Defining Nonlinear Material Properties
When adding a new material or editing an existing material, the material properties list contains several editable fields.
To define nonlinear material properties:
- From the View/Edit Material window, click a property's Type field and select Nonlinear.
From the Value field, one of the following buttons appears, depending on the property:
- B-H Curve – for nonlinear relative permeability. See: B-H Curves below.
- D-E Curve – for nonlinear relative permittivity. See: D-E Curves below.
- J-E Curve – for nonlinear bulk conductivity. See: J-E Curves below.
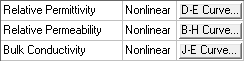
- Click an appropriate button.
The [BH / DE / JE] Curve window appears.
Each of these windows contains a Coordinates table where you can define curve values, as well as buttons for importing and exporting datasets. If imported data are swapped in the Coordinates table, use the Swap X-Y Data button to correct this.
- Define the coordinates using either the Coordinates table or Import Dataset. The curve previews in the graph to the right.
- When you are finished, click OK.
- Click OK again to close the View/Edit Material window.
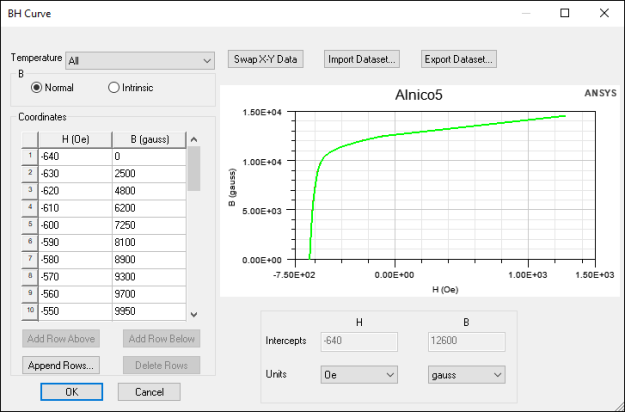
B-H Curves
For nonlinear relative permeability, you must specify magnetization characteristics using BH curves, where B is total magnetic flux density and H is the magnetic field. SIwave can also model temperature dependencies of the nonlinear material property when you provide two or more temperature-dependent BH curves.
When BH curves are specified, the thermal modifier for permeability is disabled.
To define a single B-H curve:
- Select whether B values are Normal or Intrinsic.
Important:
- For a Normal curve, the slope of the curve can not be less than that of free space anywhere along the curve.
- For an Intrinsic curve, the slope of the curve can not be less than 0.
- Normal curves are extrapolated; Intrinsic curves are not.
- Use the Units drop-down menus to define units for B and H.
- Enter B and H values in the Coordinates table or Import Dataset.
Note:
- The initial value of B must be 0.
- The value of B must increase along the curve.
- The slope of the last two user-defined data points is used to extrapolate the BH curve. Therefore, you must enter enough points for accurate representation.
- Preview the graph to ensure it looks correct.
- Click OK.
To define temperature-dependent BH curves:
- Use the Temperature drop-down menu to select Edit Temperature Dependency.
The Edit Temperature Dependency window appears.
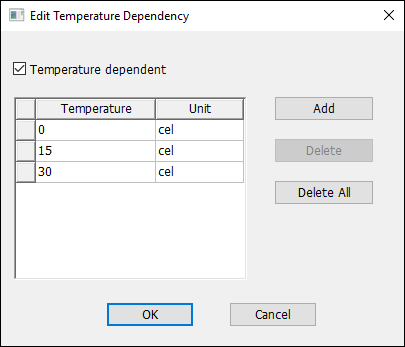
- Select the Temperature Dependent check box and add rows for the temperatures at which you wish to define BH values.
- Click OK.
- Back in the BH Curve window, use the Temperature drop-down box to select each temperature.
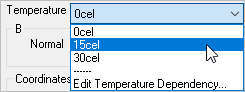
- Define each temperature's BH values using the Coordinates field.
- Click OK.
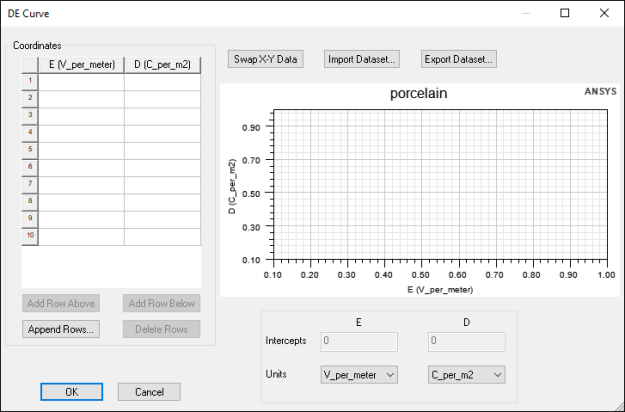
D-E Curves
For nonlinear relative permittivity, you must specify magnetization characteristics using DE curves, where D is the electric flux density and E is electric field strength.
To define a D-E curve:
- Use the Units drop-down menus to select units for D and E.
- Enter values using the Coordinates table or Import Dataset.
Note:
- The initial value of D and E must be 0.
- The slope of the curve cannot be less than 0.
- The slope of the last two user-defined data points is used to extrapolate the DE curve. Therefore, you must enter enough points for accurate representation.
- Click OK.
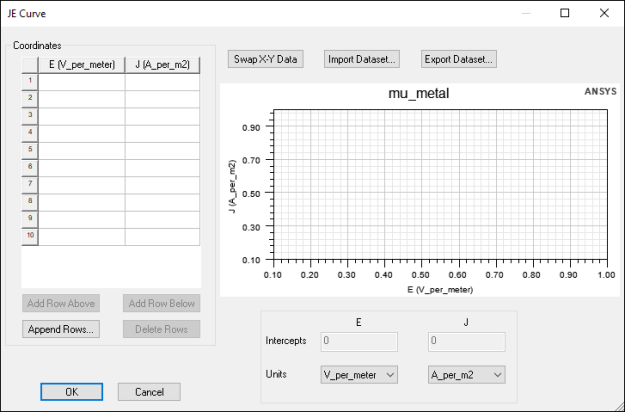
J-E Curves
For nonlinear bulk conductivity, you must specify the J-E Curve, where J is the current density and E is the electric field.
To define a J-E curve:
- Use the Units drop-down menus to select units for J and E.
- Enter values using the Coordinates table or Import Dataset.
Note:
- The initial value of J and E must be 0.
- The slope of the curve cannot be less than 0.
- The slope of the last two user-defined data points is used to extrapolate the JE curve. Therefore, you must enter enough points for accurate representation.
- Click OK.