There are two types of UDS diffusivity that you can specify in Ansys Fluent: isotropic and anisotropic. Diffusion is isotropic when it is the same in all directions. Isotropic diffusion coefficients can be specified in two ways: either as a single user-defined that applies to all UDS transport equations defined for your model; or on a per-scalar basis as constants, polynomial functions of temperature, or user-defined functions.
Diffusion is anisotropic when the diffusion coefficients are
different in different directions. Anisotropic diffusion can be specified
by a tensor diffusion coefficient matrix (Equation 8–59) for each UDS (in both fluid
and solid zones) in four different ways: general anisotropic, orthotropic, cyl-orthotropic, and user-defined-anisotropic. All UDS diffusivity
parameters are set from the Create/Edit Materials Dialog Box and are discussed below. Note that details about how to define
and use UDFs in UDS transport equations is discussed in the Fluent Customization Manual.
The second-order diffusion term in the most general form is
(8–59) |
where is a 3
3 tensor in 3D.
For additional information, see the following sections:
For isotropic diffusion, in Equation 8–59 is equal to a scalar
times the identity matrix and the equation
reduces to
(8–60) |
You can specify isotropic diffusivity as a single user-defined function that applies to all UDS transport equations. For this case, choose user-defined from the drop-down list for UDS Diffusivity in the Create/Edit Materials Dialog Box.
Setup →
![]() Materials
Materials
If you have previously loaded a compiled UDF library or have
interpreted the UDF, then the User-Defined Functions Dialog Box will open, allowing you
to hook the DEFINE_DIFFUSIVITY UDF to Ansys Fluent.
If no functions have been loaded, you will get an error message. More
information about user-defined functions can be found in the Fluent Customization Manual.
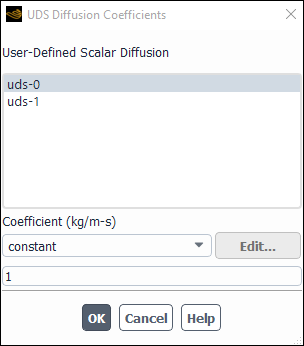
Isotropic diffusion coefficients can also be defined on a per-scalar basis by selecting defined-per-uds from the drop-down list for UDS Diffusivity in the Create/Edit Materials Dialog Box. This will open the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box (Figure 8.29: The UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box).
In the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box,
select a scalar equation (for example, uds-0)
and then choose a constant, polynomial, or user-defined function from the Coefficient drop-down list. For the default fluid (air),
the constant diffusion coefficient is kg/m-s. If you choose polynomial, the Polynomial Profile Dialog Box will open and you can specify your coefficients as a function of
temperature. See Inputs for Polynomial Functions for details.
When you select the user-defined option,
the User-Defined Functions Dialog Box will open, allowing
you to hook a DEFINE_DIFFUSIVITY UDF only if you have previously loaded a compiled UDF library
or interpreted a UDF. Otherwise, you will get an error message. More
information about user-defined functions can be found in the Fluent Customization Manual.
You can specify anisotropic diffusion coefficients in both fluid
and solid zones by defining the tensor diffusion coefficient matrix (Equation 8–59) on a per-scalar basis. You
can use anisotropic diffusivity for UDS scalar transport equations
to model species transport equations in porous media and in solids
where species diffusion shows anisotropic behavior.
Important:
Note that the anisotropic diffusion options discussed in the following sections are available with the pressure-based solver and the density-based solvers.
UDS diffusion coefficients can be postprocessed only in those cells that have isotropic diffusivity. In all other cells, the diffusion coefficient will be zero.
In all cases, you enable anisotropic diffusion by selecting defined-per-uds under UDS Diffusivity in the Create/Edit Materials Dialog Box. This will open the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box (Figure 8.29: The UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box).
Setup →
![]() Materials
Materials
In the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box, select a scalar equation (for example, uds-0) and then choose one of the following methods under Coefficient to specify the anisotropic diffusion coefficient. These methods are described in detail below.
anisotropic
orthotropic
cylindrical orthotropic
user-defined anisotropic
For anisotropic diffusivity, you can specify in Equation 8–59 in the form
where
is a constant
matrix in 3D and
is a scalar multiplier.
The diffusion coefficient matrix is specified as
(8–61) |
where is the diffusivity and
is a matrix (2
2 for two dimensions and 3
3 for three-dimensional problems). Note
that
can
be a non-symmetric matrix.
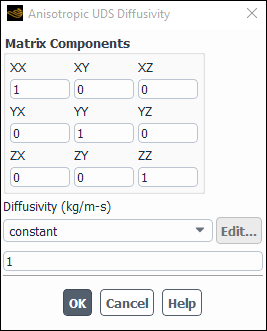
To specify anisotropic diffusion coefficients, first select a scalar equation (for example, uds-0) from the User-Defined Scalar Diffusion list in the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box (Figure 8.29: The UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box). Then choose anisotropic in the drop-down list under Coefficient. This will open the Anisotropic UDS Diffusivity dialog box (Figure 8.30: The Anisotropic UDS Diffusivity Dialog Box).
In the Anisotropic UDS Diffusivity dialog box, enter the Matrix Components and then select the Diffusivity to be a constant, polynomial function of temperature (polynomial, piecewise-linear, piecewise-polynomial), or user-defined. See Inputs for Polynomial Functions, Inputs for Piecewise-Linear Functions, and Inputs for Piecewise-Polynomial Functions for details on polynomial temperature functions.
When you select the user-defined option,
the User-Defined Functions Dialog Box will open, allowing
you to hook a DEFINE_DIFFUSIVITY UDF only if you have previously loaded a compiled UDF library
or interpreted a UDF. Otherwise, you will get an error message. More
information about user-defined functions can be found in the Fluent Customization Manual.
For orthotropic diffusivity, you can specify in Equation 8–59 through ’principal’
direction vectors and diffusion coefficients along these directions. Ansys Fluent,
in turn, computes
from parameters that you supply. The principal
directions are the same everywhere, but each of he directional diffusion
coefficients can be specified as a constant, polynomial function of
temperature, or through user-defined functions.
When orthotropic diffusivity is used, the diffusion coefficients in the principal directions
are specified. The diffusivity matrix is then computed
as
(8–62) |
Important: For two-dimensional problems, only the functions and the unit vector
need to
be specified.
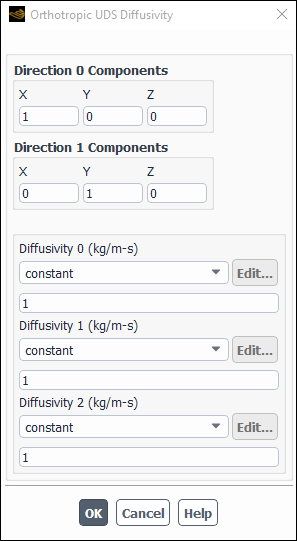
To specify orthotropic diffusion coefficients, first select a scalar equation (for example, uds-0) from the User-Defined Scalar Diffusion list in the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box (Figure 8.29: The UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box). Then choose orthotropic in the drop-down list under Coefficient. This will open the Orthotropic UDS Diffusivity dialog box (Figure 8.31: The Orthotropic UDS Diffusivity Dialog Box).
Since the directions are mutually orthogonal, only the first two need
to be specified for three-dimensional problems.
is defined using X,Y,Z under Direction 0 Components, and
is defined using X,Y,Z under Direction 1 Components. You can define Diffusivity
0
, Diffusivity 1
, and Diffusivity
2
as constant, polynomial, piecewise-linear, piecewise-polynomial functions of temperature, or user-defined. See Inputs for Polynomial Functions, Inputs for Piecewise-Linear Functions, and Inputs for Piecewise-Polynomial Functions for details on polynomial
temperature functions.
When you select the user-defined option,
the User-Defined Functions Dialog Box will open, allowing
you to hook a DEFINE_DIFFUSIVITY UDF only if you have previously loaded a compiled UDF library
or interpreted a UDF. If no functions have been loaded, you will get
an error message. More information about user-defined functions can
be found in the Fluent Customization Manual.
Orthotropic UDS diffusivity can also be specified on a per-scalar basis in cylindrical coordinates. This method is similar to orthotropic UDS diffusivity, except that the principal directions are specified as radial, tangential, and axial.
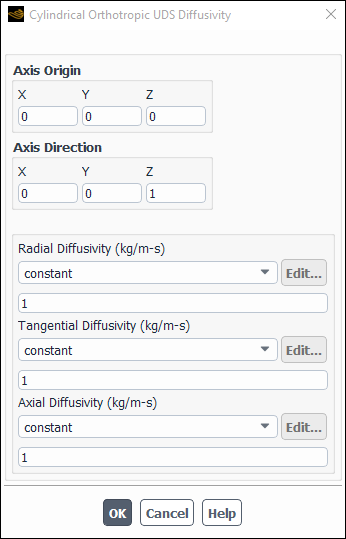
To specify cylindrical orthotropic diffusion coefficients, first select a scalar equation (for example, uds-0) from the User-Defined Scalar Diffusion list in the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box (Figure 8.29: The UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box). Then choose cyl-orthotropic in the drop-down list under Coefficient. This will open the Cylindrical Orthotropic UDS Diffusivity dialog box (Figure 8.32: The Cylindrical Orthotropic UDS Diffusivity Dialog Box).
In three-dimensional cases, the origin and the direction of the cylindrical coordinate system must be specified along with the radial, tangential, and axial direction conductivities. In two-dimensional cases, the origin of the cylindrical coordinate system must be specified along with the radial and tangential direction conductivities. Note that in two-dimensional cases, the direction is always along the +z axis. Ansys Fluent will automatically compute the anisotropic diffusivity matrix at each cell from this input. The calculation is based on the location of the cell in the cylindrical coordinate system specified.
You can define the Radial Diffusivity, Tangential Diffusivity, and Axial Diffusivity as constant, polynomial, piecewise-linear, piecewise-polynomial, or as user-defined functions of temperature, using the drop-down list below each of the diffusivities. See Inputs for Polynomial Functions, Inputs for Piecewise-Linear Functions, and Inputs for Piecewise-Polynomial Functions for details on polynomial temperature functions.
When you select the user-defined option,
the User-Defined Functions Dialog Box will open, allowing
you to hook a DEFINE_DIFFUSIVITY UDF only if you have previously loaded a compiled UDF library
or interpreted a UDF. If no functions have been loaded, you will get
an error message. More information about user-defined functions can
be found in the Fluent Customization Manual.
You can specify in Equation 8–59 on a per-scalar basis, directly, through user-defined functions
(UDFs).
To specify a UDF for anisotropic diffusivity on a per-scalar basis, first select a scalar equation (for example, uds-0) from the User-Defined Scalar Diffusion list in the UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box (Figure 8.33: The UDS Diffusion Coefficients Dialog Box).
Then choose user-defined-anisotropic in
the drop-down list under Coefficient. The User-Defined Functions Dialog Box will open, allowing you
to hook a DEFINE_ANISOTROPIC_DIFFUSIVITY UDF only if you have previously loaded a compiled UDF library
or interpreted a UDF. Otherwise, you will get an error message. More
information about user-defined functions can be found in the Fluent Customization Manual.