All solid and surface geometry created in the Ansys DesignModeler application must be manifold. This means that for Solid bodies, each edge connects to exactly two faces.
For Surface bodies, each interior edge connects to two faces, and each boundary edge connects to exactly one face. Most often, non-manifold solids can occur during Enclosure operations, where bodies touch at an edge or vertex.
For Surface bodies, any type of 'T' intersection is considered non-manifold and is not permitted in Boolean operations. Bodies that are oriented in this manner should be kept separate by leaving one or both bodies frozen. If you wish to share topology between bodies that form a 'T' intersection, consider using the Joint feature.
Line bodies do not have any such restrictions.
Below are some examples of valid (manifold) and invalid (non-manifold) geometry:
 This solid is invalid because the top edge connects to four faces instead of two. | 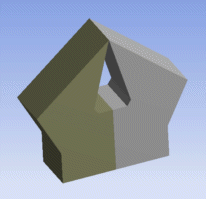 When split into two bodies, this geometry becomes manifold. |
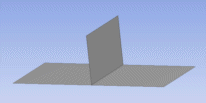 This surface body is invalid because it contains a "T" intersection. The middle edge is connected to three faces. | 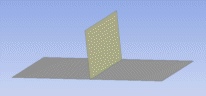 When kept separate, two bodies remain manifold. |
Other Boolean Operations:


