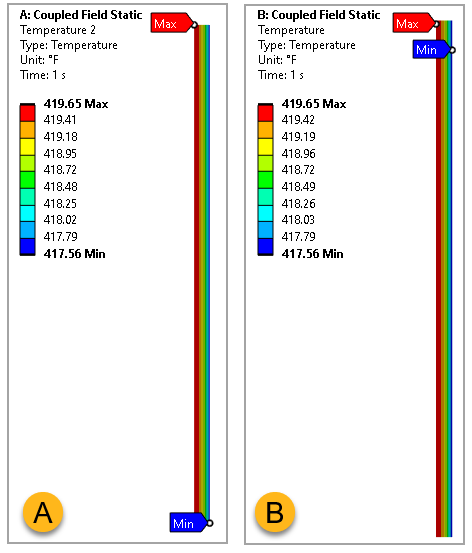
The Workbench results are compared with target specified in reference book.
| Target | Mechanical | Error (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2D | Centerline Temperature, °F | 419.9 | 419.645 | -0.061 |
| Ts, °F | 417.9 | 417.556 | -0.082 | |
| q, Btu/hr | 341.5 | 341.213 | -0.084 | |
|
3D | Centerline Temperature, °F | 419.9 | 419.652 | -0.059 |
| Ts, °F | 417.9 | 417.562 | -0.081 | |
| q, Btu/hr | 341.5 | 341.219 | -0.082 | |