This section describes how to start Fluent in Workbench using Fluent-based systems and how you can use Fluent Launcher within Workbench.
For more information, see the following sections:
You can start Ansys Fluent by double-clicking the Setup cell in a Fluid Flow (Fluent) analysis system or a Fluent component system. Fluent launches and loads the Setup cell’s input data (for example, mesh) and the Setup cell’s local data, if it exists (for example, Fluent settings or setup output case file). If no mesh has been specified, Fluent launches and waits for your input.
You can also start Ansys Fluent by double-clicking the Solution cell in a Fluid Flow (Fluent) analysis system or a Fluent component system. Fluent launches and loads the current case and data files, as well as the Setup cell’s input data (for example, mesh), the Setup cell’s local data, if it exists (for example, Fluent settings), and the Solution cell’s initial data, if it exists. If no mesh has been specified, Fluent launches and waits for your input.
Important: When Fluent is launched from the Setup cell, it loads only the mesh and settings that served as the starting point for your analysis and are associated with the Setup cell. In order to load the current case and data files or the initial data file, you must launch Fluent from the Solution cell.
You can use Fluent in Workbench on either Windows or Linux machines, both interactively and in batch mode. You can also start Fluent on Linux from a Workbench session running on Windows and you can use the same Fluent-specific project (and related files) in Workbench using both Linux and Windows hardware interchangeably. The information is this section is the same for both Windows and Linux, except where noted.
When you start Ansys Fluent from either type of Fluent-based system within Workbench, Fluent Launcher will appear by default. Most Fluent Launcher settings are available, except for the following options:
Version (disabled)
Working Directory (disabled)
Note: In some instances, the working directory shown in the Fluent Launcher may not match the true working directory. You can confirm the working directory in Fluent by entering
pwdinto the Fluent console.
The Do not show this panel again option allows you to bypass Fluent Launcher for subsequent Fluent sessions. This option is only available when running Fluent in Workbench.
Important: Note that, when using Fluent with Workbench on Linux, the Fluent Root Path option is disabled in the General tab of Fluent Launcher.
To start your Fluent simulation on a Linux cluster from a Workbench session running on Windows, use the Use Remote Linux Nodes option in Fluent Launcher. This option is available in the Remote tab.
Important: The Remote tab of Fluent Launcher can only be used for 64-bit Linux machines.
Important: If you are using the Select IP Interface option in the
Parallel tab of Fluent Launcher, the selected interface address is not
saved. As a workaround, you can define the
FLUENT_HOST_IP=host:ip-address environment variable.
For more information about Fluent Launcher, see Starting Ansys Fluent Using Fluent Launcher. For more information about using Fluent Launcher to access remote Linux clusters, see Setting Remote Options in Fluent Launcher.
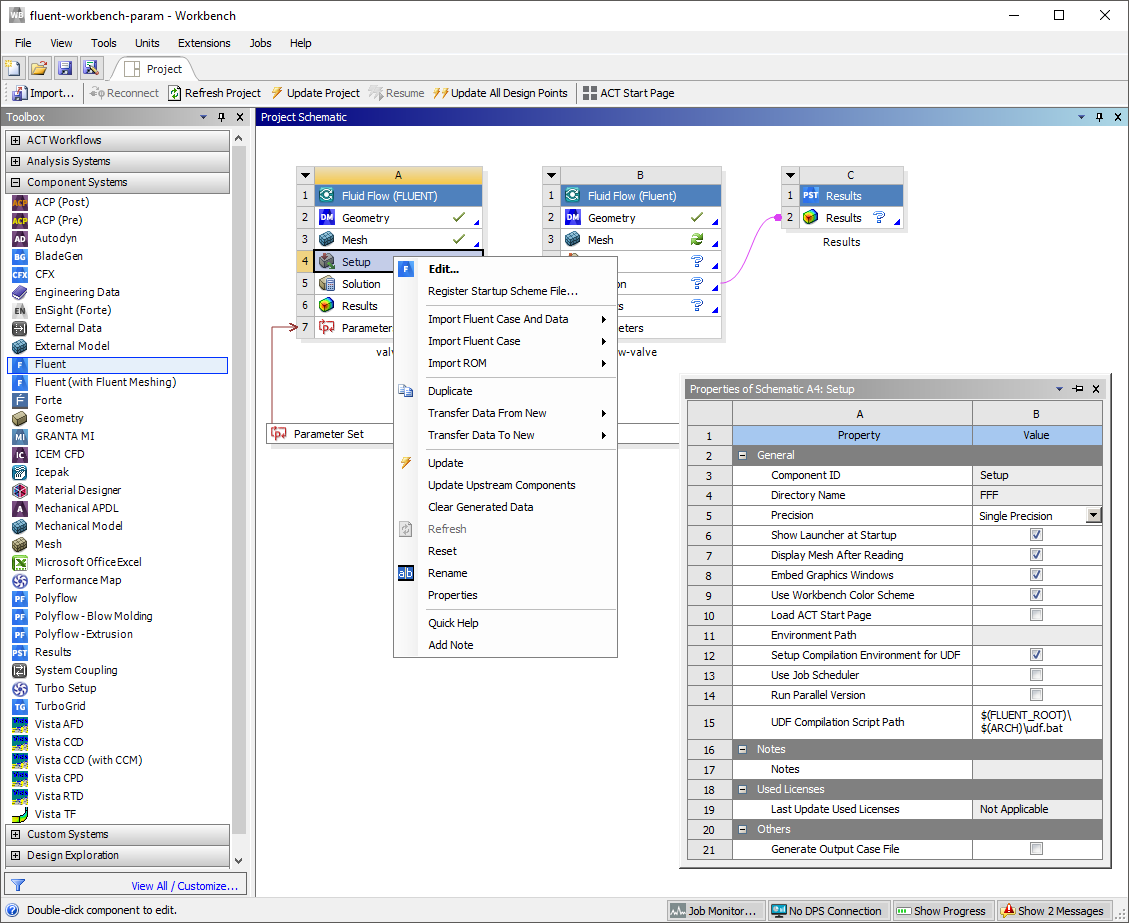
You can view the properties of a selected cell in Workbench by selecting the Properties option under the View menu, or by right-clicking a cell and selecting Properties from the context menu. The properties of the selected cell are displayed in the Properties pane in Workbench.
The Fluent-based system Setup and Solution cells have the following properties that you can set for Fluent Launcher:
- Use Setup Launcher Settings
(for Solution cells only) allows you to specify that the current systems Solution cell should use the Fluent Launcher property settings from the current system’s Setup cell. By default, the Fluent-based system Setup and Solution cells share Fluent Launcher settings, however, if required, these settings can be set autonomously using this property.
- Precision
allows you to choose either the single-precision or the double-precision solver
- Show Launcher at Startup
allows you to show or hide Fluent Launcher when Fluent starts.
- Display Mesh After Reading
allows you to show or hide the mesh after the mesh or case/data is read into Fluent.
- Embed Graphics Windows
allows you to embed the graphics windows in the Fluent application window, or to have them free-standing.
- Set up Compilation Environment for UDF
allows you to specify compiler settings for compiling user-defined functions (UDFs) with Fluent.
- Use Job Scheduler
allows you to specify settings for running Fluent with the available job scheduler. On Linux, you can use Ansys Remote Solve Manager (RSM) as the job scheduler. On Windows, you can use the Microsoft Job Scheduler or RSM.
Note: Select Submit to Remote Solve Manager from the Update Options drop-down in the Properties of Solution to use RSM. See Specifying Other Setup and Solution Cell Settings for additional information.
- Run Parallel Version
allows you to choose to run the parallel version of Fluent or not.
- UDF Compilation Script Path
(if Set up Compilation Environment for UDF is selected) allows you to specify the path to the UDF compilation script.
- Initialization Method
allows you to initialize your Fluent simulation. Available options are:
Program Controlled (default) allows Fluent to use any existing results (solution data) to initialize the solution.
For a new calculation, if no results are available, then the system initializes the solution using the settings specified in Fluent.
For existing projects, if the system is not connected to another upstream system through the Solution cell, then the system uses results available from the previous calculation. If the results are not compatible with the mesh, then the system initializes the solution using the settings specified in Fluent.
For existing projects, if the system is connected to another upstream system through the Solution cell, then the Initialization Method is not available for the downstream Solution cell. In this case, the downstream Solution cell always uses results coming from the upstream Solution cell to initialize its solution for the initial design point (DP0) as well as any other design points. If the solution data file from the upstream Solution cell is not available or not compatible with the mesh, then Workbench uses the upstream data interpolation (
*.ip) file for solution initialization. If the*.ipfile is also not available, or the results are not compatible with the mesh, then the system initializes the solution using the settings specified in Fluent.
Solver Controlled allows Fluent to always initialize the solution using settings specified in Fluent, enforcing the initialization method available in Fluent for new and existing projects. This option is not available for Solution cells connected with upstream Solution cells.
Use Solution Data from File allows you to import a solution data file (
*.dat) or data interpolation file (*.ip) that Fluent will use to initialize the solution. If selected, you are prompted to provide an Initial Data File. For new and existing calculations, the Solution cell uses a registered file as the initial data in Workbench.
For more information, see Using the Update Command.
- Use Remote Linux Nodes
(available only when Run Parallel Version is selected) allows you to run your Fluent simulation on 64-bit Linux machines.
If Run Parallel Version is selected, the following additional properties are available:
- Number of Processors
allows you to set the number of processors you want to use for the parallel calculations (for example, 2, 4, and so on).
- Interconnect
allows you to set the interconnects you want to use for the parallel calculations (for example, infiniband).
- MPI Type
allows you to set the MPI type you want to use for the parallel calculations (for example, intel, msmpi, and so on).
- Use Shared Memory
allows you to specify if shared memory is to be used or not.
- Machine Specification
(if Use Shared Memory is not selected) allows you to specify a list of machine names, or a file that contains machine names.
- Machine List
(if Use Shared Memory is not selected and Machine List is selected as the Machine Specification) allows you to specify a list of machine names to run the parallel job.
- Machine Filename
(if Use Shared Memory is not selected and File Containing Machine List is selected as the Machine Specification) allows you to specify the name of the file that contains a list of machines to run the parallel job.
If Use Remote Linux Nodes is selected on Windows, the following additional properties are available (for 64-bit Linux machines only):
- Remote FLUENT Root Path
allows you to specify the remote Fluent Linux installation root path.
- Use Specified Remote Working Directory
allows you to specify a directory other than
tempdirectory as the working directory for the remote Linux nodes. When this property is selected, you can specify the directory in the Remote Working Directory property that appears.- Remote Spawn Command
allows you to select one of the following commands to connect to the remote node:
SSH (the default) will use SSH to spawn nodes from the local Windows machine to the Linux head node, as well as from the Linux head node to the compute nodes. To use SSH with Ansys Fluent, you must set up password-less SSH access.
Other allows you to provide other compatible remote shell commands.
- Use Remote Cluster Head Node
allows you to specify the remote node that Fluent will connect to for spawning (for example, via
ssh). When this property is selected, you can specify the remote node in the Remote Host Name property that appears.Important: When the PBSPro option is selected for the Job Scheduler, the host specified in the Use Remote Cluster Head Node field should be the PBS Pro submission host.
If Use Job Scheduler is selected on Windows, the following additional properties are available:
- Computer Cluster Head Node Name
allows you to specify the name of the compute cluster head node.
- Job Template
(available only when running Microsoft HPC Pack 2008 or newer) allows you to create a custom submission policy to define the job parameters for an application. The cluster administrator can use job templates to manage job submission and optimize cluster usage.
- Node Group
(available only when running Microsoft HPC Pack 2008 or newer) allows you to specify a collection of nodes. Cluster administrators can create groups and assign nodes to one or more groups.
- Processor Unit
(available only when running Microsoft HPC Pack 2008 or newer) allows you to choose the following:
Core refers to a single, named host in the cluster.
Socket refers to a set of processors with a dedicated memory bus. This is also known as a non-uniform memory access (NUMA) node.
Node refers to an individual CPU on a node. For example, a dual-core processor is considered two cores.
- Start When Resources Are Available
allows you to start the job when resources are available.
- Create Job Submission XML
allows you to create the job submission XML file.
- Job Submission XML File
(if Create Job Submission XML is selected) allows you to specify the name of the job submission XML file.
If Use Job Scheduler and (for Windows) Use Remote Linux Nodes are selected, the Scheduler Settings header becomes Remote, allowing you to specify Remote FLUENT Root Path, Use Specified Remote Working Directory, Remote Working Directory, Remote Spawn Command, Use Remote Cluster Head Node, and Remote Host Name. These fields are described earlier in this section.
Properties for Setup and Solution cells related to problem setup and solution processes are discussed in Specifying Other Setup and Solution Cell Settings.
Typically, Fluent Launcher settings are specified in the Fluent Launcher dialog box when Fluent is launched from the Setup cell.
By default, the Solution cell uses the same Fluent Launcher property settings as the Setup cell. If you want the Solution cell’s Fluent Launcher settings to be different than those specified for the Setup cell, you can disable the Use Setup Launcher Settings property setting (see Specifying Fluent Launcher Settings Within Workbench) and then set the Solution cell’s Fluent Launcher property settings without impacting the settings for the Setup cell.
You can copy the Setup cell’s Fluent Launcher settings to the Solution cell by selecting the Copy Launcher settings to Solution cell command from the Setup cell’s context menu (available only when the Use Setup Launcher Settings property setting is disabled). Note that the values that are written are retained, even if you later disable this setting. Likewise, you can also copy the Solution cell’s Fluent Launcher settings to the Setup cell by selecting the Copy Launcher settings to Setup cell command from the Solution cell’s context menu (available only when the Use Setup Launcher Settings property setting is disabled).
The Setup cell has the following property related to the problem setup process:
Others
Generate Output Case File: enables or disables the generation of the setup output case file,
name-Setup-Output.cas.h5. If the state for the Setup cell is Update Required and the upstream mesh has not been modified, Fluent will read the output case file (name-Setup-Output.cas.h5) as opposed to the mesh and settings files when editing the Setup cell. This way you can improve the Fluent run time speed provided the upstream mesh data has not changed.The output case file will be generated when
recorded mesh operations (Recording Mesh Manipulation Operations and Resolving Mesh Incompatibility in Fluent) have been performed prior to running the simulation in Fluent, or
Fluent session is started with a mesh file only
This setting overrides the Enable Generation of Setup Output Case File preference in the Options settings.
The Solution cell contains additional general properties and some specific properties related to the solution process:
General
Component ID: the name of the cell (not editable).
Directory Name: the name of the directory (“
FFF”) where solution files are located (not editable).Use Setup Launcher Settings: enables or disables the use of the Setup cell's Fluent Launcher settings (see above).
Solution Monitoring: allows you to be able to graphically view Fluent solution convergence and monitor data without having Fluent open. When this option is enabled, you can use the Show Solution Monitoring option in the Solution cell context menu to display a convergence and monitor charts. This property overrides the Enable Solution Monitoring preference in the Options settings.
Note:A report definition will only be included in a solution monitor chart if it is included in a report plot.
Each report plot will be shown as a separate solution monitor chart.
A single report definition will only appear once in the solution monitor charts, even if that report definition is included in multiple report plots.
Generate Solution Monitor Plots for Report: when selected, Fluent will automatically generate the report images during a Solution cell update or project report export. See Generating Fluent Project Reports for information about exporting project reports and the types of report images. This option is disabled by default.
Generate Data Interpolation File: enables or disables generation of the interpolation file at the end of the Fluent solver run. The solver will automatically create an
*.ipfile that can be used when restarting the Fluent session, even if the project mesh or case file has been modified and is no longer compatible with the existing data file (if available). This setting overrides the Enable Generation of Interpolation File preference in the Options settings. Note, that you can use the Clear Generated Data command to delete the generated interpolation file (see Using the Clear Generated Data Command for details).
Solution Process
Update Option: enables the solution process to be either Run in Foreground (solutions are run within the current Workbench session), Run in Background (solutions are run in the background on the local machine), or Submit to Remote Solve Manager (solutions are run in the background by submitting the solution to Remote Solve Manager (RSM)). For more information about these options and the Remote Solve Manager, refer to Submitting Solutions to Remote Solve Manager in the Ansys Workbench User's Guide.