The By imprint option extends Imprint Face to include splitting the 3D block between source Edges and Target Face(s). The new, 3D block is converted to mapped (if all faces are mapped faces) or swept (if the block contains two matching free faces and all others are mapped).
Note: This option applies to 3D blocks only.
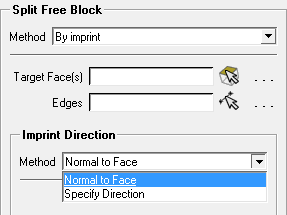
Imprint Direction supports Method options similarly to Imprint Face.
- Normal to Face
The default option will attempt to imprint source edge(s) by projection along the normal of the target face. If the source and target have side faces that directly connect them, these side faces will be used to compute the normal. The shape for the internal edges created by the split will be linked to the edges, corresponding to the nearest curves, of the side faces.
- Specify Direction
Allows you to set the imprint direction.
To align the imprint direction with one of the axes of the global coordinate system, select X Direction (or Y Direction or Z Direction).
To align the direction with a user-defined vector, select 2 Point Vector. The start and end points may be determined by graphical selection or by manually entering their coordinates. Syntax for manual entry is {x1 y1 z1} {x2 y2 z2}. If only one point is specified as {x y z}, the vector start point will be the origin.
To link the direction to a feature, select Split along curve.
The software prompts you to select start and end vertices. If the selected vertices can be connected over one or more edges of a single block, then the split shape will be linked to the set of edges.
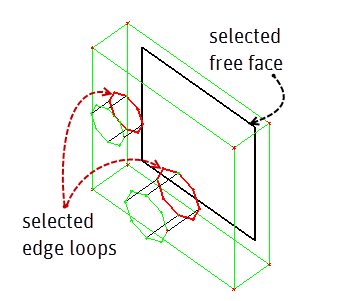
Figure 358: By imprint example illustrates how to select a free face and two edge-loops to imprint and split in one operation.
Figure 358: By imprint example
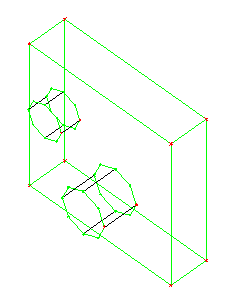
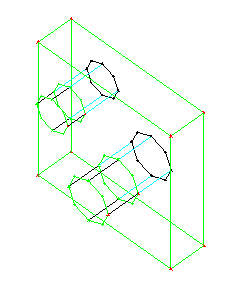
(A) The initial blocking consists of a single block with two extrusions on one side. The goal is to project the edge loops from the extrusions to the free face on the back side of the rectangular block.
(B) The selected face and edges are identified.
The side faces of the new block(s) will be mapped; and the resulting block type depends on the type of face attached to the edges selected for imprinting. If selected edges surround a mapped face, the imprint should result in a mapped block. If the edges surround a free face, the imprint should result in a swept block.
The region surrounding the new blocks will be free or swept depending on the type of its side faces. If the side faces were mapped, the surrounding region will be a swept block; free side faces will result in a free block.
Tip: If you do not get the expected results, you can adjust the face and block type using Convert Block Type.
Note: In addition to the simple, internal loops shown in the example, this option supports the same loop structures as Imprint Face.