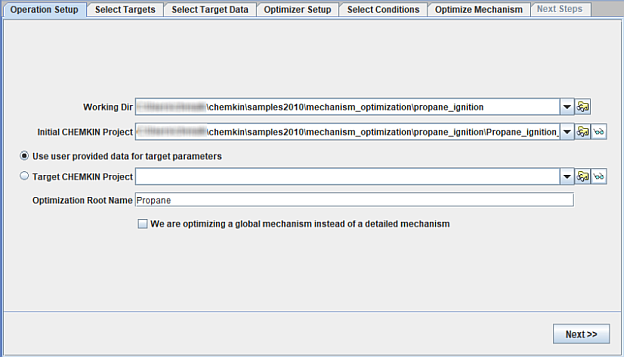
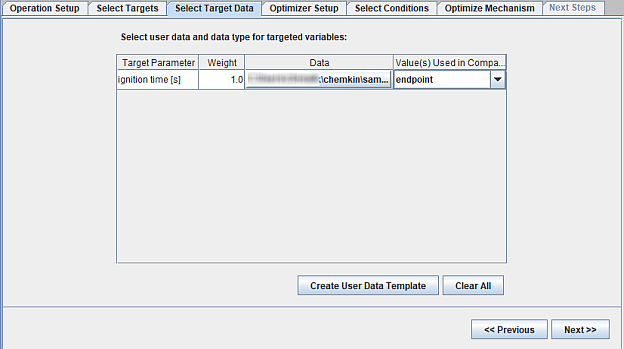
Mechanism optimization follows a similar work flow used for Mechanism Reduction described in Guided Mechanism Reduction. Two options for targets are available, as shown in Figure 2.22: Operation Setup for global mechanism optimization : user provided data or Chemkin project. If a Chemkin project is used, it must have the same initial conditions and parameter study setup as that used in the Initial Chemkin project. The mechanism in the initial project will be optimized. An option to optimize all the rate parameters can be selected for a mechanism involving only global reaction steps. On the second tab, the targets for optimization can be selected as illustrated in Figure 2.19: Select targets for mechanism reduction operation . The third panel for selecting the target data appears slightly different depending on the selection made on the Setup panel, as shown in Figure 2.23: Selecting target data for global mechanism optimization using user provided data and Figure 2.24: Selecting target data for global mechanism optimization using the target project specified on the Operation Setup panel . When user data are used as optimization targets, they must be imported in a comma-separated (.csv) file format. A template can be written in the working directory from the panel, as shown in Figure 2.23: Selecting target data for global mechanism optimization using user provided data . When multiple targets are used, a non-uniform weight can be provided to different targets (Figure 2.24: Selecting target data for global mechanism optimization using the target project specified on the Operation Setup panel ). Targets of higher importance can be assigned a higher-weight value, which will result in their preferential treatment during optimization.
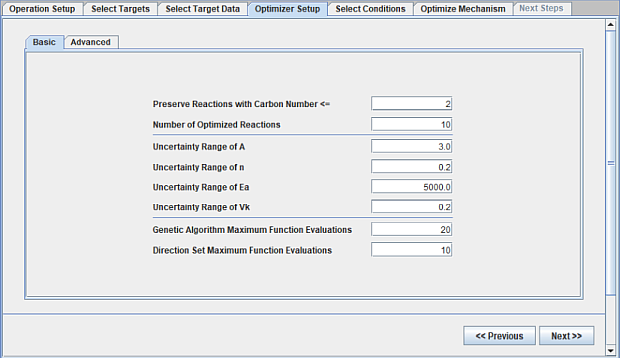
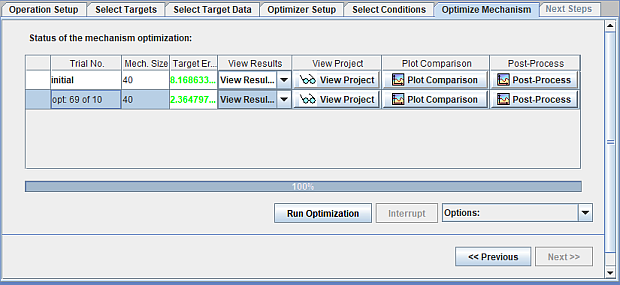
The Optimizer Setup tab includes several settings that can significantly influence the effectiveness and compute cost of the optimization process. Reactions involving small hydrocarbons can be preserved using the Carbon Number setting. The number of reactions and ranges of Arrhenius parameters for optimization should be specified. A larger range of uncertainty values for the rate parameters should typically require more function evaluations for optimization. However, function evaluation for the two optimization methods implemented can be restricted on this panel. The progress of the optimization process can be observed, as illustrated in Figure 2.26: Monitor the progress of the global mechanism optimization .
Note: The maximum number of evaluations set is not strictly honored but used as guidance only. The actual number of function evaluations or iterations during optimization will be slightly larger than the value specified.
Figure 2.24: Selecting target data for global mechanism optimization using the target project specified on the Operation Setup panel