In an Explicit Dynamics Analysis, if any bodies have a reference frame set to Eulerian (Virtual), an Euler domain is created that encloses all bodies in the model. The Euler domain is a structured hexahedral mesh. The exact size and resolution of the Eulerian domain can be controlled in the Euler Domain Controls section of the Analysis Settings Details view.
Bodies with a reference frame set to Eulerian (Virtual) are used to initialize material into the Euler domain. After the initialization of the solve, the mesh associated with such bodies is discarded. The surfaces of the Eulerian bodies are not tracked exactly; the location of materials in the Euler domain is stored as a material (volume) fraction for each of the Euler cells. A representation of the material surface can be displayed as an isosurface for a material fraction value of 50%.
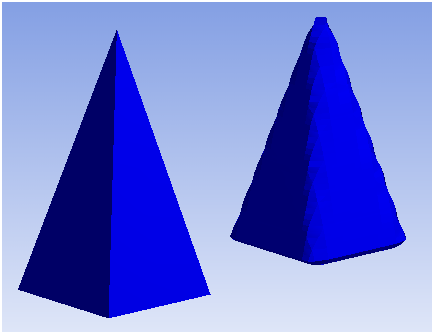
A comparison of Lagrangian (left) and Eulerian (right) representations of the same body is shown below.
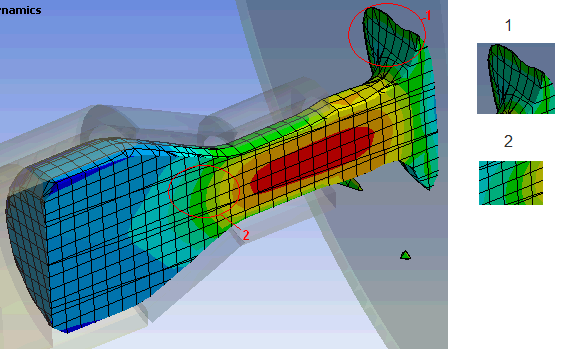
Results cannot therefore be displayed on the original mesh applied to the Euler bodies. Instead, a mesh is reconstructed for each material associated with the original body to which the result object is scoped. The reconstruction of the mesh is approximate and includes:
Finding the exterior surface of each material in its current location in the Euler domain. This is achieved by forming an isosurface on the volume fraction of each material in a cell (at 50%).
Filling the interior of the material with cells from the Euler domain that are completely inside the material.
Reconstructing an unstructured mesh for any gaps between the exterior surface and interior cells.
The example below illustrates a typical mesh displayed for a Results object scoped to a Body with Eulerian (Virtual) reference frame:
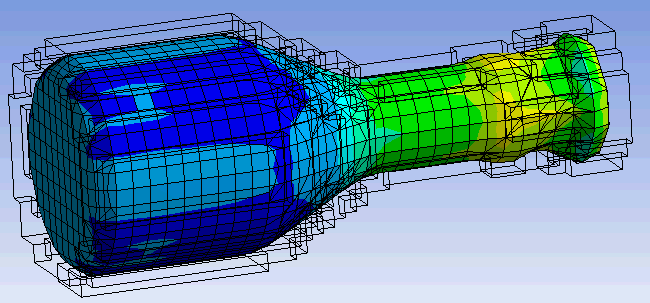
When the Show Undeformed Wireframe option is selected for a results object scoped to Euler bodies, the wireframe of the background Euler domain is displayed. Only the Euler domain cells that contain material at a given point in time are used to construct the wireframe (cells that only contain void are not displayed). An example is given below:
If the Euler Tracking By Body option is selected in the Analysis Settings Details view, results may be scoped to Eulerian bodies in the same way as for Lagrangian bodies, and body trackers are available for Eulerian parts.
Additional considerations:
Displacement, strain, and BOND_STATUS results are not available for scoped results.
Probes and path plots are not supported for Eulerian bodies.
External Force and Contact Force trackers will return zero for Eulerian bodies.
Point trackers for Strain are not supported.
Deformation scaling (i.e. Undeformed, .5 Auto, AutoScaling, 2x Auto, 5x Auto ) is not available for Eulerian bodies.
Show undeformed model is not available for Eulerian bodies.
Although it is not possible to view the Eulerian domain directly within the Mechanical application, the size and resolution of the domain are indicated in the graphics window when Analysis Settings are selected in the outline view; if required, the model may be transferred to an Autodyn component system where the Euler mesh can be displayed.
There may be issues with solver efficiency for analyses containing more than ten Eulerian bodies.
When attempting to use the Euler capabilities in the Explicit Dynamics analysis system, the following license restrictions are observed:
Set-up and solve of Euler capabilities in the Explicit Dynamics system are supported for the full Ansys Autodyn (acdi_ad3dfull) license.
Set-up but not solve of Euler capabilities in the Explicit Dynamics system are supported for the pre-post Ansys Autodyn (acdi_prepost) license.
Set-up and solve of Euler capabilities in the Explicit Dynamics system are supported for the Ansys Mechanical Enterprise licenses.
Further discussion of the Eulerian solver used by Explicit Dynamics analyses, including a description of the theory, can be found in Key Concepts of Euler (Virtual) Solutions.


