For general information about User Defined Results, see User Defined Results in the Mechanical User's Guide
The following table contains User Defined Results that are specific to an Explicit Dynamics analysis. The User Defined Results available for analyses using LS-DYNA are noted. Additional User Defined results available for LS-DYNA are described in History Variable Output.
| Expression | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| BEAM_AXIAL_FX | Beam axial force | Element Nodal |
| BEAM_BENDING_MY | Beam bending moment S | Element Nodal |
|
BEAM_BENDING_MZ | Beam bending moment T | Element Nodal |
| BEAM_LEN | Beam length | Element Nodal |
| BEAM_MISES_STR | Combined normal stress in a beam cross-section | Elemental |
|
BEAM_SHEAR_FY | S shear resultant | Element Nodal |
|
BEAM_SHEAR_FZ | T shear resultant | Element Nodal |
|
BEAM_TORSION_MX | Torsional resultant | Element Nodal |
| BOND_STATUS | The number of nodes bonded to the faces on an element during the analysis. A value of -1 is shown where all the bonds for the face have broken. | Elemental |
| C_S_AREA | Beam cross section area. | Element Nodal |
| COMPRESSALL |
Material compression: Compression, μ = ρ/ρ0 . | Element Nodal |
| CROSS_SECTION | Beam cross section number. | Elemental |
| DAMAGEALL |
Material Damage: 0– intact material. 1- fully fractured. | Element Nodal |
| DENSITY | Material Density. | Element Nodal |
| EFF_STN | Effective Geometric Strain. | Element Nodal |
| EFF_PL_STNALL | Effective Plastic Strain. Note: This is calculated incrementally, unlike the equivalent plastic strain (EPPLEQV_RST), which is calculated as an instantaneous value. | Element Nodal |
| ENERGY_DAM | Energy resulting from fracture for the Johnson-Holmquist brittle strength model. | Element Nodal |
| EROSION |
Erosion Status: 0 - no erosion. >0 - eroded (will not be displayed). | Elemental |
| EPS | Effective Plastic Strain. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| EPS_RATE | Effective Plastic Strain Rate. | Element Nodal |
| F_AXIAL | Beam axial force. | Element Nodal |
| INT_ENERGYALL | Internal energy of the material. | Element Nodal |
| MASSALL | Mass of material in an element. | Element Nodal |
| MATERIAL |
Material index. The material index as defined in the Explicit solver. There is not always a direct one-to-one correlation with materials defined in Engineering Data and those used in the Explicit solver. For layered section shells, the MATERIAL for individual layers can be shown by using the Layer property in the results details view. | Elemental |
| MOM_TOR | Beam rotation inertia. | Element Nodal |
| POROSITY |
Material Porosity: Porosity, α = ρSolid/ρ | Elemental |
| PRESSURE | Pressure. | Element Nodal |
| PRES_BULK | Dilation pressure for the Johnson-Holmquist brittle strength model. | Elemental |
| RB_CONTACT_ENERGY | Energy in Rigid Body contact. | Element Nodal |
| SOUNDSPEED | Material soundspeed. | Element Nodal |
| SPH_DENSITY | Density of SPH particles. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| SPH_INTERNAL_ENERGY | SPH internal energy. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| SPH_MASS | Mass of each SPH particle. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| SPH_NUMBER_NEIGHBORS | Number of neighboring SPH particles. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| SPH_PLASTIC_STRAIN | SPH plastic strain. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| SPH_PRESSURE | SPH pressure. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| SPH_RADIUS_INFLUENCE | SPH radius of influence. This result is only available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| STATUS |
Material Status: 1 – elastic. 2 – undergoing plastic flow. 3 – failed due to effective criteria (with healing). 4 – failed due to effective criteria. 5 – failed due to stress/strain in principal direction 1. 6 – failed due to stress/strain in principal direction 2. 7 – failed due to stress/strain in principal direction 3. 8 – failed due to shear stress/strain in principal direction 12. 9 – failed due to shear stress/strain in principal direction 23. 10 – failed due to shear stress/strain in principal direction 31. For layered section shells, the STATUS for individual layers can be shown by selecting the Layer number in the results details view. | Elemental |
| STOCH_FACT | Stochastic factor applied when the stochastic property as defined in the material failure model. | Elemental |
| STRAIN_1 | Axial strain (beams) | Element Nodal |
| STRAIN_XX | Total strain XX. | Element Nodal |
| STRAIN_YY | Total strain YY. | Element Nodal |
| STRAIN_ZZ | Total strain ZZ. | Element Nodal |
| STRAIN_XY | Total strain XY. These are tensor shear strains, and not engineering shear strains. | Element Nodal |
| STRAIN_YZ | Total strain YZ. These are tensor shear strains, and not engineering shear strains. | Element Nodal |
| STRAIN_ZX | Total strain ZX. These are tensor shear strains, and not engineering shear strains. | Element Nodal |
| TASK_NO | Assigned task number for parallel processing. | Elemental |
| TEMPERATUREALL | Material Temperature. | Element Nodal |
| THICKNESS | Shell Thickness. This result is available for LS-DYNA. | Element Nodal |
| TIMESTEP | Element computational time step. | Element Nodal |
| TYPE |
Element category (element number returned): HEX: 100-101. PENTA: 102. TET: 103-104,106. PYRAMID: 105. QUAD: 107. TRI: 108. SHL: 200-202, 204. BEAM: 203. | Elemental |
| VISC_PRES | Viscous pressure due to artificial viscosity. No results will display for an Eulerian part. | Element Nodal |
| VTXX | Viscoelastic stress XX. | Element Nodal |
| VTYY | Viscoelastic stress YY. | Element Nodal |
| VTZZ | Viscoelastic stress ZZ. | Element Nodal |
| VTXY | Viscoelastic stress XY. | Element Nodal |
| VTYZ | Viscoelastic stress YZ. | Element Nodal |
| VTZX | Viscoelastic stress ZX. | Element Nodal |
Note: For BEAM_AXIAL_FX, BEAM_SHEAR_F, BEAM_TORSION_MX, and BEAM_BENDING_M results in LS-DYNA, a plane through N1, N2, and N3 defines the orientation of the principal R-S plane of the beam. R is the axis between N1 and N2. T and S are determined by the position of the N3 orientation. These axes generally do not correspond with the global coordinate axes.
For Euler (Virtual) Analyses
The following results are multi-material variables:
EFF_PL_STN
INT_ENERGY
MASS
COMPRESS
DET_INIT_TIME
ALPHA
DAMAGE
TEMPERATURE
For each Eulerian (Virtual) body in the analysis, a separate component will be available, which will allow the user to plot the result for the particular material associated with that body. The component name will be derived from the body name. There will also be an "ALL" component, which displays results for all materials. Results for Lagrangian bodies can be viewed by selecting this "ALL" component. For a purely Lagrangian analysis, only the "ALL" component will be available to the user.
For example, an analysis has two Eulerian (Virtual) bodies (Solid, Solid) and a Lagrangian Body (Surface Body), as shown in the image of the Outline View below.
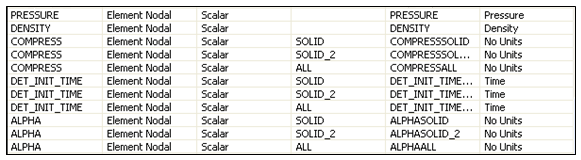
In the User Defined Result Expression Worksheet, there are three components available for the multi-material results named SOLID, SOLID_2, and ALL.
Note: It may be necessary to delete and reinsert multi-material results in order to view result for databases created prior to Release 13.0
For NBS Tetrahedral Elements
The element variables listed below can be used to visualize the variable values at the nodes. The variable values presented in the element are a volume weighted average of those at the nodes.
TEMPERATURE
SOUNDSPEED
DENSITY
COMPRESS
STRAINS (NORMAL AND SHEAR)
EFF_PL_STN
TIMESTEP
INT_ENERGY
The following variables are available as calculated directly from the solver in the element:
EFF_STN


