The analysis is performed in two steps:
Step 1 (Inverse-Solving Analysis): A nonlinear static analysis using inverse solving (INVOPT,ON) is performed on the hot geometry of the model to obtain the cold geometry (for manufacturing) and the stress/strain results on the hot geometry.
Step 2 (Forward-Solving Analysis): Consider the results of this analysis as a reference demonstrating the correctness of the inverse-solving analysis. The cold geometry obtained from Solution 1 is solved again but with a traditional forward-solving analysis to obtain the hot geometry with stress/strain results.
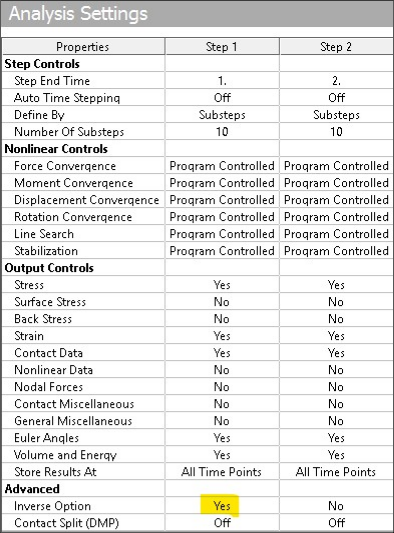
To include large-deflection effects Large Deflection is set to On in Analysis Settings. Also, set the , available only for Step 1, to Yes to enable Inverse solving. The rest of the analysis settings are the same for both steps and mostly default settings as listed below.
An inverse-solving analysis followed by a forward-solving analysis is known as a loop test, as the forward-solving analysis should always result in the same hot geometry (input to the inverse-solving analysis). Furthermore, simulating the running condition by applying the same loads in both analyses should result in the same results (mechanical stress and strain and thermal strain).