A rectangular beam with perforated holes is modeled to compute the effective damping coefficient, stiffness coefficient, and damping ratio. The surface of the structure is modeled with FLUID136 elements to represent the thin film. The structure is modeled with SOLID185 elements. This example computes the Rayleigh damping coefficients (α and β) and modal damping ratios ξi for use in a transient dynamic analysis.
The problem is defined as an extension to the earlier squeeze film example. After modeling the fluid domain, the structure of the beam is modeled and meshed with SOLID185 elements. A modal analysis is performed on the structure and the first two eigenvalues and eigenvectors are computed. RMFLVEC is used to extract the eigenvectors for use in the modal projection method to compute the thin-film damping parameters. The command macro ABEXTRACT is used to compute the Rayleigh parameters from the lowest two eigenmodes. Modal damping ratios are also provided by the ABEXTRACT macro for the two eigenmodes.
Table 4.1: Modal Damping Parameters for First Two Eigenfrequencies lists the results from the damping parameter extraction. Computed Rayleigh parameters are: ALPHAD=65212, BETAD=1.829e-8. The input file for this example is shown below.
Table 4.1: Modal Damping Parameters for First Two Eigenfrequencies
| Frequency (Hz.) | Modal Damping Coefficient | Modal Squeeze Stiffness Coefficient | Damping Ratio | Stiffness Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55294 | 67419 | .2758e9 | .9703e-1 | .2285e-2 |
| 157497 | 83123 | .3568e10 | .4200e-1 | .3644e-2 |
The input file for this example is shown below.
/batch,list /PREP7 /title, Damping Ratio and Rayleigh Damping Calculations for a Perforated Plate /com uMKS units ET, 1,136,1 ! 4-node option, High Knudsen Number ET, 2,138,1 ! Circular hole option, Hugh Knudsen Number ET,3,185,,3 ! Structural element s_l=100 ! Half Plate length (um) s_l1=60 ! Plate hole location s_w=20 ! Plate width s_t=1 ! Plate thickness c_r=3 ! Hole radius d_el=2 ! Gap pamb=.1 ! ambient pressure (MPa) visc=18.3e-12 ! viscosity kg/(um)(s) pref=.1 ! Reference pressure (MPa) mfp=64e-3 ! mean free path (um) Knud=mfp/d_el ! Knudsen number mp,visc,1,visc ! Dynamic viscosity gap mp,visc,2,visc ! Dynamic viscosity holes mp,ex,3,79e3 ! Gold mp,dens,3,19300e-18 mp,nuxy,3,.1 r,1,d_el,,,pamb ! Real constants - gap rmore,pref,mfp r,2,c_r,,,pamb ! Real constants - hole rmore,pref,mfp ! Build the model rectng,-s_l,s_l,-s_w,s_w ! Plate domain pcirc,c_r ! Hole domain agen,3,2,,,-s_l1/3 agen,3,2,,,s_l1/3 ASBA, 1, all TYPE, 1 MAT, 1 smrtsize,4 AMESH, all ! Mesh plate domain ! Begin Hole generation *do,i,1,5 nsel,all *GET, numb, node, , num, max ! Create nodes for link elements N, numb+1,-s_l1+i*s_l1/3,, N, numb+2,-s_l1+i*s_l1/3,, s_t TYPE,2 MAT, 2 REAL,2 NSEL, all E, numb+1, numb+2 ! Define 2D link element ESEL, s, type,,1 NSLE,s,1 local,11,1,-s_l1+i*s_l1/3 csys,11 NSEL,r, loc, x, c_r ! Select all nodes on the hole circumference NSEL,a, node, ,numb+1 *GET, next, node, , num, min CP, i, pres, numb+1, next nsel,u,node, ,numb+1 nsel,u,node, ,next CP, i, pres,all !Coupled DOF set for constant pressure csys,0 *enddo ! End hole generation esize,,2 type,3 mat,3 real,3 vext,all,,,,,s_t ! Extrude structural domain nsel,s,loc,x,-s_l nsel,a,loc,x,s_l nsel,a,loc,y,-s_w nsel,a,loc,y,s_w nsel,r,loc,z,-1e-9,1e-9 d,all,pres ! Fix pressure at outer plate boundary nsel,all esel,s,type,,2 nsle,s,1 nsel,r,loc,z,s_t d,all,pres,0 ! P=0 at top of plate dlist,all esel,s,type,,1 nsle,s,1 nsel,u,cp,,1,5 cm,FLUN,node allsel nsel,s,loc,x,-s_l nsel,a,loc,x,s_l d,all,ux d,all,uy d,all,uz allsel fini /solu antype,modal ! Modal analysis modopt,lanb,2 ! Extract lowest two eigenmodes eqslv,sparse mxpand,2 ! Expand lowest two eigenmodes solve fini /post1 RMFLVEC ! Extract eigenvectors fini /solu abextract,1,2 ! Extract damping ratios and Rayleigh constants finish
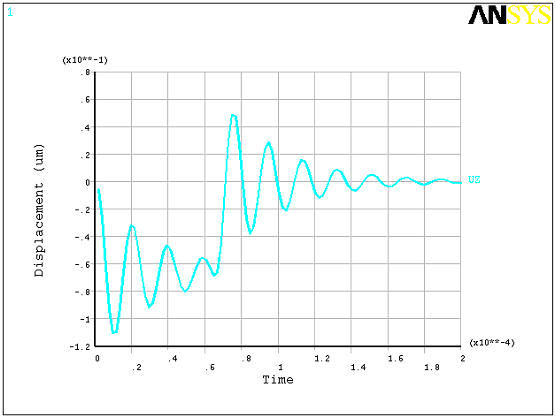
A transient dynamic analysis on the switch can be performed using the extracted damping parameters. The following input illustrates a coupled electrostatic-structural time-transient solution. The electrostatic field is assumed to be normal to the plate in the gap, and fringing effects are ignored. TRANS126 elements are used to model the coupled electrostatic-structural interaction with the switch. The EMTGEN command is used to generate the transducer elements. A step voltage pulse is applied over a short duration (65 micro-seconds) then released. Rayleigh damping parameters, when used, are applied to the global mass (ALPHAD parameter) and stiffness (BETAD parameter) matrices. We want to apply these only to the mass and stiffness matrix of the SOLID185 elements, and not the TRANS126 elements, because doing so may overdamp the system. The TRANS126 elements produce a damping matrix and a stiffness matrix only. Hence, we can use the ALPHAD parameter for the global mass matrix since there is no contribution from the TRANS126 elements. To isolate the SOLID185 elements for beta damping, we can apply the beta damping via a material damping option (MP,BETD). Figure 4.4: Time-Transient Response from Voltage Pulse illustrates the displacement of a node near the center of the plate over time. The maximum amplitude of displacement (0.11 microns) is small enough to ignore large deflection damping effects.
/batch,list /PREP7 /title, Damped Transient Dynamic Response of an RF MEMS switch /com uMKS units /com, Small deflection assumption et,1,200,6 ET,3,185,,3 ! Structural element s_l=100 ! Plate length (um) s_l1=60 ! Plate hole location s_w=20 ! Plate width s_t=1 ! Plate thickness c_r=3 ! Hole radius d_el=2 ! Gap pamb=.1 ! ambient pressure (MPa) visc=18.3e-12 ! viscosity kg/(um)(s) pref=.1 ! Reference pressure (MPa) mfp=64e-3 ! mean free path (um) Knud=mfp/d_el ! Knudsen number mp,ex,3,79e3 ! Gold mp,dens,3,19300e-18 mp,nuxy,3,.1 mp,betd,1,1.829e-8 ! Material damping (from squeeze film results) ! Build the model rectng,-s_l,s_l,-s_w,s_w ! Plate domain pcirc,c_r ! Hole domain agen,3,2,,,-s_l1/3 agen,3,2,,,s_l1/3 ASBA, 1, all TYPE, 1 MAT, 1 smrtsize,4 AMESH, all ! Mesh plate domain esize,,2 type,3 mat,3 real,3 vext,all,,,,,s_t ! Extrude structural domain nsel,s,loc,x,-s_l nsel,a,loc,x,s_l d,all,ux d,all,uy d,all,uz allsel aclear,all save nsel,s,loc,z cm,base,nodes emtgen,'base',,,'uz',-d_el ! generate Transducer elements allsel,all nsel,s,loc,z,-d_el d,all,uz,0 d,all,volt,0 cmsel,s,base d,all,volt,10 allsel,all fini /solu antyp,trans alphad,65211 ! alpha damping computed from Squeeze-film theory kbc,1 time,.000065 deltime,2.0e-6 outres,all,none outres,nsol,all solve time,.0002 cmsel,s,base d,all,volt,0 allsel,all solve fini n1=node(0,2,0) /post26 nsol,2,n1,uz prvar,2 plvar,2 finish