This section describes how to compute efficiencies for a variety of scenarios. For mathematical definitions of the various efficiency types, refer to Efficiency Calculation in the Fluent Theory Guide.
For additional information, see the following sections:
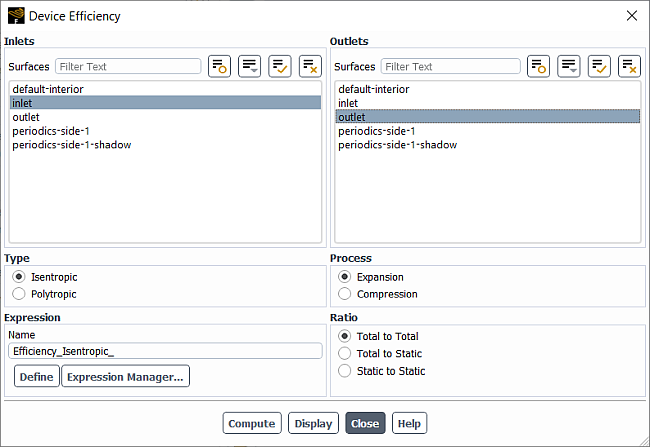
You can define and evaluate efficiency for a generic device using the Device Efficiency dialog box (Figure 41.34: The Device Efficiency Dialog Box) accessed from:
→ Results → Reports → Efficiency...
Locations for the Inlets and Outlets can be selected using the corresponding surface lists. These lists are filtered to include only the surfaces of supported types.
Under Type, select whether to compute the Isentropic or Polytropic efficiency.
Under Process, select whether to compute the efficiency for the Expansion or Compression process.
Under Ratio, you can select which values are used when computing the device efficiency: Total to Total, Total to Static, or Static to Static.
You can optionally define an expression based on the dialog box input. Edit or keep the default name (an integer number will be appended to the name automatically) and click Define. All available expressions can be viewed by clicking Expression Manager…. For more details, see Calculating Efficiency using Named Expressions.
If the solution is initialized or computed, you can click Compute to get an efficiency value for the selected input.
Click Display to visualize the selected surfaces.
You can also access this tool by using the following console command and following the prompts:
/report/efficiency
Note that the Device Efficiency dialog box is applicable to devices of various types, including but not limited to turbomachines, such as diffusers, nozzles, valves, and other devices with compressible throughflow. However, specifically for turbomachines, an additional option is available to compute efficiency using the Turbo Report dialog box as described in Generating Reports of Turbomachinery Data.
→ Results → Model
Specific → Turbo
Post → Report...
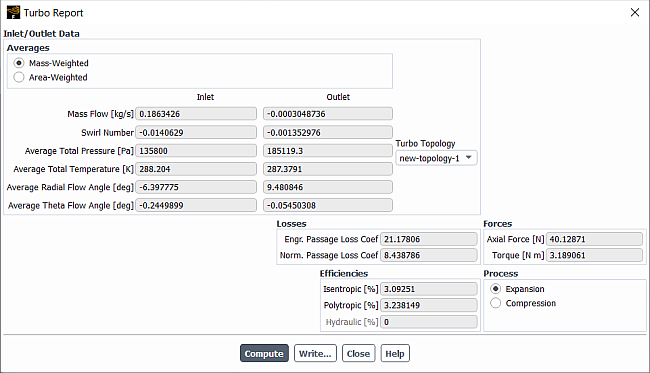
By default, the Turbo Report dialog box computes the Total to Total values of isentropic and polytropic efficiencies assuming constant values of the specific heat capacity Cp and heat capacity ratio γ. You can switch to the more general equations which are implemented from the Device Efficiency dialog box, by using the following console command:
/report/efficiency/use-in-turbo-report?
Note that for an ideal gas with constant Cp value, the two methods give nearly identical results. However, for other cases, only the method from the Device Efficiency dialog box is able to provide appropriate efficiency values.
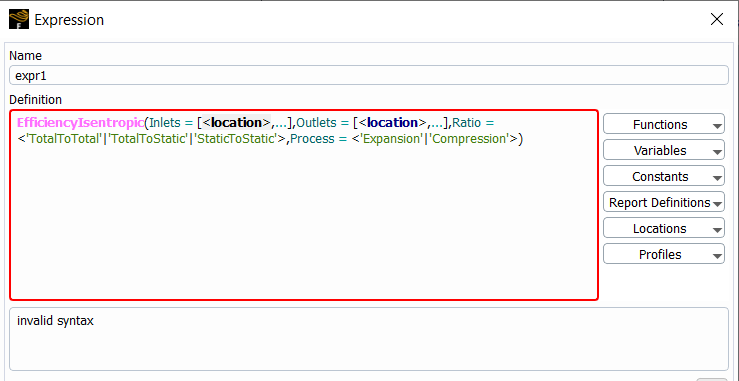
You can compute the values of isentropic and polytropic efficiencies for a device with compressible throughflow using Named Expressions as shown in Figure 41.35: Expression Dialog Box with Efficiency Calculation.
→ User Defined → User
Defined → Named
Expressions → New...
Functions for both efficiency types are listed under
Functions → Reduction as
EfficiencyIsentropic and
EfficiencyPolytropic.
Permeable boundaries of various types (for example, inlets, outlets, interfaces), as
well as cut-planes and iso-surfaces, can be chosen as locations. Also, groups of surfaces
for postprocessing are supported. For the argument Inlets, you can
select one or more locations of mixed types. However, multiple locations will still be
treated as the single-stream inlet with properties averaged over all selected locations.
This averaged inlet can be considered as the starting point for efficiency calculation.
Similarly, the end point will be determined by locations selected for the argument
Outlets. Options for the argument Process(Expansion
and Compression) specify whether the flow expands or compresses when moving
from the inlet to the outlet. Options for the argument Ratio
(TotaltoTotal, TotaltoStatic and
StatictoStatic) determines the values used in computing the
efficiency.
Efficiency can be evaluated only for compressible flows of ideal gas, single-component real gas, and condensing water vapor (Wet Steam model).
Only the following locations are supported: Pressure Inlet, Pressure Outlet, Mass-Flow Inlet, Mass-Flow Outlet, Velocity Inlet, Pressure-far-field, Inlet Vent, Outlet Vent, Intake Fan, Exhaust Fan, Interior, Interface, Cut-plane, Iso-surface, Groups of listed surfaces.
Multiple inlet or outlet locations are reduced to a single stream with flow properties averaged over all selected.