VM-WB-MECH-034
VM-WB-MECH-034
Rubber Cylinder Pressed Between Two Plates
Overview
| Reference: |
Tussman, T., & Bathe, K. J. (1987). A Finite Element Formulation for Nonlinear Incompressible Elastic and Inelastic Analysis. Computers and Structures, 26(1/2), 357-409. |
| Solver(s): | Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Nonlinear Static Structural Analysis (Large Deformation ON) |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
Test Case
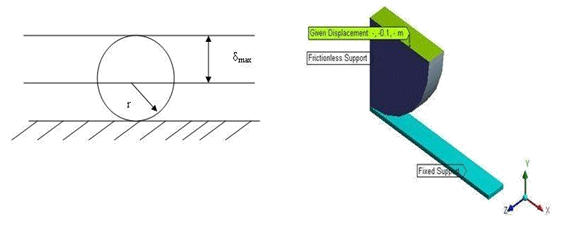
A rubber cylinder is pressed between two rigid plates using a maximum imposed displacement of δmax. Determine the total deformation.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Solid1:
| Solid1:
| Displacement in Y direction = -0.1 m | ||||
Solid2: Mooney-Rivlin Constants
| Solid2: Quarter Circular Cylinder
|
Analysis
Due to geometric and loading symmetry, the analysis can be performed using one quarter of the cross section.
Frictionless supports are applied on 3 faces (X = 0, Z = 0 and Z = 0.05 m).
Given displacement of 0.1 m is applied on the top surface.
The bottom surface of Solid1 is completely fixed.
Frictionless Contact with Contact stiffness factor of 100 is used to simulate the rigid target.
Augmented Lagrange is used for Contact formulation.