VM-WB-MECH-089
VM-WB-MECH-089
Delamination Analysis of a Double Cantilever Beam Using
Contact-Based Debonding
Overview
| Reference: | Alfano, G., & Crisfield, M. A. (2001). Finite element interface models for the delamination analysis of laminated composites: Mechanical and computation issues. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 50(7), 1701-1736. |
| Solver(s): | Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Static Structural |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
Test Case
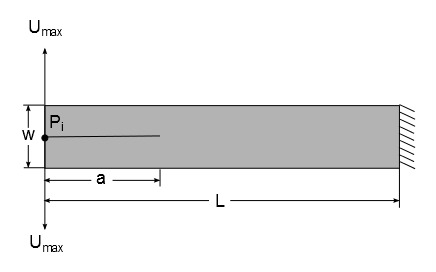
A double cantilever beam of length l, width w, and height h with an initial crack of length a at the free end is subjected to a maximum vertical displacement Umax at the top and bottom free end nodes. Determine the vertical reaction at point P, based on the vertical displacement using the contact-based debonding capability.
This problem is also presented in VM255
in the Mechanical APDL Verification Manual.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Umax = 10 mm |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
A double cantilever beam is analyzed under displacement control using 2-D plane strain formulation elements. An imposed displacement of Uy = 10 mm acts at the top and bottom free vertex. Contact debonding is inserted at the interface.
Defined fracture-energy based debonding material is used to define the material for contact debonding. Equivalent separation-distance based debonding material is also used for the contact debonding object.
Based on the interface material parameters used, results obtained using Mechanical are compared to results shown in Figure 15(a) of the reference material.