Activate the Radiation model option if radiation heat transfer is considered in the simulation. Ansys Forte can calculate radiative heat transfer between high-temperature gas and solid walls, if the gas contains radiative gaseous species, soot particles, or both.
Select Include Soot Particle Contribution if you would like to consider soot particles in the radiation model. Note that, in order to consider soot particles' effect on radiation, you must have used one of the soot models described in Soot Model.
In the Radiation Species list, you can select which
radiative species are considered in the radiation model. The radiative species are automatically
determined when a gas-phase mechanism is loaded during the Chemistry model
step (see Chemistry). Species are considered as radiative species if they have an
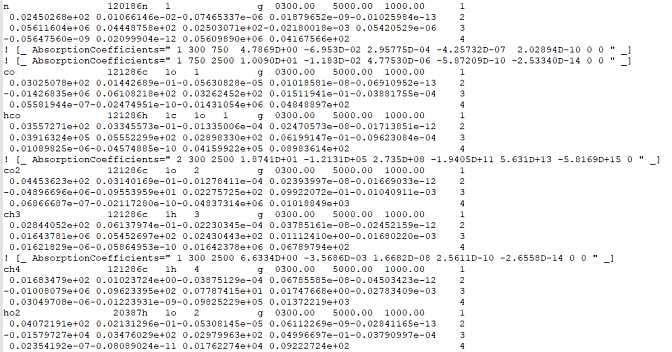
absorption coefficient correlation in the thermodynamic data file. The absorption coefficient
correlation can be identified in the thermodynamic data file by the
AbsorptionCoefficients keyword. So, it is important that you check the
thermodynamic data file used in the gas-phase mechanism and see which species have the
absorption coefficient, before using the radiation heat transfer model. Figure 3.16: Excerpt of sample thermodynamic data file used in the mechanism, containing absorption
coefficient data for CO, CO2, CH4
shows an
example of the thermodynamic data file which includes several radiative species. For more
information about the absorption coefficient data format in this file, refer to Gas Species Radiation Absorption Coefficients in the Chemkin Input Manual.
Figure 3.16: Excerpt of sample thermodynamic data file used in the mechanism, containing absorption coefficient data for CO, CO2, CH4