VM-WB-MECH-101
VM-WB-MECH-101
Natural Frequency of a Submerged Ring
Overview
| Reference: | Schroeder, E. A., & Marcus, M. S. (1975). Finite element solution of fluid structure interaction problems. In Shock and Vibration Symposium (pp. 1-10). San Diego, CA. |
| Solver(s): |
Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Modal Analysis |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
Test Case
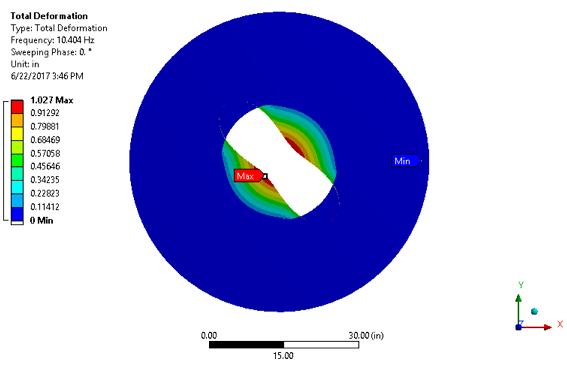
A steel ring is submerged in compressible fluid (water). Determine the lowest natural frequency for x-y plane bending modes of the fluid-structure system.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|