VM-WB-MECH-025
VM-WB-MECH-025
Stresses Due to Shrink Fit Between Two Cylinders
Overview
| Reference: |
Timoshenko, S. P. Strength of Materials, Part 2 - Advanced Theory and Problems (3rd ed., pp. 208-214). |
| Solver(s): | Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Linear Static Structural Analysis |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
Test Case
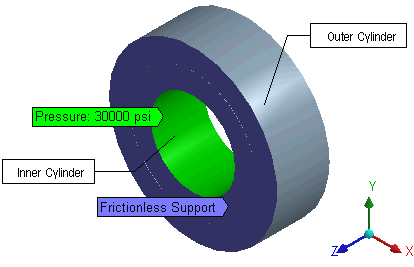
One hollow cylinder is shrink fitted inside another. Both cylinders have length L and both the flat faces of each cylinder are constrained in the axial direction. They are free to move in radial and tangential directions. An internal pressure of P is applied on the inner surface of the inner cylinder. To get accurate results, apply a global element size of 0.8 inches.
Find the maximum tangential stresses in both cylinders.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes for Ansys Mechanical
The following figure shows the finite element model in Ansys Mechanical:
Note: Tangential stresses can be obtained in the Mechanical application using a cylindrical coordinate system.
To simulate interference, set Contact Type to Rough with interface treatment set to add offset with Offset = 0.