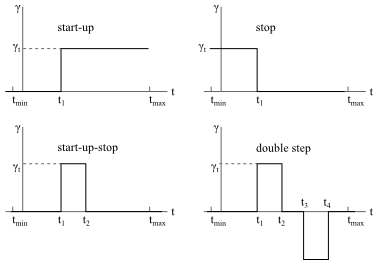
It can also be interesting to calculate the response of a viscoelastic material to one or more instantaneous variations of shear rate. The main types of transient shear flows are described below, and Figure 7.5: Transient Shear Flows shows the shear rate as a function of time for these flows.
For transient shear flow fields, the transient property curves for the properties defined by Equation 7–2 – Equation 7–9 can be computed. Click Select transient curves in the Load Curves (Part I) menu to open the Load Curves (Part II) menu, where you can then select Transient Shear Rate, Transient Shear Stress, Transient Shear Viscosity, Transient 1st Normal Stress Difference, Transient 2nd Normal Stress Difference, Transient 1st Normal Stress Coefficient, and/or Transient 2nd Normal Stress Coefficient if you want Ansys Polymat to compute one (or more) of these curves.
To compute each of these curves, you will need to define the desired number of time
intervals during which a constant shear rate is applied. The time interval
is bounded by the time values
and
. All times
must be included between the specified minimum and maximum times,
(
and
). The number of sampling points per time interval must also be
specified. See Defining Numerical Parameters and
Defining Numerical Parameters for information
about specifying numerical parameters for viscometric property curves. See Specifying the Curves to be Calculated for information about
specifying which curves you want to compute and plot. (Note that, if you use the
automatic fitting method, Ansys Polymat will automatically compute and plot the curves
for all properties for which experimental data curves have been defined.)