VM199
VM199
Oil Film Bearing Supporting a Rotating Shaft and Subjected to a Static
Load
Overview
| Reference: | Friswell, M.I., Penny, J.E.T., Garvey, S.D., Lees, A.W., Dynamics of Rotating Machines, Cambridge University Press, 2010, pg. 181 |
| Analysis Type(s): | |
| Element Type(s): | |
| Input Listing: | vm199.dat |
Test Case
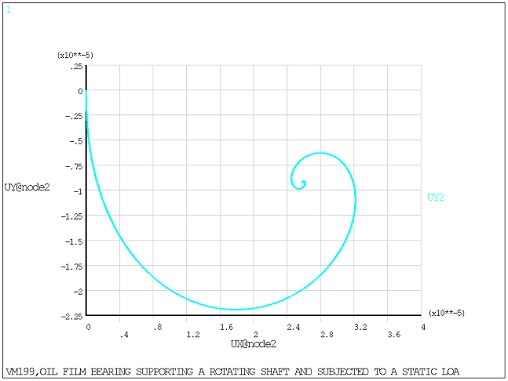
An oil film bearing defined by its radial clearance, diameter, and length supports a rotating shaft and is subjected to a static vertical load of 525 N. Calculate the bearing eccentricity ratio and the bearing coefficients under these conditions.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
A simplistic bearing-shaft model is created using:
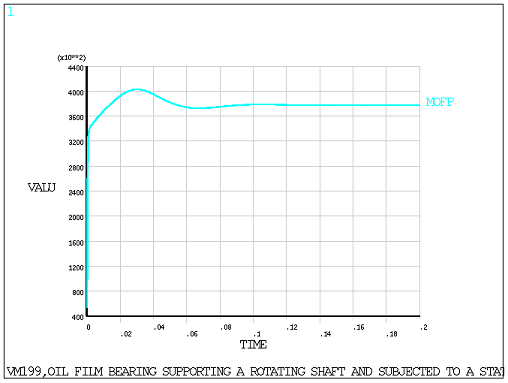
Nonlinear transient analysis is first performed on the model with an end time of 0.20 seconds (5 cycles)
For the 2D model, a time increment of 1.0 x 10-4 seconds is set to determine the shaft equilibrium position and eccentricity ratio. The shaft rotational velocity in rad/sec is specified using nodal constraint (D,,OMGZ).
The shaft equilibrium position obtained from transient analysis, along with a small perturbation increment, is used in a static analysis to determine the bearing stiffness and damping coefficients:
For the 2D model: The shaft equilibrium position is input via the D command and the perturbation increment is input via COMBI214 real constants. The shaft rotational velocity in rad/sec is specified via the OMEGA command in the linear static solve.
For the 3D model: The shaft equilibrium position is input via FLUID218 real constants. A small perturbation (1E-6) is given about the equilibrium position and the bearing forces are calculated. Using these bearing forces, the stiffness and damping characteristics are evaluated.
Results Comparison
| 2D | Units | Target | Mechanical APDL | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eccentricity Ratio | - | 0.266 | 0.275 | 0.969 |
| KXX | MN/m | 12.810 | 12.567 | 1.019 |
| KYY | MN/m | 8.815 | 8.712 | 1.012 |
| KXY | MN/m | 16.390 | 15.818 | 1.036 |
| KYX | MN/m | -25.060 | -24.433 | 1.026 |
| CXX | kNs/m | 232.900 | 225.410 | 1.033 |
| CYY | kNs/m | 294.900 | 287.068 | 1.027 |
| CXY | kNs/m | -81.920 | -80.406 | 1.019 |
| CYX | kNs/m | -81.920 | -80.461 | 1.018 |
| 3D | Units | Target | Mechanical APDL | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KXX | MN/m | 12.810 | 12.139 | 1.055 |
| KYY | MN/m | 8.815 | 8.017 | 1.100 |
| KXY | MN/m | 16.390 | 15.910 | 1.030 |
| KYX | MN/m | -25.060 | -24.210 | 1.035 |
| CXX | kNs/m | 232.900 | 224.511 | 1.037 |
| CYY | kNs/m | 294.900 | 285.459 | 1.033 |
| CXY | kNs/m | -81.920 | -76.167 | 1.076 |
| CYX | kNs/m | -81.920 | -84.654 | 0.968 |