VM-WB-MECH-103
VM-WB-MECH-103
Harmonic Response Analysis of a Piston-Fluid System
Overview
| Reference: | Axisa, F., & Anutes, J. (2006). Modelling of Mechanical Systems: Fluid-Structure Interaction (p. 486). Butterworth-Heinemann. |
| Solver(s): |
Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Harmonic Analysis |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
Test Case
A simple piston-fluid system is modeled using a spring attached to a mass moving in a frictionless fluid filled cylinder.
The piston is driven by a harmonic force F0eiωt along the axial direction. A full harmonic analysis is performed to investigate the displacement of the piston and the pressure amplitude at mid-column.
This problem is also presented in VM282
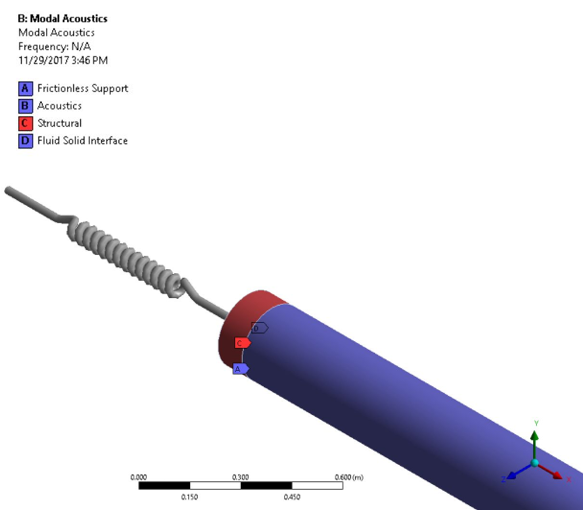
Figure 138: Finite Element Representation of a Spring-Mass System Coupled to a Compressible Fluid Column in a Tubet
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fluid Properties:
Structural Properties:
|
Tube radius, R = 12.5 cm Tube length, L = 24 m |
F0 = 1000 N f = 0 - 100 Hz |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The piston is modeled as a spring-mass system with one end fixed. The fluid column is modeled as a straight tube of constant cross-sectional area filled with a compressible fluid. The tube is closed at the outlet. The contact region is defined as the interface between the mass and the fluid in the tube.
A modal acoustics analysis of the piston-fluid system is performed to obtain the first five frequencies.
A harmonic acoustics analysis is performed with the applied force to determine the piston-displacement amplitude and the fluid-pressure amplitude.
Ansys Mechanical does not support mode-superposition harmonic-acoustic analysis as performed in VM282. The portion of that analysis including damping is not reproduced in this test.
Results Comparison
| Modal Frequency | Target | Mechanical | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| f1, Hz | 9.916 | 9.895 | -0.213 |
| f2, Hz | 24.583 | 24.603 | 0.081 |
| f3, Hz | 43.729 | 43.734 | 0.011 |
| f4, Hz | 63.895 | 63.905 | 0.016 |
| f5, Hz | 83.395 | 84.394 | 1.198 |
| Result | Target | Mechanical | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piston displacement amplitude at 1.0 Hz, m | 0.00025 | 0.00024988 | -0.048 |
| Fluid pressure amplitude at 1.0 Hz, MPa | 10300 | 10422 | 1.18 |


