SHSD
SHSD,
RID, Action,
CHCH_Opt, CGAP,
CPEN
Creates or deletes a shell-solid interface to be used in shell-to-solid
assemblies.
RIDThe real constant set ID that identifies the contact pair on which a shell-to-solid assembly is defined. If ALL, all selected contact pairs will be considered for assembly.
ActionAction to be performed:
EDGE
—
Create virtual shell elements based on the shell edge (default).
SURFACE
—
Create virtual shell elements based on the solid element surface.
DELETE
—
Delete the nodes and elements created during a previous execution of SHSD for the real constant set identified by
RID.CNCH_OptCNCHECK option to close initial penetration or gap:
CGAPControl parameter for opening gap; must be greater than or equal to zero. Close the gap if the gap distance is smaller than the
CGAPvalue.CGAPdefaults to 0.25*PINB (where PINB is the pinball radius) for bonded and no-separation contact. Otherwise, it defaults to the value of real constant ICONT.CPENControl parameter for initial penetration; must be greater than or equal to zero. Close the penetration if the penetration distance is smaller than the
CPENvalue.CPENdefaults to 0.25*PINB (where PINB is the pinball radius) for any type of interface behavior (either bonded or standard contact).
Notes
The SHSD command creates a shell-solid interface to be used in
shell-to-solid assemblies, or deletes a previously-created shell-solid interface.
Virtual shell elements and additional CONTA175
or CONTA177 elements are created
at the contact pair identified by RID when
Action = EDGE or SURFACE. Set
Action = DELETE to remove the generated nodes and elements at the
contact pair identified by RID.
The SHSD command is active only when the following element KEYOPTs of associated CONTA175 or CONTA177 element types are predefined:
| Element | KEYOPT | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| CONTA175 or CONTA177 | KEYOPT(2) = 2 | MPC algorithm |
| KEYOPT(12) = 5, 6 | Bonded contact | |
| KEYOPT(4) = 0 | Contact normal perpendicular to target surface |
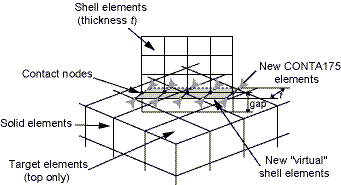
When ACTION = EDGE, the
virtual shell elements are built perpendicular to the pre-existing shell elements attached to the
contact elements. They geometrically follow the contact interface edge and are built on both
sides of this interface in such a way that each new shell element
(SHELL181) has two nodes that belong to the associated pre-existing
shell element in the shell edge. (See Figure 28: Virtual Shell Elements Following the Contact Interface Edge.) The width of the new shell
elements is half the thickness of the pre-existing shell element. If CONTA175 is used at the shell nodes, the
CONTA175 elements are then created at each node of the virtual shell
elements where no CONTA175 element exists. If
CONTA177 is used at the shell edge, new
CONTA174 elements are created and overlayed on the virtual
shell. The new contact elements are identified by the same contact pair ID as the
pre-existing contact elements. The virtual shell elements are assigned the next available
element type number and material number.
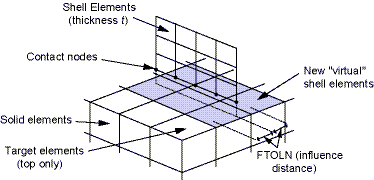
When ACTION = SURFACE,
the virtual shell elements (SHELL181 - low order;
SHELL281 - high order) overlap the existing low or high order target
elements identified with the RID argument, and share their nodes. Only
those target elements close enough to the contact interface (identified using the PINB real
constant) are overlapped. The program uses the FTOLN real constant (defaults to half the shell
element thickness) to define an influence distance. The associated virtual shell elements are
created only for target elements that lie partially inside the influence distance region (see
Figure 29: Virtual Shell Elements Overlapping Target Elements).
For the bonded always option (KEYOPT(12) = 5), any contact node inside the pinball region (gap < PINB) is included in the KEYOPT(5) = 2 process. A relatively small PINB value may be used to prevent false contact. PINB defaults to 25% of the contact depth for small deformation analyses.
For the bonded initial option (KEYOPT(12) = 6), only those contact nodes which initially lie inside the adjustment zone (gap < ICONT) are always included in the KEYOPT(5) = 2 process. ICONT defaults to 5% of the contact depth.
For both processes, the new nodes and elements are stored in internally-named components.
The internal naming convention is based on the real constant set ID specified by
RID, as illustrated in the following table.
| Nodes | SHSD_ND_RID |
| Contact Elements | SHSD_CN_RID |
| Shell Elements | SHSD_SH_RID |
Issuing SHSD,RID,DELETE deletes components
based on their generated names. Only components whose names match the internal naming
convention will be deleted.
Caution: Do not rename or manually delete generated components. Use the SHSD command to delete generated components.
Renaming or manually deleting generated components will cause these components to be
ignored when SHSD,RID,DELETE is executed and when
the program searches for these components to verify if SHSD,RID,EDGE or SURFACE can be
safely executed. Manually renaming or deleting generated components and reissuing SHSD,RID,EDGE or
SURFACE may result in erroneous generation of virtual shell or contact
elements.
SHSD does not support assemblies that contain a preintegrated shell section (SECTYPE,,GENS).
See Modeling a Shell-Solid Assembly in the Contact Technology Guide for more information.