In this section, the following topics are covered:
For information on Ansys licensing, refer to the Ansys Licensing Guide.
Windows
The following Sherlock folder locations are for installations running on Windows. Folder locations for Linux are listed in the section below.
In Windows, Sherlock uses two standard folder locations for its files: the Ansys installation folder and the Sherlock user data folder. The Sherlock installation folder contains all the common files needed to run Sherlock on any system. Usually the installation folder is located in the following location (64-bit platforms):
| c:\Program Files\Ansys Inc\242 |
Although you may change this location at installation time, no files in the installation folder need to be changed after installation.
The Sherlock user data folder is created in the following location
| c:\Users\USERID\AppData\Roaming\Sherlock |
where USERID is the Windows user ID. The Sherlock user data folder contains all log and property files. This is also the default location for the user project folder in older versions of Sherlock prior to the implementation of the default project directory setting. These folders are only visible in Windows Explorer if the option to display hidden files is selected in Windows. Alternately, you can type the full path into Windows Explorer.
You can set the default project directory in Settings > General Settings > Advanced where your projects will be created. The user project folder holds design, result, and report files created by a given user. (See Project Management for more details.)
Linux
On Linux systems, the location of the Ansys installation folder:
| /ansys_inc/v242 |
Although you may change this location at installation time, no files in the installation folder need to be changed after installation.
Sherlock user settings (where $Home is your home directory):
| $HOME/.sherlock |
The user data folder contains all log and property files. User data files and documents default location:
| $HOME/.sherlock |
Default project folder:
| $HOME/Sherlock/projects |
You can set the default project directory in Settings > General Settings > Advanced where your projects will be created. The user project folder holds design, result, and report files created by a given user. (See Project Management for more details.)
This user's guide was written with Windows users in mind. Where the Linux version of Sherlock differs, you will find explanatory notes in the relevant sections of this user's guide. Below is a list of the most important differences:
Be sure to refer to the Sherlock Installation Guide for Linux.
Abaqus and NX Nastran solvers are not supported by Sherlock when running on Linux.
On Linux, there is no separate client console window. For its output, Sherlock uses the terminal window which was used to launch Sherlock.
By default, you cannot open Sherlock files by double-clicking them. You must manually associate file types to specific applications within Linux. The procedure for doing this depends on the windowing environment you are using.
In Linux, you can launch certain features using commands in the operating system:
To launch the 3D Viewer, use
runSherlock -3dViewerTo launch the Results Viewer, use
runSherlock -resultViewerTo launch the Life Cycle Manager, use
runSherlock -lifecycleTo launch Sherlock in single-project mode, use
runSherlock -singleProject
The following may also be used with additional Sherlock license features enabled:
Abaqus (Windows only)
NX Nastran (Windows only)
You can perform the following simple tests to confirm that Sherlock is installed properly and that all required software components are configured properly.
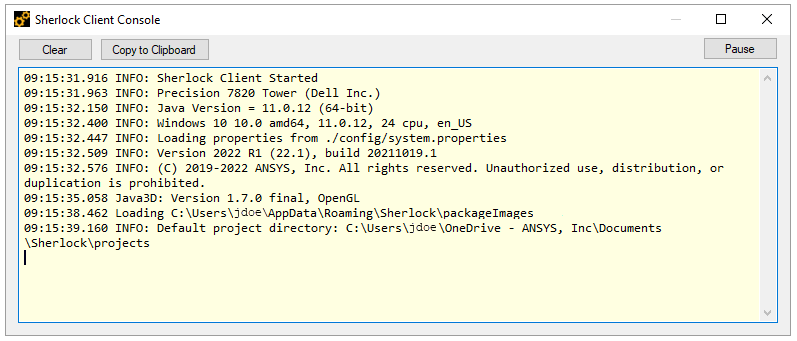
When running on Windows, the Sherlock Client Console opens when Sherlock is started. You can also open it manually by selecting Help > Show Console. As shown below, the Client Console window displays key file system properties.
Linux
On Linux, there there is no separate client console window. For its output, Sherlock uses the terminal window used to launch the application.
For information on configuring memory settings in Sherlock, refer to Launcher Settings.
If your video card does not support Sherlock's 3D Viewer, try these troubleshooting steps:
Update your graphics driver.
In some cases, modifying your graphics driver settings can resolve the issue. If an Intel HD graphics card is being used, right-click your Desktop, then Graphics Properties, then 3D. Look for the OpenGL options to enable Vertical Sync, also known as Asynchronous Flip.
If you are running Sherlock on a remote desktop or a virtual machine, you might be able to resolve the issue by enabling 3D graphics acceleration on the virtual/remote machine.
Laptops
3D Viewer compatibility issues can arise on laptops that have both an internal Intel graphics adaptor and a second adapter such as an NVIDIA graphics card. Configuring the laptop so it always uses the NVIDIA card often resolves the issue. To force the laptop to use the NVIDIA card only, do the following:
Right-click Windows desktop.
Select the NVIDIA Control Panel from the context menu.
Navigate to 3D Settings > Manage 3D Settings.
Select NVIDIA for the preferred graphics processor.
Restart Sherlock.


