VM292
VM292
Interference Fit Between Two Cylinders
Overview
Test Case
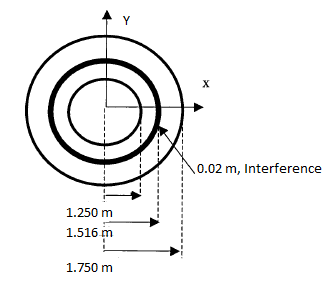
Two cylinders connected by means of standard frictionless contact are modeled with an interference fit between them. Static analysis is performed to predict the contact pressure between the two cylinders.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Interference overclosure = 0.02 m |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The cylinders are modeled using 3D 8-Node Structural Solid (SOLID185) elements. The cylinders are connected by means of standard frictionless contact pairs (CONTA174 and TARGE170 elements) by including initial geometric gap/offset with ramped effects. The cylinders are modeled with dissimiliar mesh and the projection-based method was used for the contact location detection point. The top and bottom sides of two cylinders are constrained in the vertical direction and UZ degrees of freedom are constrained on nodes at location Z = 0 m and Z = 1.5 m. The Poisson's ratio of 0.0 is used as it is not considered in the reference calculation.
The geometry correction for the cylinder is done using SECTYPE,CONTACT. The contact pressure between the cylinders is computed and compared against the reference solution (equation 3.57, pg. 116). The contact pressure is not uniform along the top and bottom edges because the contact surface normal along the edges does not align perfectly with the global X or Y direction. Mesh refinement is usually required to achieve an accurate solution on the edges.
The reference solution is computed by:
where
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|