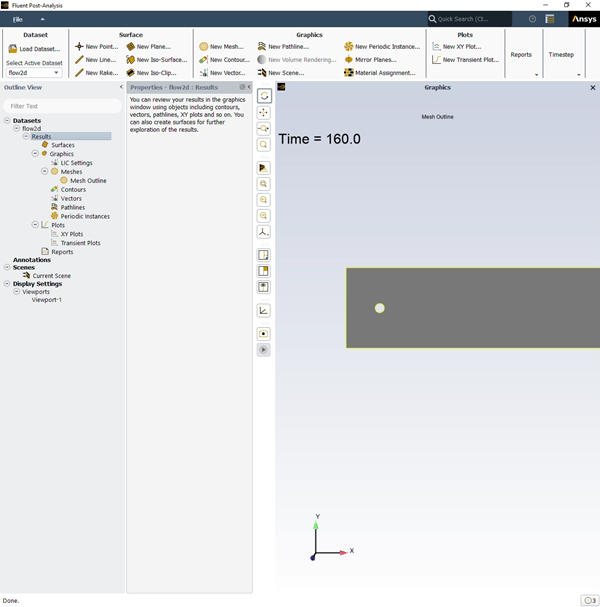
The graphical user interface (GUI) of Fluent Post-Analysis is very similar to the solution mode of Fluent, in that:
It includes a ribbon, an Outline View, a Graphics window, a Console, toolbars, dialog boxes, and Quick Search (as described in GUI Components in the Fluent User's Guide).
It can be modified (as described in Customizing the Graphical User Interface in the Fluent User's Guide).
It can be set to match your preferences (as described in Setting User Preferences/Options in the Fluent User's Guide). Preferences specific to the Fluent Post-Analysis workspace are described in Setting Preferences.
It has access to the help system (as described in Using the Help System in the Fluent User's Guide).
When setting up your simulation, the majority of your actions will start by performing actions in the Ribbon or the Outline View and the associated Properties panels.
The workspace ribbon represents a horizontal workflow, and is structured similarly to, and interacts with, elements of the Outline View.
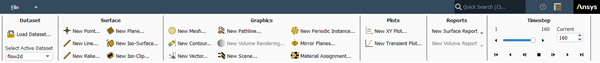
In the Ribbon, the dataset can be defined by adding objects to the Dataset section of the ribbon.
Surface-specific options are accessible from the Surface section.
, , , , , , and more can be created in the Graphics section. These options allow you to post-process objects such as velocity, pressure, or temperature, among others.
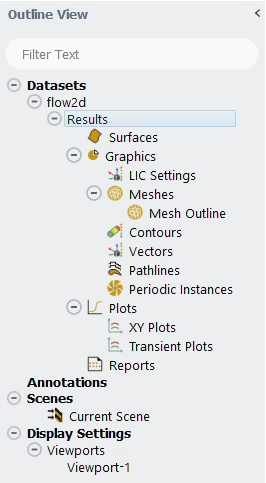
In the Outline View, the simulation can be defined by adding objects to the Dataset section of the tree.
You can perform wildcard and regular expression searches in the tree using the
Filter Text entry box at the top of the tree where you can
search and organize a list using a text string. The text string can include
wildcards and regular expressions, which allow you to perform pattern matching. For
example, searching *lin* finds surfaces such as
lines and pathlines, including those
with longer names, such as cylinder. If you have text separated
by a number, you can search example-line-?-23, which would
show example-line-1-23,
example-line-2-23, and so on. Filtering begins as soon
as you enter text. Clicking Enter expands any sub-branches
containing matches to the entered string.
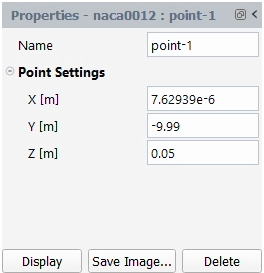
Right-click an item in the Outline View and use the menu that opens to perform a function (such as create a object from the Surfaces item); and you can left-click an item to open a related Properties window.
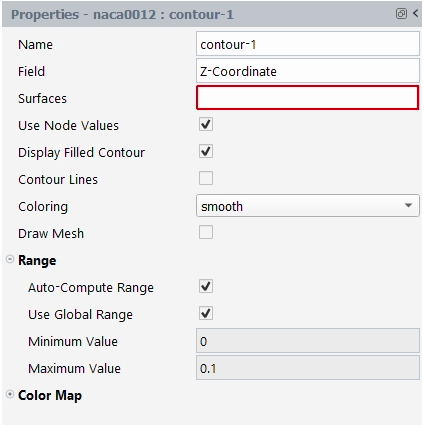
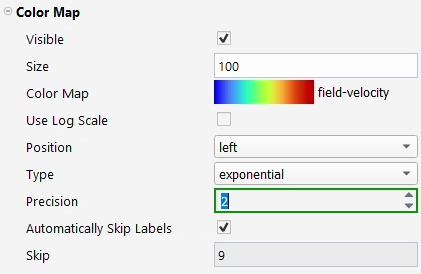
The Properties windows are similar to task pages or dialog boxes, in that they allow you to define settings, setup your analysis and postprocess results.
Note: Your settings are saved as you define them in a Properties window, unlike dialog boxes (which you may open from the Outline View or settings in the Properties window) which require you to click an button.
Properties that require your attention will be highlighted in red with red text. Valid inputs will be highlighted in green.
The Console does not interact with a text user interface (TUI), but does allow Python scripting, however, you should instead read Python commands from a journal / script file, as this allows for each command to complete before the next command is executed. This is especially important for interdependent commands. Typing or pasting a series of Python commands directly into the Console could result in undesirable behavior, as there is no waiting for the previous command to complete before the next command is executed.
Use the help menu (![]() ) icon in the upper right-hand corner of the workspace to access
its documentation. Some workspaces even have field-level user assistance that
provide information and guidance about a particular field.
) icon in the upper right-hand corner of the workspace to access
its documentation. Some workspaces even have field-level user assistance that
provide information and guidance about a particular field.
In addition to Online Technical Resources..., and the Product Improvement Program, you can also obtain information about the version and release of Fluent you are running by selecting the Version... option in help menu.