SURF155
3D Thermal Surface Effect
SURF155 Element Description
SURF155 can be used for various load and surface-effect applications. The element is applicable to 3D thermal analyses. It can be overlaid onto an edge of any 3D thermal solid element. Various loads and surface effects can exist simultaneously.
SURF155 Input Data
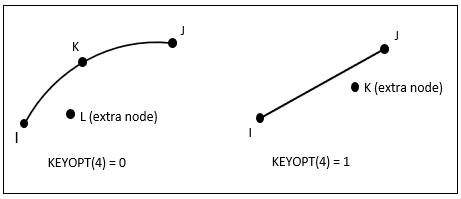
The element is defined by two to four node points and by the material properties. The nodes for this element must share the nodes of the underlying solid element. An extra node (away from the base element) can be used for convection effects.
See Element Loading for a description of element loads. Convections or heat fluxes can be input as surface loads on the element.
The convection surface conductivity matrix calculation uses the film coefficient (input on the SFE command with KVAL = 0 and CONV as the label). If the extra node option is used, its temperature becomes the bulk temperature. If the extra node is not used, the CONV value input with KVAL = 2 becomes the bulk temperature. The convection surface heat flow vector calculation uses the bulk temperature. On a given face, either a heat flux or a convection can be specified, but not both simultaneously.
Setting KEYOPT(7) = 1 multiplies the evaluated film coefficient by the empirical term |TS-TB|n, where TS is the element surface temperature, TB is the fluid bulk temperature, and n is an empirical coefficient (real constant ENN).
A film coefficient specified by the SFE command can be modified by activating the user subroutine USERCV with the USRCAL command. USERCV can be used to modify the film coefficient of a surface element with or without an extra node. It can be used if the film coefficient is a function of temperature and/or location.
Heat generation rates are input on a per unit volume basis and can be input as an element body load at the nodes, using the BFE command. Element body loads are not applied to other elements connected at the same nodes. The node I heat generation HG(I) defaults to zero. The node J heat generation defaults to HG(I). The heat generation load vector calculation uses the heat generation rate values.
As an alternative to using the BFE command, you can specify heat generation rates directly at the nodes using the BF command. For more information on body loads, see Body Loads in the Basic Analysis Guide.
When KEYOPT(4) = 0, an edge with a removed midside node implies that the temperature varies linearly, rather than parabolically, along that edge. See Quadratic Elements (Midside Nodes) in the Modeling and Meshing Guide for more information about the use of midside nodes.
Following is a summary of the element input. A general description of element input is given in Element Input. For axisymmetric applications see Harmonic Axisymmetric Elements.
SURF155 Input Summary
- Nodes
I, J if KEYOPT (4) = 1, and KEYOPT (5) = 0 I, J, K if KEYOPT (4) = 1, and KEYOPT(5) = 1 I, J, K if KEYOPT (4) = 0, and KEYOPT(5) = 0 I, J, K, L if KEYOPT (4) = 0, and KEYOPT(5) = 1 - Degrees of Freedom
TEMP
- Real Constants
(Blank), AREA, PERIMETER, ENN See Table 155.1: SURF155 Real Constants and Figure 155.2: AREA and PERIMETER used only in specific heat matrix and heat generation load vector calculation for more information. - Material Properties
MP command: DENS, C, ENTH - Surface Loads
- Convections --
face 1 (I-J) if KEYOPT(8) > 1
- Heat Fluxes --
face 1 (I-J) if KEYOPT(8) = 1
- Body Loads
- Heat Generation --
HG(I), HG(J); also HG(K) if KEYOPT(4) = 0
- Special Features
- KEYOPT(4)
Midside nodes:
- 0 --
Has midside node
- 1 --
No midside node
- KEYOPT(5)
Extra node for convection calculations:
- 0 --
No extra nodes
- 1 --
Has extra node (optional if KEYOPT(8) > 1)
- KEYOPT(6) (used only if KEYOPT(5) = 1 and KEYOPT(8) > 1)
Use of bulk temperatures:
- 0 --
Extra node temperature used as bulk temperature
- 1 --
Adiabatic wall temperature used as bulk temperature
- KEYOPT(7)
Empirical term:
- 0 --
Do not multiply film coefficient by empirical term.
- 1 --
Multiply film coefficient by empirical term |TS-TB|n.
- KEYOPT(8)
Heat flux and convection loads:
- 0 --
Ignore heat flux and convection surface loads (if any)
- 1 --
Include heat flux, ignore convection
Use the following to include convection (ignore heat flux):
- 2 --
Evaluate film coefficient hf (if any) at average film temperature, (TS +TB)/2
- 3 --
Evaluate hf at element surface temperature, TS
- 4 --
Evaluate hf at fluid bulk temperature, TB
- 5 --
Evaluate hf at differential temperature, | TS - TB |
- KEYOPT(13)
Film coefficient matrix key:
- 0 --
Program determines whether to use diagonal or consistent film coefficient matrix (default).
- 1 --
Use a diagonal film coefficient matrix.
- 2 --
Use a consistent matrix for the film coefficient.
Table 155.1: SURF155 Real Constants
| No. | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 - 6 | (Blank) | -- |
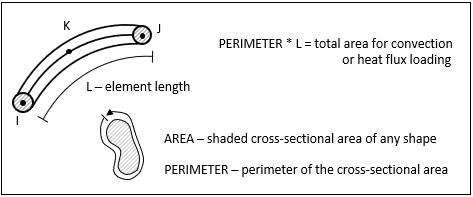
| 7 | AREA | Cross-sectional area used only in specific heat matrix and heat generation load vector calculation. It can be any arbitrary shape as depicted by the shaded area in the following figure. |
| 8 - 11 | (Blank) | -- |
| 12 | PERIMETER | Perimeter of the cross-sectional area used only in convection and heat flux load calculation (see the following figure). |
| 13 | ENN | Empirical coefficient |
| 14 - 15 | (Blank) | -- |
Figure 155.2: AREA and PERIMETER used only in specific heat matrix and heat generation load vector calculation
SURF155 Output Data
The solution output associated with the element is in two forms:
Nodal degree of freedom results included in the overall nodal solution
Additional element output as shown in Table 155.2: SURF155 Element Output Definitions
Convection heat flux is positive out of the element; applied heat flux is positive into the element. A general description of solution output is given in Solution Output. See the Basic Analysis Guide for ways to view results.
The Element Output Definitions table uses the following notation:
A colon (:) in the Name column indicates that the item can be accessed by the Component Name method (ETABLE, ESOL). The O column indicates the availability of the items in the file jobname.out. The R column indicates the availability of the items in the results file.
In either the O or R columns, “Y” indicates that the item is always available, a letter or number refers to a table footnote that describes when the item is conditionally available, and “-” indicates that the item is not available.
Table 155.2: SURF155 Element Output Definitions
| Name | Definition | O | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| EL | Element Number | Y | Y |
| SURFACE NODES | Nodes - I, J | Y | Y |
| EXTRA NODE | Extra node (if present) | Y | Y |
| MAT | Material number | Y | Y |
| LENGTH | Length | Y | Y |
| XC, YC | Location where results are reported | Y | 6 |
| VN(X, Y) | Components of unit vector normal to center of element | - | Y |
| DENSITY | Density | - | 1 |
| MASS | Mass of Element | - | 1 |
| HGEN | Heat generations HG(I), HG(J), HG(K) | 2 | - |
| HEAT GEN. RATE | Heat generation rate over entire element (HGTOT) | 2 | 2 |
| HFLUX | Input heat flux at nodes I, J | 3 | - |
| HEAT FLOW RATE | Input heat flux heat flow rate over element surface area (HFCTOT) | 3 | 3 |
| HFILM | Film coefficient at each face node | 4 | 4 |
| TBULK | Bulk temperature at each face node or temperature of extra node | 4 | 4 |
| TAVG | Average surface temperature | 4 | 4 |
| CONV. HEAT RATE | Convection heat flow rate over element surface area (HFCTOT) | 4 | 4 |
| CONV. HEAT RATE/AREA | Average convection heat flow rate per unit area | 4 | - |
Available only at centroid as a *GET item.
Table 155.3: SURF155 Item and Sequence Numbers lists output available via the ETABLE command using the Sequence Number method. (See The General Postprocessor (POST1) and The Item and Sequence Number Table for more information.) The following notation is used in the table:
- Name
output quantity
- Item
predetermined Item label for the ETABLE command
- E
sequence number for single-valued or constant element data
- I,J
sequence number for data at nodes I and J
SURF155 Assumptions and Restrictions
The element must not have a zero length.
If real constant AREA is defined for the element, the element volume is greater than zero. If BF, BFE, or BFUNIF commands are issued under this circumstance, heat generation loads are activated, and the damping matrix is activated based on the density and specific heat of the element. In order to have heat generation but no damping from the element, set density and specific heat to small values.