Blocking Types
When a blocking topology is created, the type of block is classified as Mapped, Free, or Swept:
- Mapped, or structured, blocks will have an equal number of nodes on parallel edges. Mapped blocks are filled with an all hexahedral mesh (3D) that is interpolated from mapped faces. For surface blocking, all quadrilateral elements are created.
- Free, or unstructured, blocks may have a different number of nodes on parallel edges. A free volume block may be filled with a tetrahedral or hex-dominant mesh. A free volume block's faces can be mapped, free, or a combination of mapped and free.
- Swept blocks have free (unstructured) source and target faces opposite each other, and mapped faces on the perpendicular sides between. They are filled with an all hex and/or prism mesh that is interpolated between the source and target faces.
| Block Type | Surface | Volume |
| Mapped / Structured |
Opposite sides are mapped, containing equal number of nodes. 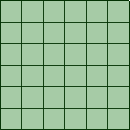
|
Parallel edges are mapped, containing equal number of nodes. 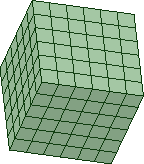
|
| Swept | N/A |
Mapped in only one direction between source and target faces. 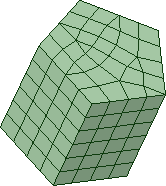
|
| Free / Unstructured |
All edges are free from mapping (even if quad or hex elements) 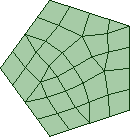
|
All edges are free from mapping (even if quad or hex elements) 
|
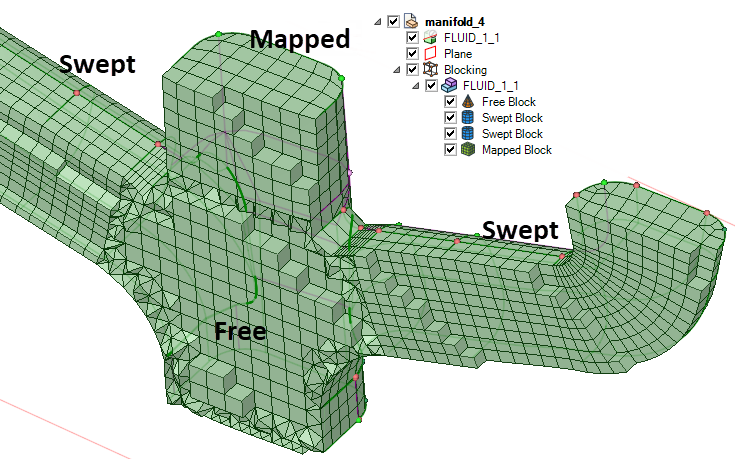
The blocking technique and resulting block type determines the volume and surface elements of the mesh. Editing a blocking describes the tools you can use to improve the blocking topology and mesh.


