VMFL015
VMFL015
Flow Through
an Engine Inlet Valve
Overview
| Reference | A. Chen, K.C. Lee, M. Yianneskis, G. Ganti, “Velocity Characteristics of Steady Flow Through a Straight Generic Inlet Port”. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, Vol 21, pp. 571-590, 1995. | |
| Solver | Ansys Fluent | |
| Physics/Models | 3–D turbulent flow | |
| Input File |
| |
| Project Files | Link to Project Files Download Page |
Test Case
Flow in an idealized engine cylinder with a straight inlet port and a valve lift of 10 mm (the distance from the top of the cylinder to the bottom of the valve). The configuration of the inlet port, valve, and cylinder is shown in Figure 36: Flow Domain.
| Material Properties | Geometry | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|
|
Density : 894 kg/m3 Viscosity: 0.001529 kg/m-s |
All dimensions shown in Figure 36: Flow Domain are in mm. |
Inlet velocity = 0.9282 m/s Inlet turbulent intensity = 10% Inlet turbulent length scale = 0.046m Outlet gauge pressure = 0 Pa |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The flow is steady, isothermal and incompressible. The standard k-ε model with standard wall functions is used. The length of the cylinder is chosen to be large enough that it will not affect the flow in the cylinder.
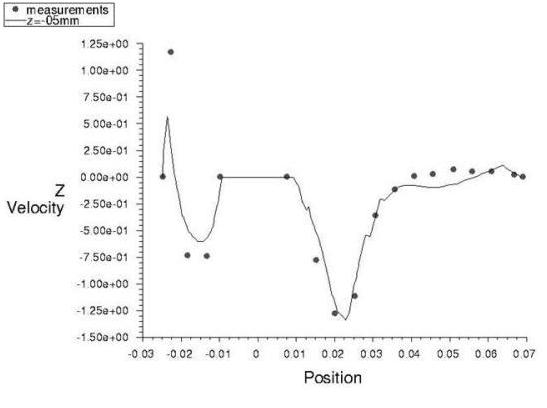
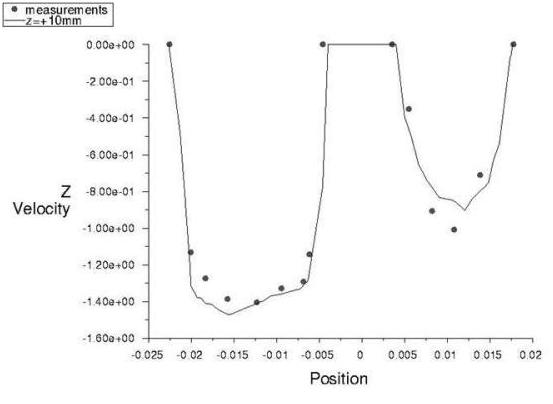
Results Comparison for Ansys Fluent
Figure 37: Z-Velocity Component at Z= -5mm and Figure 38: Z-Velocity Component at Z = +10mm compare Ansys Fluent's results with the experimental data (z-component of velocity at different heights).