Within an Explicit Dynamics analysis, the body interaction feature represents contact between bodies and includes settings that allow you to control these interactions. If the geometry you use has two or more bodies in contact, a Body Interactions object folder appears by default under Connections in the tree. Included in a Body Interactions folder are one or more Body Interaction objects, with each object representing a contact pair.
You can also manually add these two objects:
To add a Body Interactions folder, highlight the Connections folder and choose Body Interactions from the Connect group in the Context tab. A Body Interactions folder is added and includes one Body Interaction object.
To add a Body Interaction object to an existing Body Interactions folder, highlight the Connections folder, the Body Interactions folder, or an existing Body Interaction object, and choose Body Interaction from the Connect group in the Context tab.
General Notes
Each Body Interaction object activates an interaction for the bodies scoped in the object. With body interactions, contact detection is completely automated in the solver. At any time point during the analysis any node of the bodies scoped in the interaction may interact with any face of the bodies scoped in the interaction. The interactions are automatically detected during the solution.
The default frictionless interaction type that is scoped to all bodies activates frictionless contact between any external node and face that may come into contact in the model during the analysis.
To improve the efficiency of analyses involving large number of bodies, you are advised to suppress the default frictionless interaction that is scoped to all bodies, and instead insert additional Body Interaction objects which limit interactions to specific bodies. The union of all frictional/frictionless body interactions defines the matrix of possible body interactions during the analysis.
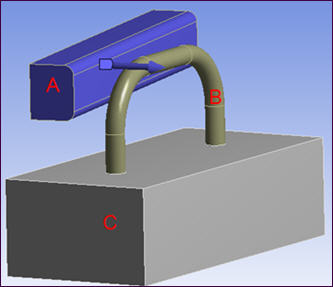
For example, in the model shown below:
Body A is traveling towards body B and we require frictional contact to occur. A frictional body interaction type scoped only to bodies A and B will achieve this. Body A will not come close to body C during the analysis so it does not need to be included in the interaction.
Body B is bonded to body C. A bonded body interaction type, scoped to bodies B and C will achieve this.
If the bond between bodies B and C breaks during the analysis, we want frictional contact to take place between bodies B and C. A frictional body interaction type scoped only to bodies B and C will achieve this.
A bonded body interaction type can be applied in addition to a frictional/frictionless body interaction.
A reinforcement body interaction type be can be applied in addition to a frictional/frictionless body interaction.
Object property settings are included in the Details view for both the Body Interactions folder and the individual Body Interaction objects. Refer to the following sections for descriptions of these properties.


