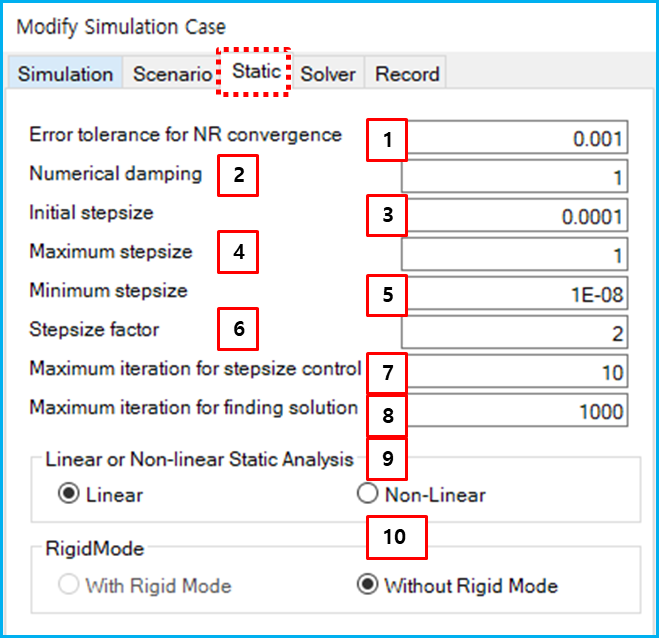
As shown in the figure below, the Error tolerance, Numerical damping, and several other parameters for the simulation can be defined in the Static tab of simulation configuration dialog. The parameters are described in the table below. The solution scheme of the static analysis is very similar to that of dynamic analysis, so these parameters are same as the parameters for Dynamic Analysis.
Figure 9.24: Static parameters in the simulation configuration
| Feature | Description | Dimension (Range) |
| 1. Error tolerance… | Use to set the error tolerance to check the convergence of the nonlinear equation solver. For more information, see Dynamic Parameters for Simulation Configuration. |
N/A (Real>0.0) |
| 2. Numerical damping | Use to set the numerical damping. For more information, see Dynamic Parameters for Simulation Configuration. | N/A (0≤Real<4) |
| 3. Initial step size | Use to set the initial integration step size. For more information, see Dynamic Parameters for Simulation Configuration. |
Time (Real>0.0) |
| 4. Maximum step size | Use to set the maximum integration stepsize. For more information, see Dynamic Parameters for Simulation Configuration. |
Time (Real>0.0) |
| 5. Minimum step size | Use to set the minimum integration stepsize. For more information, see Dynamic Parameters for Simulation Configuration. |
Time (Real>0.0) |
| 6. Stepsize factor | Use to set the factor for increasing and decreasing the integration step size. For more information, see Dynamic Parameters for Simulation Configuration. |
N/A (Real≥1.0) |
| 7. Maximum iteration… control | Use to set the maximum number of integration steps under same integration step size. For more information, see Dynamic Parameters for Simulation Configuration. |
N/A (Integer>0) |
| 8. Maximum iteration… solution | Use to set the maximum number of the global iterations. If the Motion solver does not find a static solution within this number of iterations, the solver will be terminated with an error message. |
N/A (Integer>0) |
| 9. Linear or Non-linear… | Use to select one of methods for static analysis. When the Linear option is selected, the model is treated as a linear problem, which means that the stiffness matrix and force of the system are constant. This method is useful to find the static equilibrium of a small deformation structural problem. When the Non-Linear option is selected, the stiffness matrix and force are treated as variables. This method is therefore useful in finding the static equilibrium of a large deformation and non-linear material structural problem. | N/A |
| 10. Rigid Mode | Use to select one of the motion types in static analysis. When the Linear option is selected, the Without Rigid Mode option is only available. If the model contains rigid motion, the With Rigid Mode option must be selected to find the static position. Otherwise, the Without Rigid Mode option must be selected. | N/A |