This tutorial allows you to solve an existing optimization on a remote computer.
This tutorial demonstrates how to do the following:
Prepare PuTTY
Prepare the process chain on a local computer
Send input files to a remote computer
Execute the solver process remotely
Receive output files from a remote computer
This tutorial is written with the assumption that you are an advanced user and are familiar with scripting, PuTTY, and parametrizing text-based input and output files in optiSLang. Some steps in this tutorial will not be shown explicitly.
Before you start the tutorial, download the putty_ssh zip file from here , and extract it to your working directory.
To set up and run the tutorial, perform the following steps:
PuTTY is included as part of the optiSLang installation. The connection between local computer and server is established using key files (*.ppk).
Following the instructions in the PuTTY User Manual, generate a key file using PuTTYgen and install the public key on the compute server.
Set up and test the PuTTY connection.
Verify that you have user rights for remote access.
To run the tutorial, you need to create a script that executes the solver process on the remote computer. The following example script is based on optiSLang on a Linux server. It serves as an example for any CAE tool that can be launched by a console command.
#!/bin/bash
# First line: call bash
# Important: send any graphics output into the void
export DISPLAY=:0.0
# Variables for SLang executable, input and output files
export slang==<optislang installation path>/slang/bin/slang
export inputfile=ten_bar_truss.s
export outputfile=ten_bar_truss.out
# launch SLang and test for successful run and existing output file
if $slang -b $inputfile # this is the actual solver call
then
if test -e $outputfile
then
echo 'SLang terminated successfully'
exit 0
else
echo $outputfile 'does not exist.'
exit 1
fi
else
echo 'SLang terminated with error.' 1>&2
exit 1
fi
exit 0 # exit code for successful solver runReplace the italicized text with the optiSLang installation path.
Save the script as run_slang.cmd.
Test the script on the compute server.
Transfer the script to the local computer (no matter what operating system the local computer uses).
In optiSLang, create the ten_bar_truss system using one of the following methods:
Use the Solver wizard to create a common text based system, then delete the script node and connect the two remaining nodes manually.
For an example of this method, see the Optimization of a Damped Oscillator tutorial.
Build the system manually using individual modules.
Use the following files located in the putty_ssh folder:
Input file: Input file: ten_bar_truss.s
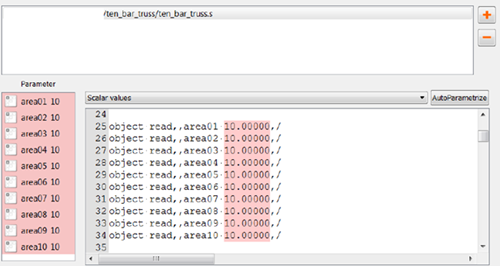
Output file: ten_bar_truss.out
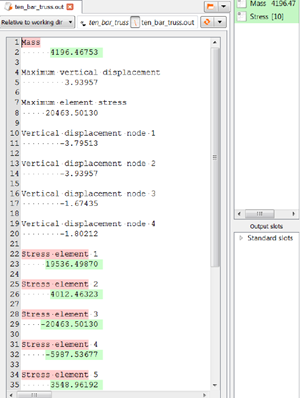
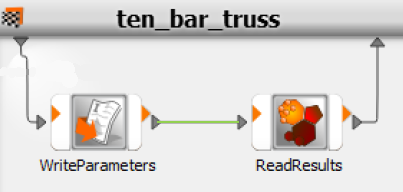
The final system should resemble the following image:
In the Modules pane, drag the PuTTY_SSH node onto the connection between WriteParameters and ReadResults.
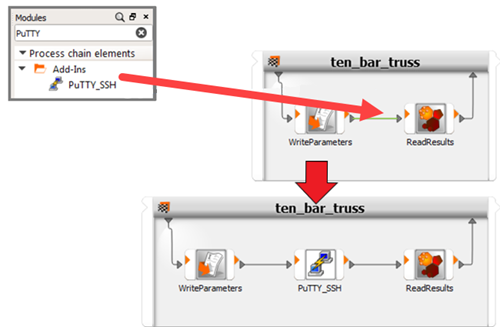
Double-click the PuTTY_SSH node to open it.
Open the run_slang.cmd file.
Optionally, set up parallel execution settings.
Click .
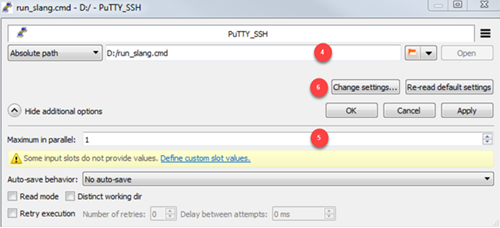
On the Process tab, enter the following:
Remote user name
Remote host name
Remote working directory
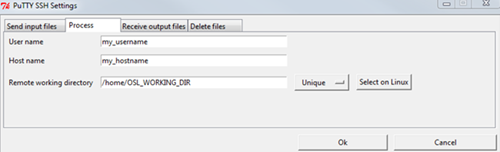
To run the process in an additional unique folder, to the right of the Remote working directory field, select .
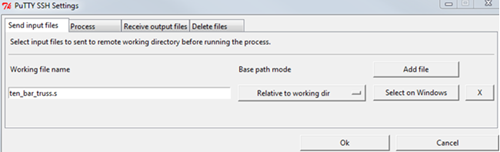
Switch to the Send input files tab.
In the Working file name field, enter
ten_bar_truss.s.To define the file source as the design directory, select .
Switch to the Receive output files tab.
In the Working file name field, enter
ten_bar_truss.out.To wait for the result file, select .
Set the maximum wait time as
20seconds.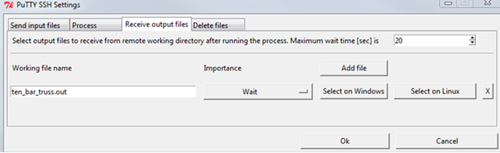
Switch to the Delete files tab.
Select the Delete remote working directory check box.
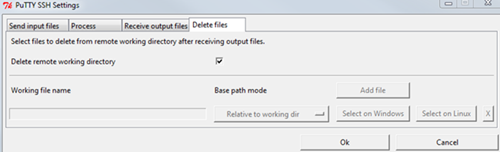
Click .
To save the project, click
 .
.Browse to the location to save the project and type a project name in the File name field.
Click .
To run the project, click
 .
.As the project runs, the PuTTY_SSH node will:
Send the ten_bar_truss.s input file to the remote working directory.
Send the run_slang.cmd script file to the remote working directory.
Run the run_slang.cmd script file in the remote working directory.
Wait (maximum 20 seconds) for the ten_bar_truss.out result file.
Receive the ten_bar_truss.out result file from the remote working directory (if it exists).
Delete the remote working directory.


