VMFL014
VMFL014
Species
Mixing in Co-axial Turbulent Jets
Overview
| Reference |
| ||
| Solver | Ansys Fluent, Ansys CFX | ||
| Physics/Models | Multi-Species flow, turbulent, jet mixing | ||
| Input File |
| ||
| Project Files | Link to Project Files Download Page |
Test Case
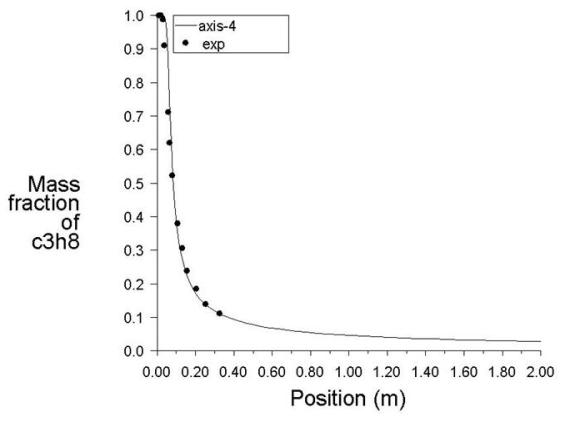
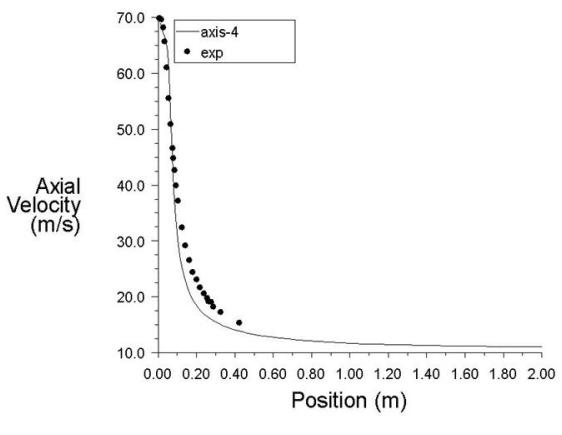
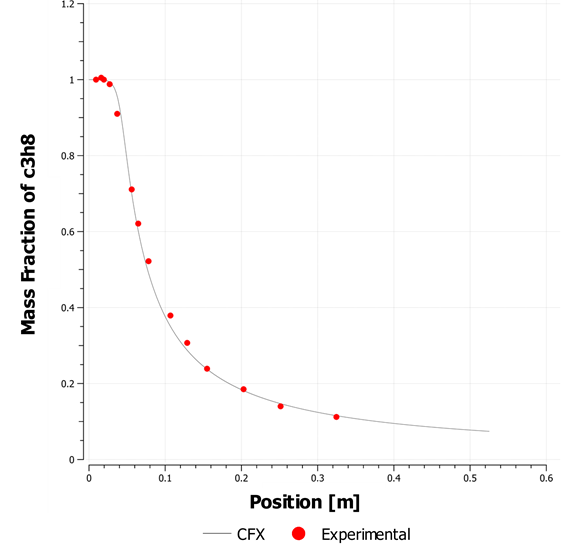
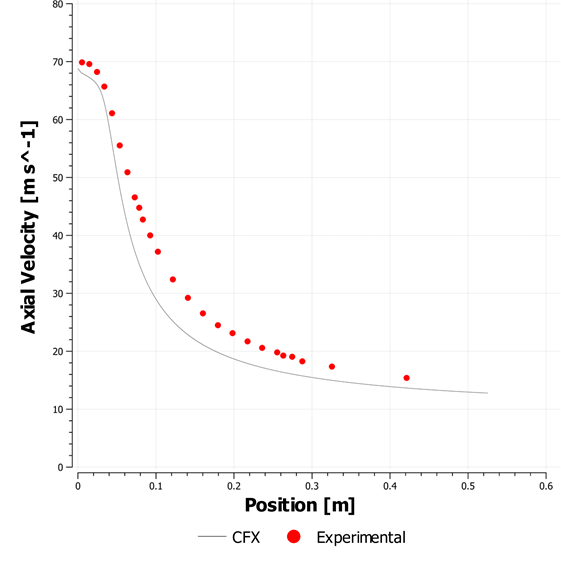
A propane jet issues into a co-axial stream of air. There is turbulent mixing between the species in the axisymmetric tunnel. Only half of the domain is considered due to axial symmetry.
| Material Properties | Geometry | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|
|
Density: Incompressible ideal gas law Viscosity: 1.72X10–5 kg/m-s |
Tunnel length = 2 m Tunnel diameter = 0.3 m Propane jet tube: Inner diameter = 5.2 mm Outer diameter = 11 mm |
Inlet velocity of air = 9.2 m/s Inlet velocity of Propane – Specified as fully developed profile Inlet temperature (both streams) = 300 K Temperature at the wall = 300 K |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The flow is steady. Species mixing is modeled with the three species; propane, oxygen, and nitrogen. There is no reaction.