VM119
VM119
Centerline Temperature of an Electrical Wire
Overview
Test Case
Determine the centerline temperature 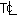 and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire carrying a current I and having a resistance
R. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the air
(at temperature Ta) is h. Also determine the
heat dissipation rate q.
and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire carrying a current I and having a resistance
R. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the air
(at temperature Ta) is h. Also determine the
heat dissipation rate q.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The problem is solved first using thermal-electric axisymmetric elements (PLANE223) and then using thermal-electric solid elements (SOLID226).
A 1 foot axial length is chosen for convenience. The voltage drop per foot is IR = 0.1 volt/ft. The resistivity ρ is calculated as ρ = RA/L = (0.0001)(π)(0.03125)2/(1) = 3.06796 x 10-7 Ω-ft.
A conversion factor 3.415 (Btu/hr)/W must be included in the resistivity ρ so that the Joule heat units match the thermal units ρ/3.415 = 8.983782 x 10-8. Current printout is divided by 3.415 to get electrical (amp) units. The steady-state convergence procedures are used.
The solution is based on a unit radian model. Since the problem is axisymmetric, only a one-element sector is needed. A small angle Θ = 10° is used for approximating the circular boundary with a straight-sided element.
POST1 is used to extract results from the solution phase. Total heat dissipation is computed parametrically at the outer surface as HRATE using q = h.area.(Ts-Ta).


