Before you start Mechanical APDL, the Parasolid file (.x_t or .xmt_txt) you wish to import must exist on your machine or on a known network location. You can use the GUI or the ~PARAIN command to import the file.
Import with the GUI
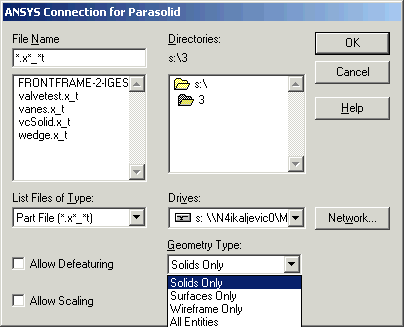
Select . The Connection for Parasolid dialog box appears, as shown in the figure below.
Select the desired Parasolid file. In addition to the file name, file location and file type options, modify the following values as necessary.
Allow Defeaturing - Check this box to store the model in the solid database format so it can be defeatured after import. If this is not checked, the model is stored in neutral database format, which restricts defeaturing after import (default).
Allow Scaling - Check this box to permit scaling of the model (if warranted by the model size).
Geometry Type - Import the file as:
Solids Only - Imported as volumes (default).
Surfaces Only - Imported as areas.
Wireframe Only - Imported as lines.
All Entities - Import all entities; use this option when the file contains multiple entity types.
Click once selections are performed.
Note: If your imported model contains multiple volumes, Boolean operators are available to further process your geometry (see Sculpting Your Model with Boolean Operations in the Modeling and Meshing Guide for more information).
Import with the ~PARAIN Command
You can also use the following command line method to import your Parasolid file.
- Command(s) Syntax:
~PARAIN,
Name,Extension,Path,Entity,FMT,Scale
Troubleshooting
For general troubleshooting information, please see Troubleshooting Connection Issues, or examine Problems Specific to the Connection for Parasolid for specific issues. In addition, please refer to the Parasolid Specific Attributes section for additional information about specific considerations associated with importing Parasolid files.
The connection for Parasolid supports the import of multiple Parasolid files for the creation of a single Mechanical APDL database. You can import Parasolid files that make up an assembly, save them as .anf files then import them into one database. See Importing Multiple Files (Create Mechanical APDL Database) for more information on working with multiple .anf files.
However, models must be saved in the text Parasolid format. The saved model files must have either the *.x_t or *.xmt_txt extension.
Scaling
When a Parasolid model is created, the measurement unit information is always represented by meters regardless of the units used to create the model. However, when the CAD package writes out the file, the measurement unit information is not included. The absolute numbers in the Parasolid file can differ from those represented in the Mechanical APDL model.
When Mechanical APDL reads a Parasolid file, the dimensions can be so small that the program must apply a scale factor to improve the success of the transfer. Mechanical APDL uses a scale factor of 10 or 100, depending on the original model size. Mechanical APDL displays the scale factor used in the output window.
Assemblies
You can directly import Parasolid assemblies into Mechanical APDL using the connection for Parasolid. After you import an assembly, you will have as many volumes in Mechanical APDL as you had parts in the assembly. You must then do the following to build a contiguous model:
Glue volumes together using the VGLUE command.
Glue dissimilar meshes together by generating constraint equations at the interfaces using the CEINTF command. You should only use this method for models with small deflection.
Define bonded contact elements such as CONTA172 to glue dissimilar meshes together.