The Ansys Fluent electric potential model allows for predicting the electric potential field and its effects. The electric potential model can be used separately (for example, to compute electric static force for charged particles in a DPM calculation) or in combination with other Ansys Fluent models.
The electric potential solver has been integrated with the electrochemical reaction model (Electrochemical Reactions in the Fluent Theory Guide). When you enable the electrochemistry in your case, Ansys Fluent automatically enables the electric potential solver. However, if you want to use the electric potential model along with other Ansys Fluent models, you need to manually enable it as described in Setting Up the Electric Potential Model.
Using the electric potential solver, you can simulate the electric potential field in both fluid and solid zones.
When defining the boundary conditions for the electric potential field, you can specify either potential or current density at the external walls.
The following sections contain details about the Electric Potential model. Only information for setting the Electric Potential model is provided here.
The following limitation exist for the electric potential model:
The electric potential model cannot be used in simulations with walls that have a shell conduction boundary condition.
The procedure for setting up the electric potential model is described below. Note that only steps that are pertinent to electric potential field modeling are listed here. You will also need to define the other settings (such as other material properties, boundary conditions, other models) as usual. For information about inputs related to other Ansys Fluent models that you are using in conjunction with the electric potential model, refer to the appropriate sections for those models.
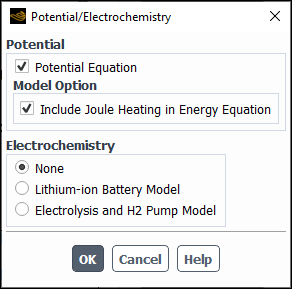
In the Potential/Electrochemistry dialog box, which is opened from the Setup → Model → Potential/Electrochemistry tree item, enable the Potential Equation option.
Once the Potential Equation is enabled, the electric conductivity material property for fluid, solid, and mixture materials defined in your case will appear in the Create/Edit Materials dialog box.
If you want to include Joule heating in the energy equation (Equation 5–1 in the Fluent Theory Guide), under the Model Option group box, enable Include Joule Heating in Energy Equation.
Note: The Include Joule Heating in Energy Equation option appears in the Potential/Electrochemistry dialog box only when Energy Equation is enabled in the Energy dialog box.
In the Create/Edit Materials dialog box, under Properties, specify Electric Conductivity for the conductive materials defined in your simulation.
Setup →
 Materials
MaterialsDefine boundary conditions on conductive walls.
Setup →
 Boundary
Conditions
Boundary
Conditions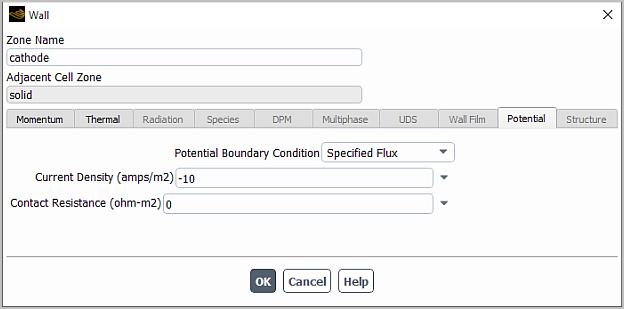
Select one of the following options from the Potential Boundary Condition drop-down list:
Specified Flux and specify Current Density
Specified Value and specify Potential
(two-sided internal walls only) Coupled
The coupled boundary condition you specify on one wall will be automatically applied to both walls in the wall / wall-shadow pair.
When you use decoupled potential boundary conditions for two-sided internal walls (Specified Flux or Specified Value), you can define different boundary conditions on the wall and wall-shadow.
Specify Contact Resistance (
in Equation 18–3 in the Fluent Theory Guide).
If required, specify electric potential conditions on other boundaries in the Potential tab of the boundary conditions dialog boxes. Note that the default setting, zero current flux, is suitable for most problems and needs not be changed.
If you want to fix a value of potential or specify a potential source in a cell zone, you can do it by setting the Fixed Values or Source Terms in the appropriate cell zone condition dialog box.


