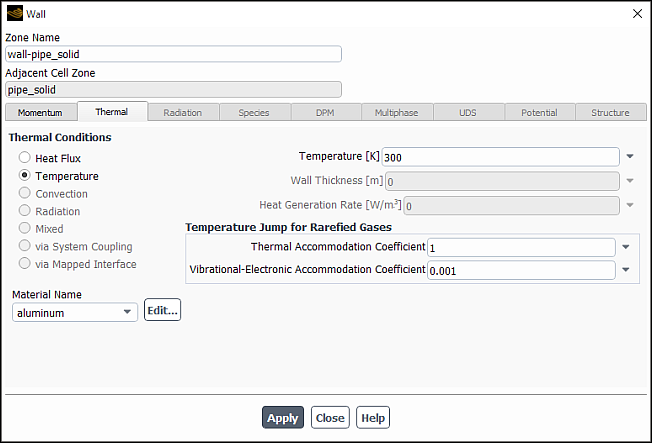
In the rarefied regime, the parietal gas temperature may differ from the imposed wall temperature, and may be calculated from the following expression:
(17–5) |
where is the parietal gas temperature,
is the heat-flux vector, and
is the thermal accommodation coefficient.
The temperature jump boundary condition is engaged automatically when the partial-slip
shear condition is selected in the momentum tab (see Figure 17.20: The Wall Dialog Box for Temperature Jump Thermal Condition).
You can enter the value of the thermal accommodation coefficient ( in Equation 17–5) in the Thermal
Accommodation Coefficient field.
If the Two-Temperature model is engaged, a jump boundary condition is applied to the vibrational-electronic energy as suggested by Nompelis et al [107]:
(17–6) |
You can enter the corresponding accommodation coefficient in the Vibrational-electronic Accommodation Coefficient field.
Note: The temperature jump for rarefied gases condition is only available in the density-based solver, and for laminar flows only. It is engaged automatically when the partial-slip shear condition is selected in the momentum tab. Wall thickness and heat-generation are not supported. The temperature jump is only offered for walls with imposed temperature and is not available for heat-flux and coupled boundaries, or simulations involving conjugate heat-transfer.