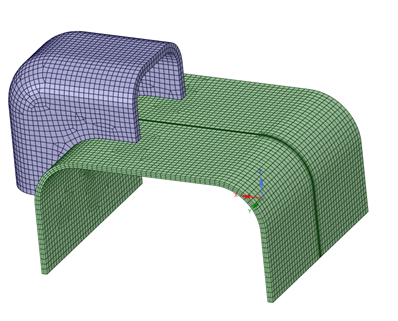
ThinSweep Method
The ThinSweep method can be used to mesh geometries recognized as having thin-walled solids, as an alternative to using the typical approach with Standard blocking. The software first detects sweep source and target surfaces. Then the 2D blocking is created on the source surfaces, and finally pulled to 3D and associated to the target surfaces in an automatic fashion.
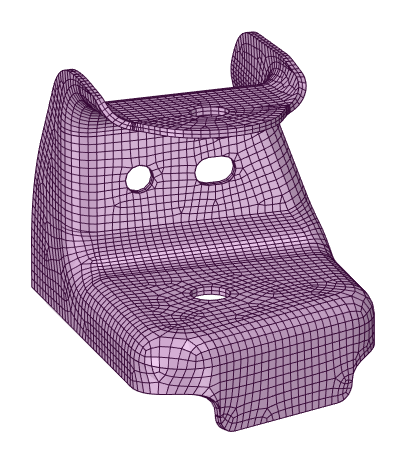

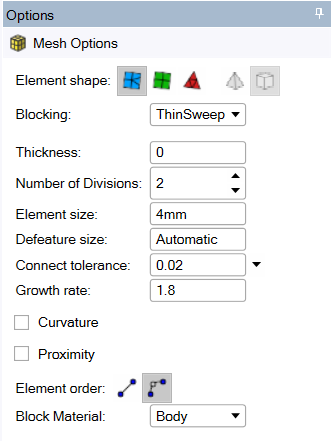
To set up the model:
Select ThinSweep in the Blocking drop-down list.
When setting up the model, you can leave the Thickness value set to
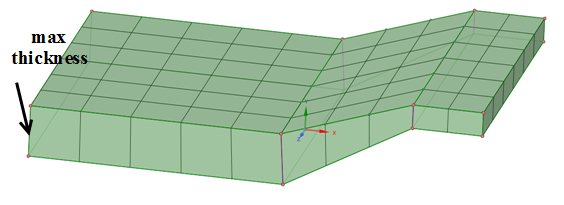
0for the software to identify the thickness automatically.Note: Automatic thickness detection may not work in some cases such as when bodies have slanted side faces or conical faces.The software can handle some variation in the thickness like the example below. For models with varying thickness, specify a Thickness value slightly more than the maximum thickness of the model.
Set an appropriate value for Number of Divisions to control the number of elements across the thickness.
(Optional) Use the Select Source/Target Faces tool guide to select the sweep surfaces. If you select the sweep source (top) and target (bottom) surfaces, the Thickness value is not used.
You can also create a Named selection for a set of source and target surfaces and select it from the Groups panel instead of selecting the individual surfaces.
Note: In general, the software attempts to automatically recognize the source, side and target faces, then meshes the source set of faces and pulls the sheet blocking to the target set of faces. If the source, side, and target faces cannot be detected correctly, you will see a warning message. In this situation you need to select the source/target faces manually:The following priority is used to determine which (non-thin) side of the solid is a sweep source:
manually selected faces
shared faces or faces with input mesh
non-smooth faces
faces containing more features
faces with the largest area
The software will then attempt to automatically determine the side faces and remaining faces are the target set of faces.
Alternatively, select the source and target set of faces as the source faces. This should be two sets of connected faces. The remaining faces will be treated as side faces.
Limitations:
The ThinSweep method has the following limitations:
This method is not yet fully supported for shared topology or Selective meshing.
This method may not respect features on the target faces that are not present on the source faces. Double-sided imprinting (for example, boundary-connected imprinting or imprinting of intersection loops) is not fully supported, so in such cases features on the target faces may be ignored.
The number of divisions will not be respected for cases where walls (side faces) are shared with source/target surfaces of connected bodies. In the example, the number of divisions was set to 3, but not respected for the top body.