VM-WB-MECH-094
VM-WB-MECH-094
Residual Vector in Stand-Alone and Linked Mode-Superposition Harmonic
Analysis
Test Case
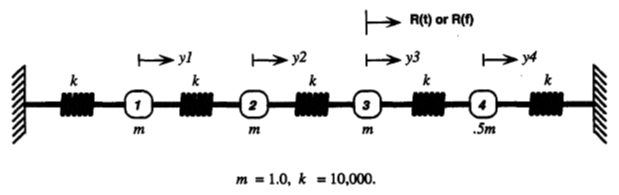
A mode-superposition harmonic analysis (stand-alone and linked) with an excitation frequency
range of 3-70 Hz and a force load along the X-direction is performed on a spring-mass model,
extracting one mode and residual vector. The spring-mass model is represented using Springs and
Point Masses. Refer to Mechanical APDL VM149 for more
details.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The spring-mass model is represented using 2-D Spring-Damper and 2-D Structural Mass
elements without rotary inertia. The X and Y-axes of the spring model are inverted from the
reference model to model it along the global X-axis. The model is fixed at both ends, and the
displacement along the Y-direction is constrained on all nodes. In order to obtain four distinct
modes, the mass at node 5 is set to half the value of the other three masses defined at nodes 2,
3, and 4. A modal analysis is performed first using the Block Lanczos eigensolver. A
mode-superposition harmonic analysis is then performed with an excitation frequency range of 3-70
Hz and a force load along the X-direction at node 4. A damping
ratio of 0.02 (2%) is defined in the analysis.