This example demonstrates a modal analysis of a rotating structure using a stationary reference frame. The analysis generates a Campbell diagram (PLCAMP).
These additional Campbell diagram examples are available in the Mechanical APDL Verification Manual:
For the Campbell diagram and critical speed analysis of a rotor on bearings, see VM247 "Campbell Diagrams and Critical Speeds Using Symmetric Bearings" and VM254 "Campbell Diagrams and Critical Speeds Using Symmetric Orthotropic Bearings".
For the Campbell diagram and stability analysis of a rotating beam on bearings with viscous internal damping, see VM261 "Rotating Beam with Internal Viscous Damping".
The geometric properties for this analysis are as follows:
| Length: 8m |
| Diameter: 0.2m |
The material properties for this analysis are as follows:
| Young's modulus (E) = 2e+11 N/m2 |
| Poisson's ratio (υ) = 0.3 |
| Density = 7800 kg/m3 |
Use this input file to perform the example modal analysis of a rotating structure using a stationary reference frame.
/batch,list /title, Spinning Simply Supported Beam !* Parameters lx=8 ! length dia=0.2 ! diameter /PREP7 ! ----- ET,1,16 R,1, dia, dia/2 MP,EX,1,2e+11 MP,DENS,1,7800 MP,PRXY,1,0.3 n,1 n,9,lx fill,1,9 e,1,2 egen,8,1,-1 d,1,uy,,, ,,uz ! simply supported left end d,9,uy,,, ,,uz ! simply supported right end d,all,ux ! supress axial motion d,all,rotx ! supress torsion finish /SOLU ! ----- antype,modal ! Use the QRDAMP eigensolver, request 8 modes, ! get complex eigensolutions modopt,qrdamp,8,,,on ! Reuse the block Lanczos eigenvectors from the first loadstep qrdopt,on ! Write 8 modes to the result file, calculate ! element results mxpand,8,,,yes ! Apply Coriolis effect and specify ! stationary reference frame coriolis,on,,,on ! Solve 2 loadsteps with rotational velocity omega,0. solve omega,30000. solve finish /POST1 ! ----- ! Plot Campbell Diagram plcamp ! Print Campbell Diagram prcamp finish
The following table describes the input listing and the general process involved in the example analysis in more detail:
| Step | Description | APDL Command(s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Set parameters. |
lx=8 dia=0.2 |
| 2. | Define nodes, elements, and material properties. |
ET,… R,… MP,... N,… E,… |
| 3. | Set boundary conditions. |
D,... |
| 4. | Set the analysis type (modal in this case). Use the QRDAMP eigensolver, request 8 modes, and specify complex eigensolutions. |
ANTYPE,MODAL MODOPT,QRDAMP,8,,,ON MXPAND,... |
| 5. | Include the Coriolis effect in a stationary reference frame. |
CORIOLIS,ON,,,ON |
| 6. | For each load step, define the rotation velocity, and then solve. |
OMEGA,… |
| 7. | Plot and print the Campbell diagram. |
The results of your analysis should be similar to those shown here:
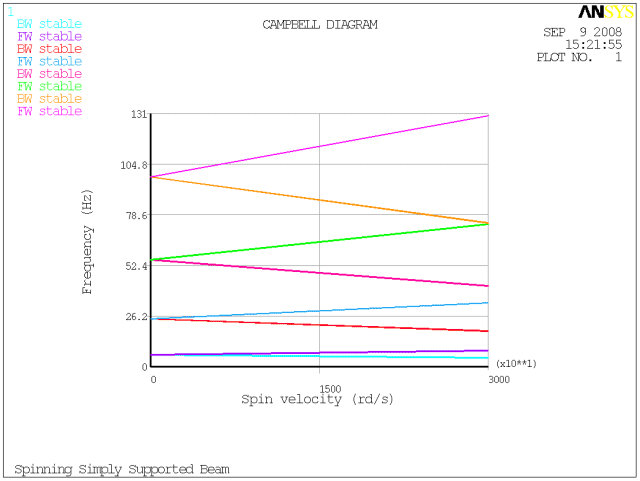
The printout (PRCAMP) should yield the following data:
PRINT CAMPBELL DIAGRAM
Sorting : ON
X axis unit : rd/s
***** FREQUENCIES (Hz) FROM CAMPBELL (sorting on) *****
Spin(rd/s) 0.000 30000.000
1 BW 6.207 4.639
2 FW 6.207 8.305
3 BW 24.750 18.547
4 FW 24.750 33.027
5 BW 55.461 41.735
6 FW 55.461 73.701
7 BW 98.248 74.337
8 FW 98.248 129.852


